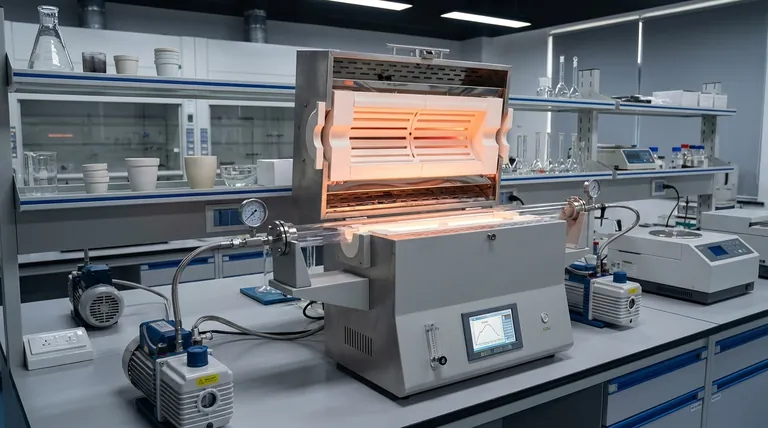
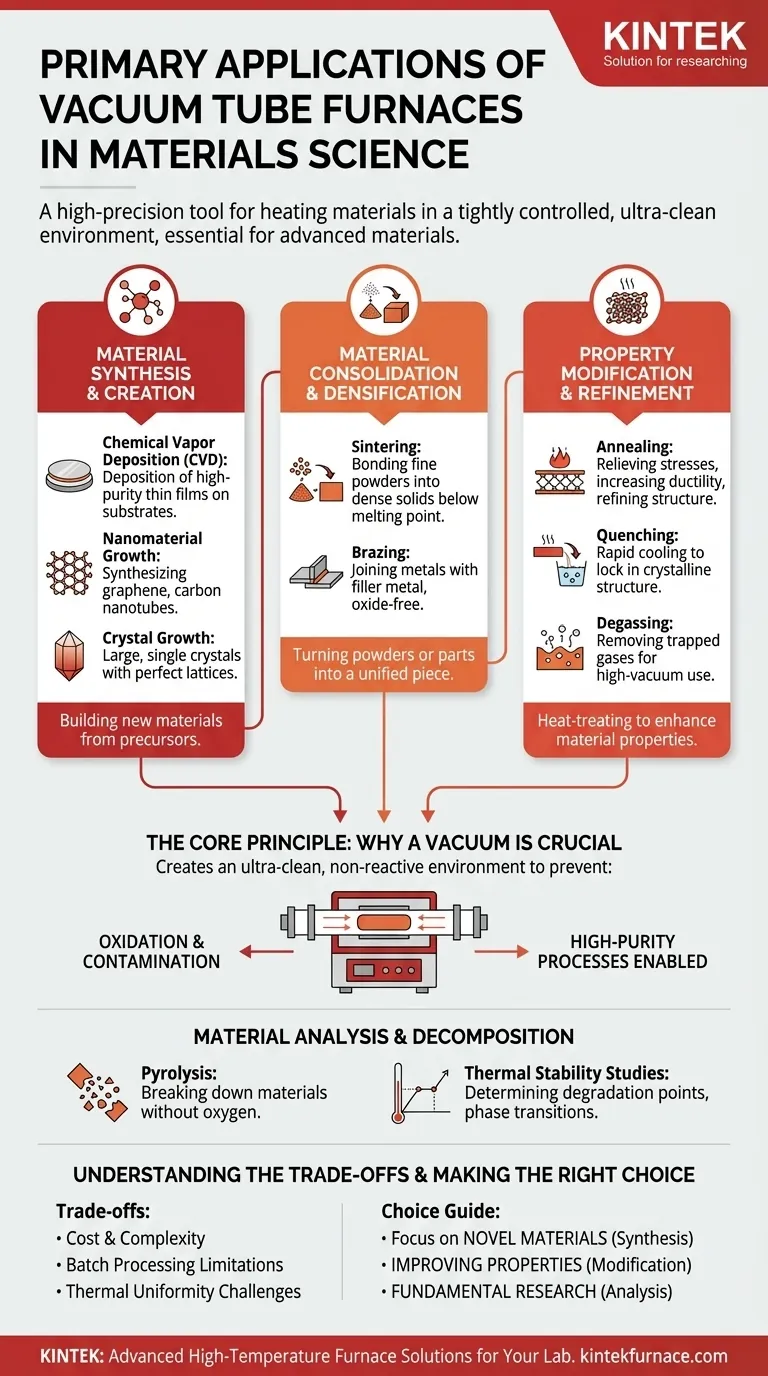
At its core, a vacuum tube furnace is a high-precision tool used for heating materials in a tightly controlled atmosphere. Its primary applications in materials science fall into three main categories: synthesizing new materials like nanomaterials and thin films, modifying the properties of existing materials through heat treatment, and analyzing how materials behave at extreme temperatures without the interference of air.
