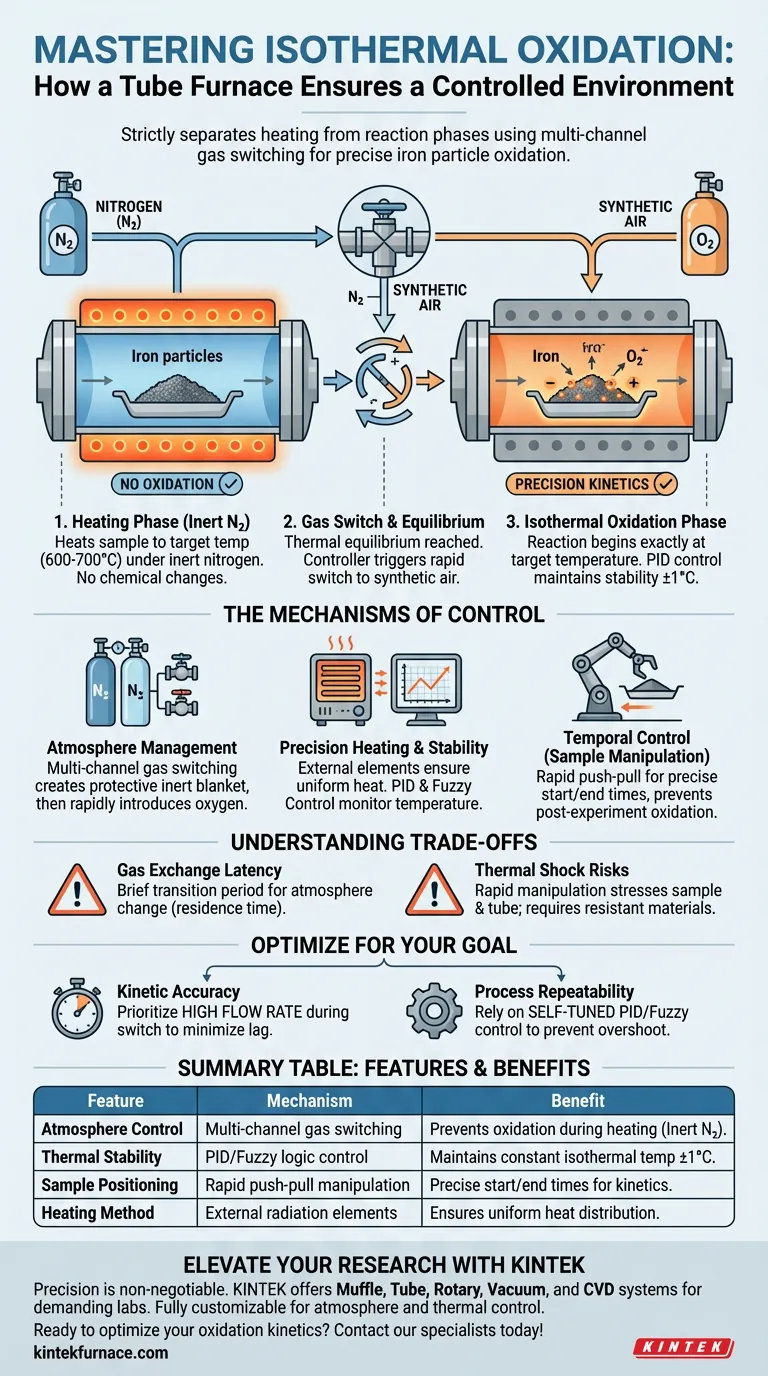
A tube furnace secures a controlled reaction environment by strictly separating the heating phase from the reaction phase using a multi-channel gas switching system. For the isothermal oxidation of iron particles, the system heats the sample to a target temperature (e.g., 600-700°C) under an inert nitrogen atmosphere, preventing any chemical changes until thermal equilibrium is reached and synthetic air is introduced.
Core Takeaway The defining feature of this setup is the elimination of "parasitic" oxidation during the temperature ramp-up. By stabilizing the sample in an inert gas before introducing oxygen, the furnace ensures that all measured oxidation kinetics occur strictly at the specific isothermal target temperature.

