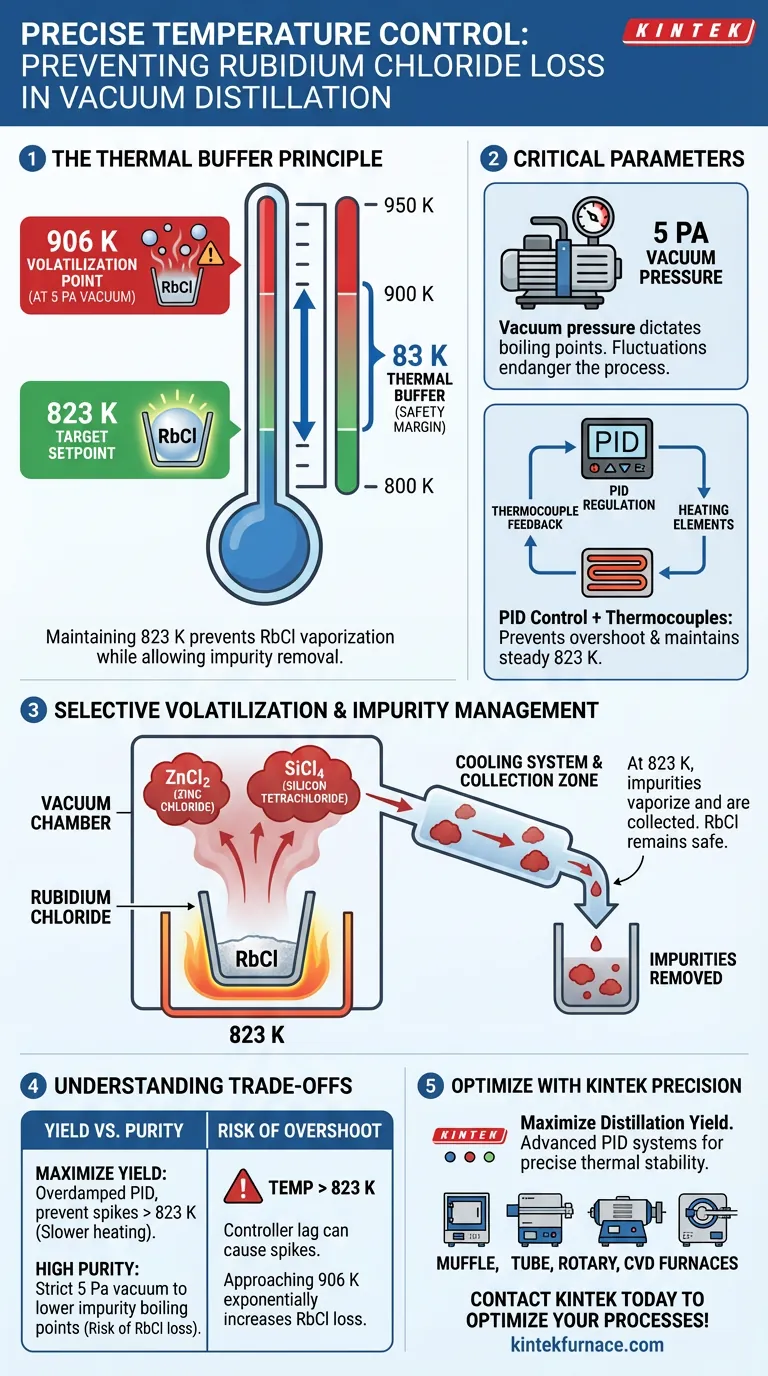
Precise temperature control prevents material loss by maintaining the system strictly at 823 K, creating a calculated thermal safety margin below the compound's volatility threshold. At a vacuum pressure of 5 Pa, Rubidium Chloride does not begin to volatilize until approximately 906 K; therefore, holding the temperature at 823 K allows impurities to be driven off without reaching the energy state required for the Rubidium Chloride to vaporize and escape.
By utilizing thermocouples and PID regulation to hold a steady 823 K, the process establishes an 83 K buffer zone. This ensures the kinetic decomposition of impurities occurs while the Rubidium Chloride remains stable in the crucible, effectively maximizing impurity removal while minimizing yield loss.

The Thermodynamics of Separation
The Critical Temperature Delta
The success of this process relies on a specific temperature gap. Under a vacuum of 5 Pa, Rubidium Chloride has a volatilization point of roughly 906 K.
