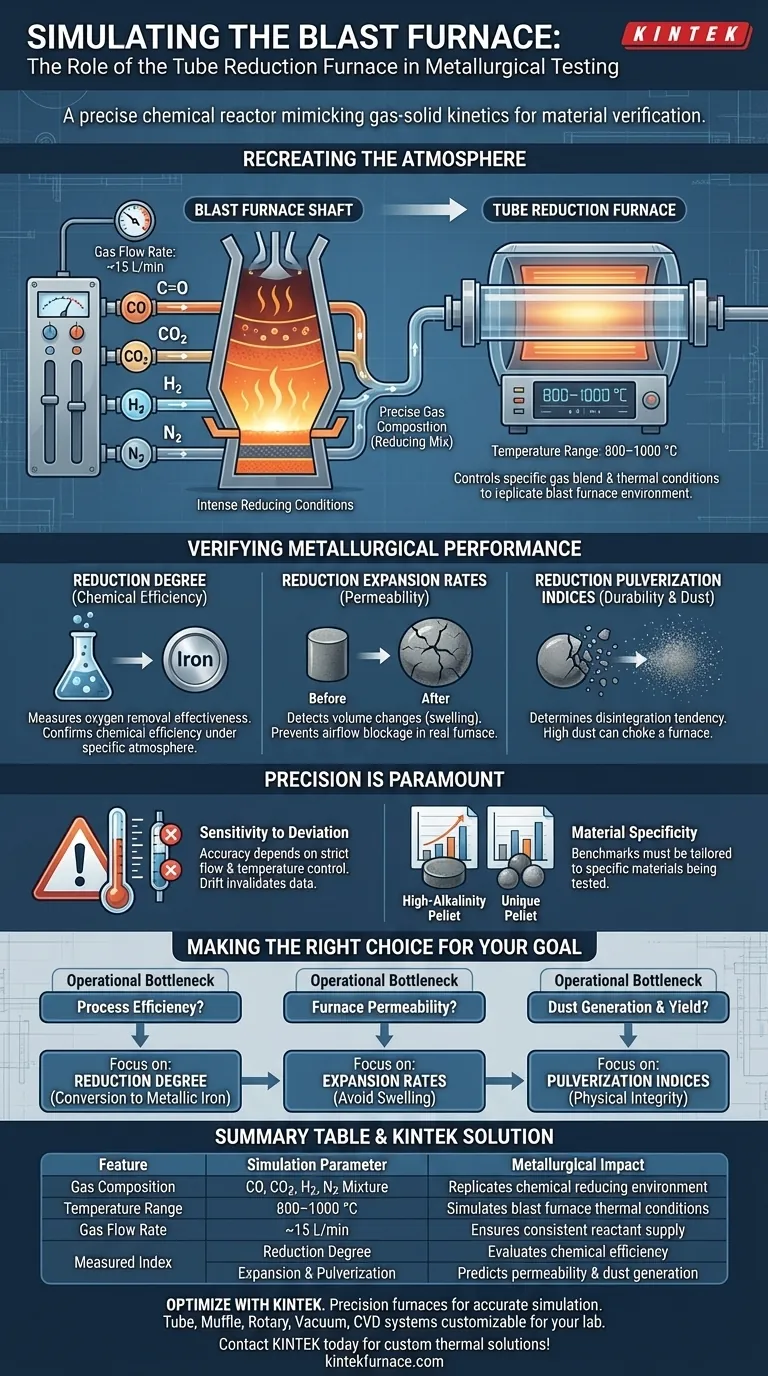
To simulate the reduction environment of a blast furnace, a tube reduction furnace creates a precisely controlled atmosphere using specific gas compositions and thermal conditions. It regulates the flow of gases—specifically Carbon Monoxide (CO), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Hydrogen (H2), and Nitrogen (N2)—typically at rates around 15 L/min. By maintaining this chemical environment within a strict temperature window of 800–1000 °C, the apparatus replicates the intense reducing conditions required to verify the metallurgical performance of materials like high-alkalinity pellets.
Core Takeaway The tube reduction furnace is not merely a heating device; it is a chemical reactor that mimics the gas-solid kinetics of a blast furnace. Its primary value lies in its ability to isolate and measure specific material behaviors—such as swelling and degradation—under controlled atmospheric conditions before full-scale industrial application.
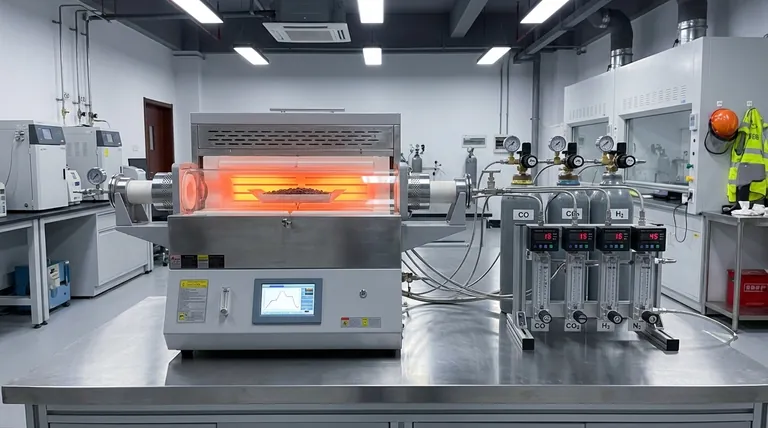

Recreating the Blast Furnace Atmosphere
To accurately predict how raw materials will behave during ironmaking, the furnace must replicate two critical variables: chemical composition and gas dynamics.