The Mechanisms of Environmental Control
To understand how a tube furnace guarantees precision, we must look at how it manages three critical variables: atmosphere, temperature, and time.
Atmosphere Management via Gas Switching
The primary reference highlights that a multi-channel gas switching system is the heart of the process.
During the initial heating phase, the furnace pumps an inert gas, such as nitrogen, into the work tube. This creates a protective blanket around the iron particles.
Once the system reaches the preset temperature, the controller triggers a rapid switch to synthetic air. This ensures the oxidation reaction begins exactly when intended, not before.
Precision Heating and Stability
As noted in the supplementary references, the furnace utilizes heating elements located outside the work tube.
This external positioning ensures that the heat radiates uniformly along the length of the tube, avoiding "hot spots" that could skew reaction data.
Advanced control algorithms, such as PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) regulation and fuzzy control, monitor the temperature. These systems can maintain stability within tight margins (often ±1°C), ensuring true isothermal conditions.
Temporal Control via Manipulation
Controlling the environment isn't just about heat and gas; it is also about the physical position of the sample.
The system utilizes a rapid push-pull sample manipulation technique.
This allows the operator to quickly insert the sample into the hot zone or withdraw it immediately after the reaction. This mechanical control provides precise definition of the total reaction time, preventing post-experiment oxidation during cooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a tube furnace offers high precision, there are inherent limitations you must account for to ensure data validity.
Gas Exchange Latency
Even with a rapid switching system, the atmosphere inside the tube does not change instantly. There is a brief transition period where nitrogen flushes out and oxygen fills the volume.
You must calculate this "residence time" based on the tube volume and gas flow rate to know exactly when the full oxidative environment is established.
Thermal Shock Risks
The rapid push-pull manipulation puts mechanical and thermal stress on both the sample and the ceramic work tube.
Introducing a cold sample boat instantly into a 700°C zone ensures a fast start, but it can cause thermal shock. This requires using high-grade, thermal-shock-resistant materials for your sample carriers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a tube furnace for iron particle oxidation, your specific research goals should dictate your operational parameters.
- If your primary focus is Kinetic Accuracy: Prioritize a high flow rate during the gas switch. This minimizes the lag between switching the valve and the oxygen actually reaching the iron particles.
- If your primary focus is Process Repeatability: Rely on the PID or fuzzy control settings. Ensure the system is "self-tuned" before the experiment to maintain the target temperature without overshooting.
By isolating the heating phase from the reaction phase, you transform a chaotic chemical process into a measurable, controlled experiment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mechanism | Benefit to Iron Oxidation |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Multi-channel gas switching | Prevents oxidation during heating using inert nitrogen. |
| Thermal Stability | PID/Fuzzy logic control | Maintains constant isothermal temperature within ±1°C. |
| Sample Positioning | Rapid push-pull manipulation | Provides precise start/end times for oxidation kinetics. |
| Heating Method | External radiation elements | Ensures uniform heat distribution across iron particles. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable in isothermal oxidation. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding lab environments. Our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring absolute control over atmosphere and thermal stability.
Ready to optimize your oxidation kinetics? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Jonas Spielmann, Ulrike I. Kramm. Exploring the oxidation behavior of undiluted and diluted iron particles for energy storage: Mössbauer spectroscopic analysis and kinetic modeling. DOI: 10.1039/d3cp03484d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of secondary calcination in a tube furnace? Enhance Cu@Zn-NC Adsorbent Longevity
- What role do controlled atmosphere tube furnaces play in recycling scrap copper wire? Precision Powder Production
- What process environment does a drop-tube furnace system provide? Expert Simulated Waste Incineration Research
- How does a Tube Furnace ensure structural consistency in Fe/MWCNT synthesis? Expert Control for Composite Quality
- Why must a tube furnace used for the pyrolysis of tungsten-based nanocomposites be equipped with a precision gas flow?
- How does a tube furnace facilitate the transformation of natural wood into a Carbonized Wood carrier? Master Pyrolysis
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