The essential value of a vacuum tube furnace is not merely its ability to reach high temperatures, but its power to create an ultra-clean, non-reactive environment. This control over the atmosphere is what enables the creation and processing of advanced materials whose sensitive properties would otherwise be destroyed by oxidation or contamination.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum is Crucial
To understand the furnace's applications, one must first grasp why the vacuum (or controlled gas) environment is so critical. At high temperatures, materials become highly reactive.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Most materials, especially metals, will rapidly react with oxygen in the air when heated. This process, oxidation, forms an unwanted surface layer (like rust) that degrades the material's structural, electrical, and chemical properties.
A vacuum tube furnace removes the air, thereby removing the oxygen and other reactive gases. This creates a pristine environment, ensuring the material being processed remains pure.
Enabling High-Purity Processes
For applications in semiconductors, aerospace, and medical implants, even microscopic contamination can lead to component failure. A vacuum environment prevents airborne particles and reactive gases from integrating into the material's structure, which is essential for achieving the required purity and performance.
Key Processes Enabled by Vacuum Furnaces
The controlled environment of a vacuum tube furnace unlocks a range of specialized thermal processes that are impossible to perform in a conventional oven.
Material Synthesis and Creation
This involves building new materials from chemical precursors.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Gases are introduced into the heated tube where they react and deposit a solid, high-purity thin film onto a substrate. This is fundamental for making semiconductors and protective coatings.
- Nanomaterial Growth: The furnace provides the precise temperature and atmospheric conditions needed to synthesize materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes for next-generation electronics and energy applications.
- Crystal Growth: Controlled heating and slow cooling within the furnace allow for the growth of large, single crystals with a perfect lattice structure, used in optics and electronics.
Material Consolidation and Densification
These processes turn powders or separate parts into a solid, unified piece.
- Sintering: Fine powders (ceramic or metallic) are heated below their melting point. In the vacuum, the particles bond and fuse, forming a dense, solid object. This is used to create strong ceramic components and precision metal parts via powder metallurgy.
- Brazing: Two or more metal items are joined together using a filler metal. Heating the assembly in a vacuum ensures a clean, strong, and oxide-free joint, which is critical for aerospace components.
Property Modification and Refinement
This is the practice of heat-treating a material to change its internal microstructure and enhance its properties.
- Annealing: A material is heated and then slowly cooled to relieve internal stresses, increase ductility, and refine its grain structure. This is a common step in semiconductor manufacturing.
- Quenching: A material is heated to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooled. This process, performed in a vacuum to prevent surface reactions, can lock in a desired crystalline structure to increase hardness.
- Degassing: Heating a material in a vacuum effectively "boils" out trapped or dissolved gases. This is vital for materials used in high-vacuum systems, like those in space or particle accelerators.
Material Analysis and Decomposition
These furnaces are also analytical tools for understanding material behavior.
- Pyrolysis: A material is broken down by heat in the absence of oxygen. This allows researchers to study its constituent components or produce other valuable substances.
- Thermal Stability Studies: Scientists can precisely determine the temperatures at which a material begins to degrade, melt, or undergo a phase transition, providing critical data for engineering applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Their specificity comes with important considerations.
Cost and Complexity
These are sophisticated systems requiring expensive vacuum pumps, robust seals, and complex controllers. Their initial cost and maintenance are significantly higher than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Batch Processing Limitations
Most tube furnaces are designed for batch processing, meaning they can only handle a limited quantity of material at one time. This makes them ideal for research, development, and small-scale production but often unsuitable for high-volume manufacturing.
Thermal Uniformity Challenges
Achieving a perfectly uniform temperature across the entire length of the processing tube can be difficult. This requires careful furnace design, calibration, and sometimes multi-zone heating to ensure consistent results, especially for larger samples.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum tube furnace should be driven by the specific requirements of the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating novel, high-purity materials: A vacuum furnace is essential for processes like CVD, nanomaterial synthesis, and growing single crystals.
- If your primary focus is improving existing material properties: The furnace provides the controlled environment needed for critical heat treatments like vacuum annealing, sintering, and brazing.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: The precise control over temperature and atmosphere makes it an indispensable analytical tool for studying thermal decomposition, phase transitions, and reaction kinetics.
Ultimately, a vacuum tube furnace is the essential instrument for manipulating matter with high precision, free from the unpredictable interference of the atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | CVD, Nanomaterial Growth, Crystal Growth | Semiconductors, Electronics, Optics |
| Property Modification | Annealing, Sintering, Brazing | Aerospace, Medical Implants, Powder Metallurgy |
| Material Analysis | Pyrolysis, Thermal Stability Studies | Research, Decomposition Studies |
Ready to enhance your materials research with precision? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum Tube Furnaces, CVD/PECVD Systems, and more, backed by deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing can deliver reliable, contamination-free results for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