Precise Gas Composition
The simulation relies on a specific mixture of reducing and inert gases. The furnace introduces CO, CO2, H2, and N2 in proportional compositions that mirror the reducing gases found in a blast furnace shaft.
This specific blend allows operators to expose materials to the exact chemical reactions they will face in production.
Controlled Flow Dynamics
Simulating the environment requires more than just the presence of gas; it requires movement. The furnace maintains a defined gas flow rate, often cited at 15 L/min.
This ensures a continuous supply of reactants to the pellet surface, replicating the dynamic gas flow experienced in a working blast furnace stack.
Verifying Metallurgical Performance
Once the environment is established, the furnace operates within a thermal range of 800–1000 °C. This temperature window allows for the measurement of three critical performance indices.
Reduction Degree
The furnace measures the reduction degree, which indicates how effectively oxygen is removed from the iron ore.
This metric confirms the chemical efficiency of the material under the specific gas atmosphere provided.
Reduction Expansion Rates
Materials often change volume during chemical reduction. The furnace allows for the detection of reduction expansion rates, particularly in high-alkalinity pellets.
Monitoring this prevents the use of materials that might swell excessively and block airflow in a real blast furnace.
Reduction Pulverization Indices
The test also determines the reduction pulverization index. This measures the tendency of the pellets to disintegrate into dust during the reduction process.
High pulverization can choke a blast furnace, making this a critical durability test.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While valuable, tube reduction furnace testing relies heavily on the strict maintenance of parameters.
Sensitivity to Parameter Deviation
The accuracy of the simulation is entirely dependent on the precision of the flow rate and temperature control.
If the gas flow drifts from the target (e.g., 15 L/min) or the temperature exits the 800–1000 °C range, the resulting data regarding expansion or pulverization may not correlate with actual blast furnace performance.
Material Specificity
The primary reference highlights the testing of high-alkalinity pellets.
While the furnace simulates the environment generally, the interpretation of expansion and pulverization indices is often specific to the type of pellet or sinter being tested, requiring distinct benchmarks for different materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When analyzing data from a tube reduction furnace, focus on the metric that aligns with your operational bottleneck.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Prioritize the reduction degree to ensure the material converts to metallic iron at an acceptable rate.
- If your primary focus is furnace permeability: Scrutinize the reduction expansion rates to ensure the pellets will not swell and impede gas flow.
- If your primary focus is dust generation and yield: Focus on the reduction pulverization indices to verify the physical integrity of the pellets under stress.
Successful metallurgical verification depends on ensuring the lab simulation strictly adheres to the defined temperature and gas flow parameters.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Simulation Parameter | Metallurgical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Composition | CO, CO2, H2, N2 Mixture | Replicates chemical reducing environment |
| Temperature Range | 800–1000 °C | Simulates blast furnace shaft thermal conditions |
| Gas Flow Rate | ~15 L/min | Ensures consistent reactant supply to materials |
| Measured Index | Reduction Degree | Evaluates chemical efficiency and oxygen removal |
| Measured Index | Expansion & Pulverization | Predicts furnace permeability and dust generation |
Optimize Your Metallurgical Testing with KINTEK
Precision is the key to accurate blast furnace simulation. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs.
Whether you are testing high-alkalinity pellets or developing new sinter materials, our furnaces provide the strict temperature and gas flow control necessary to ensure your results translate to industrial success.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom thermal processing solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Yufeng Guo, Xinyao Xia. Optimizing High-Al2O3 Limonite Pellet Performance: The Critical Role of Basicity in Consolidation and Reduction. DOI: 10.3390/met15070801
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the three main types of tube furnaces? Choose the Right One for Your Lab
- What function does the annealing treatment in a high-temperature quartz-tube furnace serve? Optimizing Glass Ceramics
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace with 5% hydrogen/argon mixed atmosphere necessary for PtPd_CoNiCu/C high-entropy alloys?
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in the carbonization of ionic liquid precursors? Master Thermal Control
- Why is environmental control in a high-temperature tube furnace necessary during NVP/C synthesis? Key to Success
- What are the steps for insulation and cooling in a multi zone tube furnace? Master Precise Thermal Control
- What critical conditions does a tube furnace provide for TR-PBO membrane treatment? Achieve Perfect Thermal Rearrangement



















