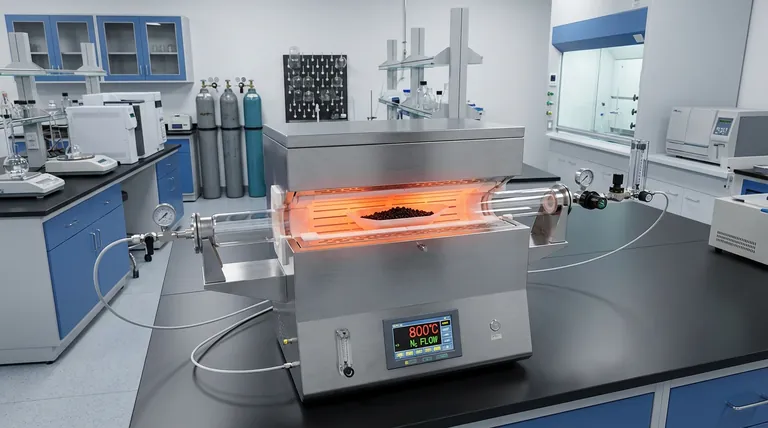
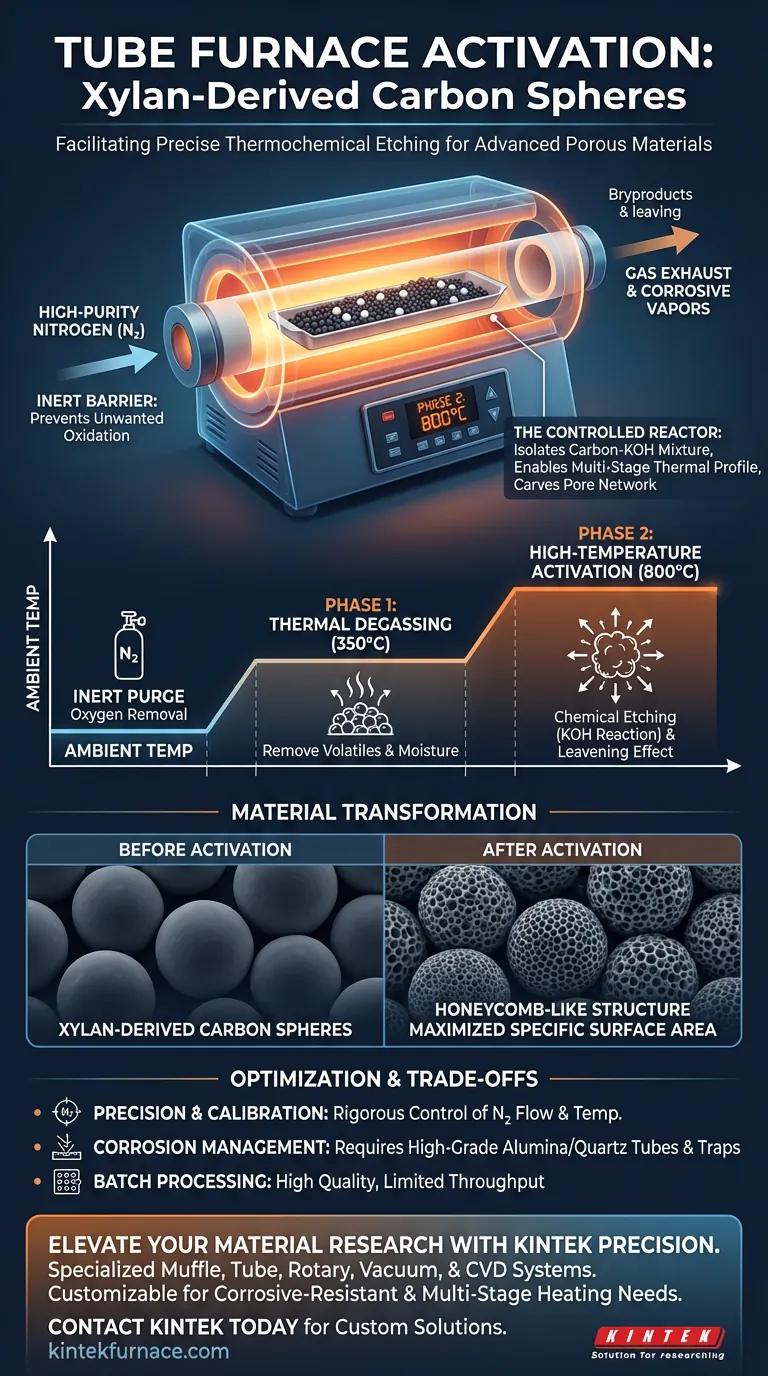
A tube furnace facilitates the activation of xylan-derived carbon spheres by providing a strictly controlled, oxygen-free environment essential for precise thermochemical etching. It employs a stepped heating protocol under high-purity nitrogen—typically degassing at moderate temperatures before ramping to high heat—to trigger a reaction between the carbon matrix and potassium hydroxide (KOH), transforming the material's internal structure.