The control system targets a setpoint of 823 K. By strictly adhering to this limit, the system ensures the thermal energy is insufficient to vaporize the primary product.
The Role of Vacuum Pressure
It is critical to remember that these temperature values are dependent on pressure.
The specific volatilization point of 906 K is valid specifically at 5 Pa. If the vacuum pressure fluctuates, the boiling points of both the product and the impurities will shift, potentially endangering the material.
Mechanism of Control
PID Regulation
To maintain the delicate balance between 823 K and 906 K, the system employs PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) regulation.
Simple on/off heating would cause temperature oscillations. PID control modulates power continuously to prevent "overshoot," ensuring the temperature never accidentally spikes near the 906 K danger zone.
Thermocouple Feedback
Precision requires accurate real-time data.
Thermocouples provide constant temperature readings from the distillation zone. This feedback loop allows the PID controller to make micro-adjustments instantly.
Managing Impurities
Selective Volatilization
The 823 K setpoint is not arbitrary; it is high enough to trigger the kinetic decomposition and volatilization of specific impurities.
Contaminants such as ZnCl2 (Zinc Chloride) and SiCl4 (Silicon Tetrachloride) are vaporized at this temperature.
Preventing Re-contamination
Once impurities are vaporized, they must be removed permanently.
A circulating cooling water system creates a sharp temperature gradient. This rapidly condenses the volatilized impurity gases back into solids or liquids in a separate collection zone, preventing vapor backflow that could re-contaminate the Rubidium Chloride.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Overshoot
The primary risk in this process is controller lag or failure.
If the PID loop is poorly tuned, the temperature could momentarily drift above 823 K. As you approach 906 K, the rate of Rubidium Chloride loss increases exponentially, even if the average temperature remains lower.
Yield vs. Purity
There is an inherent tension between saving material and removing impurities.
Operating too far below 823 K ensures zero loss of Rubidium Chloride, but it may fail to fully volatilize stubborn impurities. Operating too close to 906 K maximizes purity but drastically increases the risk of losing valuable raw material.
Optimizing Your Distillation Strategy
To achieve the best results, you must align your control strategy with your specific production metrics.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Yield: Ensure your PID controller is overdamped to prevent any temperature spikes above 823 K, even if it means a slightly slower heating ramp.
- If your primary focus is High Purity: Verify that your vacuum system maintains a strict 5 Pa or lower, as a loss in vacuum will raise volatilization points and make the 823 K setpoint less effective at removing impurities.
Ultimately, the efficiency of the process depends on the stability of the 83 K thermal buffer between the purification setpoint and the volatilization threshold.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Value/Setting | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Target Setpoint | 823 K | Optimal temp for impurity removal without RbCl loss |
| Volatilization Point | ~906 K (at 5 Pa) | The threshold where Rubidium Chloride begins to vaporize |
| Thermal Buffer | 83 K | Safety margin to prevent accidental product vaporization |
| Vacuum Pressure | 5 Pa | Critical environment for lowering impurity boiling points |
| Control Method | PID Regulation | Prevents temperature overshoot and oscillation |
| Impurity Targets | ZnCl2, SiCl4 | Contaminants vaporized and removed at 823 K |
Maximize Your Distillation Yield with KINTEK Precision
Don't let thermal overshoot compromise your high-purity materials. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance vacuum systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD furnaces, all customizable for your unique distillation needs.
Our advanced PID regulation systems provide the precise temperature stability required to maintain critical thermal buffers for Rubidium Chloride and other sensitive compounds. Contact us today to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
References
- Cui Xi, Tao Qu. A Study on the Removal of Impurity Elements Silicon and Zinc from Rubidium Chloride by Vacuum Distillation. DOI: 10.3390/ma17091960
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can you describe a process example using a vacuum hardening furnace? Achieve Clean, Precise Metal Hardening
- What is the primary function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the production of cemented carbide? Achieve Peak Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven in the phosphor preparation process? Achieve Higher Purity Today
- What are the tool and die industry applications of furnace brazing? Boost Performance and Cut Costs
- Why are vanadium windows used in vacuum furnaces for neutron scattering? Achieve Peak Signal Integrity for SDSS2507
- What are the main benefits of using a vacuum furnace for industrial processes? Achieve Superior Material Quality & Control
- What components are used in the construction of vacuum graphitizing furnaces? A Guide to High-Temp Performance
- What are the environmental advantages of vacuum furnaces? Reduce Emissions and Energy Use



