The tube furnace acts as a controlled reactor that isolates the carbon-KOH mixture from atmospheric oxygen, allowing a multi-stage thermal profile to chemically carve a vast network of pores into the carbon spheres without burning them away.

The Role of Atmosphere Control
Creating the Inert Barrier
The fundamental requirement for activating xylan-derived carbon is the total exclusion of oxygen. The tube furnace maintains a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen throughout the process.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
Without this inert nitrogen blanket, the high processing temperatures would cause the carbon spheres to combust and turn into ash. The furnace ensures that the carbon remains stable so it can react solely with the chemical activator (KOH).
The Stepped Heating Mechanism
Phase 1: Thermal Degassing
The process relies on a precise "stepped" heating profile rather than a simple ramp. The furnace first stabilizes at a moderate temperature, specifically 350 degrees Celsius.
Removing Volatiles
At this stage, the furnace drives off residual volatile components and moisture from the xylan precursors. This purification step prepares the carbon matrix for the aggressive chemical reactions to follow.
Phase 2: High-Temperature Activation
Once degassed, the furnace ramps the temperature to 800 degrees Celsius. This is the critical activation window where the chemical kinetics required for pore formation are unlocked.
Surface Engineering and Pore Creation
Triggering the Chemical Etching
At 800°C, the potassium hydroxide (KOH) mixed with the carbon spheres melts and reacts violently with the carbon lattice. The furnace’s thermal stability ensures this reaction is uniform across the sample.
The Leavening Effect
This reaction releases gases (such as carbon dioxide and water vapor) which expand within the material. This creates a "leavening" effect, forcing open new channels within the carbon walls.
Maximizing Specific Surface Area
The result of this controlled etching is a dramatic transformation of the material's topography. The dense xylan-derived spheres are converted into a honeycomb-like structure with a rich pore network and a significantly increased specific surface area.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Limitations and Precision
While tube furnaces offer high precision, they require rigorous calibration. Any fluctuation in the nitrogen flow rate can introduce oxygen, compromising the entire batch.
Corrosive Byproducts
The activation process involving KOH at 800°C produces corrosive vapors. If the tube furnace is not equipped with appropriate tube materials (like high-grade alumina or quartz) and downstream traps, the heating elements and seals can degrade rapidly.
Throughput vs. Control
Tube furnaces are batch-processing tools designed for precision, not volume. They excel at producing high-quality laboratory or pilot-scale materials but may present bottlenecks if rapid, industrial-scale throughput is the primary goal.
Optimizing the Activation Process
To achieve the best results with xylan-derived carbon spheres, align your furnace settings with your specific material goals:
- If your primary focus is maximizing surface area: Ensure the residence time at 800°C is sufficient for the KOH to fully penetrate and etch the carbon matrix without collapsing the structure.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Pay strict attention to the 350°C degassing stage, ensuring all volatiles are evacuated by the nitrogen flow before the high-temperature ramp begins.
Precision in thermal profiling is the single most critical factor in converting raw biomass into high-performance carbon materials.
Summary Table:
| Activation Phase | Temperature (°C) | Primary Function | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Purge | Ambient | Oxygen removal via High-Purity Nitrogen | Prevents carbon combustion/oxidation |
| Phase 1: Degassing | 350°C | Volatile removal & moisture evacuation | Purifies the carbon matrix for activation |
| Phase 2: Activation | 800°C | Chemical etching (KOH reaction) | Creates porous honeycomb-like structures |
| Surface Engineering | 800°C | Gas release & lattice expansion | Maximizes specific surface area |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your carbon synthesis with high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to handle the rigorous demands of chemical activation and biomass conversion. Whether you need corrosive-resistant alumina tubes for KOH processing or precise multi-stage heating for xylan-derived materials, our laboratory high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ready to optimize your activation process? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on our custom furnace solutions.
Visual Guide
References
- Jihai Cai, Xiaoying Wang. Xylan derived carbon sphere/graphene composite film with low resistance for supercapacitor electrode. DOI: 10.1186/s42825-024-00154-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes vacuum tube furnaces stand out in terms of equipment diversification? Discover Their Modular Design & Precision Control
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace during FePt annealing? Achieve the L1₀ Magnetic Phase
- What factors influence the heating process in a tube furnace? Master Temperature Control and Efficiency
- How does a high-precision tube furnace facilitate the formation of the ZnPd alloy phase? Master Catalyst Reduction
- What is the core function of a multi-zone tube furnace in 2D superlattice synthesis? Optimize Your CVD Process
- Why is a vacuum-sealed quartz tube required during the high-temperature annealing of CoTeO4 to enhance crystallinity?
- What types of heating methods are used in split tube furnaces? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- What are the primary applications of vacuum tube furnaces in materials science? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment



















