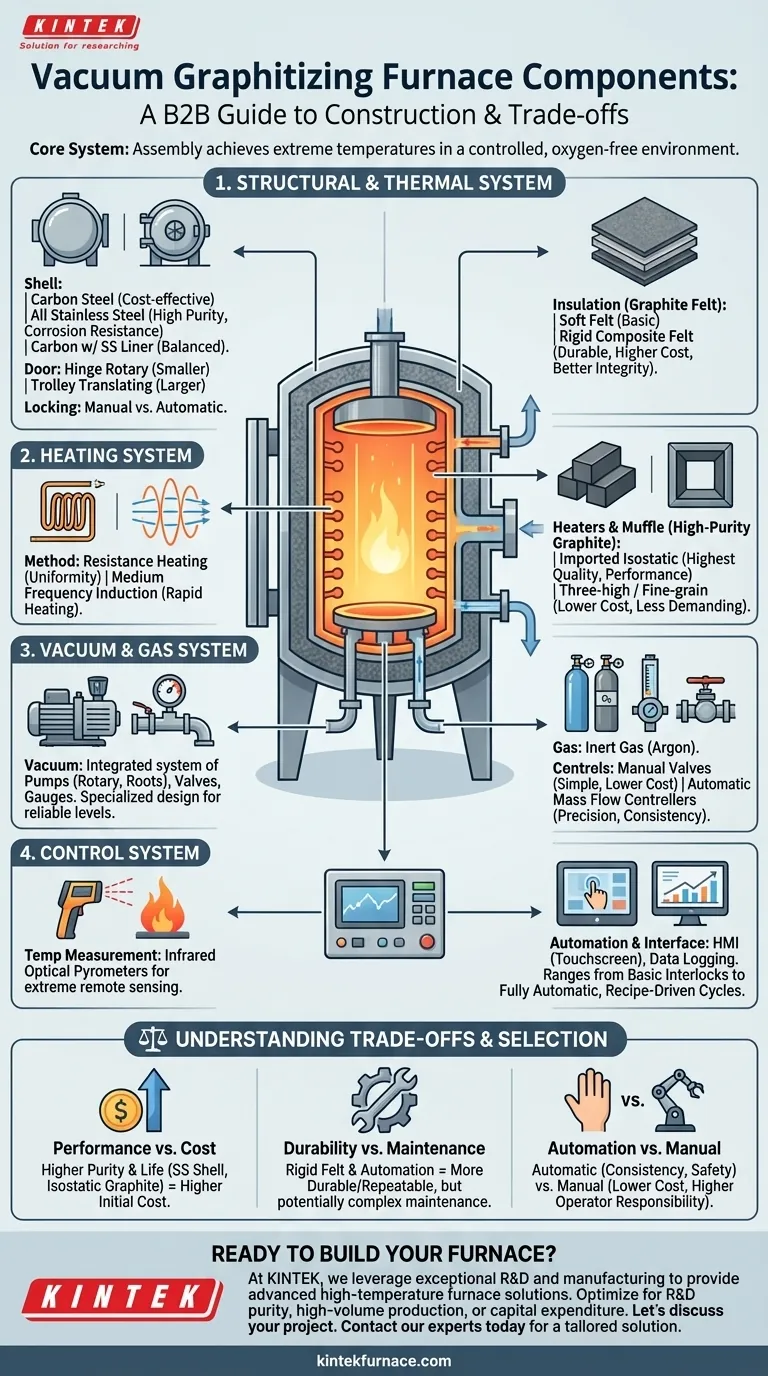
At its core, a vacuum graphitizing furnace is an assembly of several critical systems working in concert to achieve extreme temperatures in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. The key components fall into four main categories: the structural and thermal enclosure, the heating system, the vacuum and process gas system, and the instrumentation and control system. Each category offers a range of options that directly impact the furnace's performance, longevity, and cost.
The selection of components for a vacuum graphitizing furnace is not merely a checklist of parts. It is a series of deliberate engineering trade-offs between initial cost, operational performance, material purity, and long-term durability.
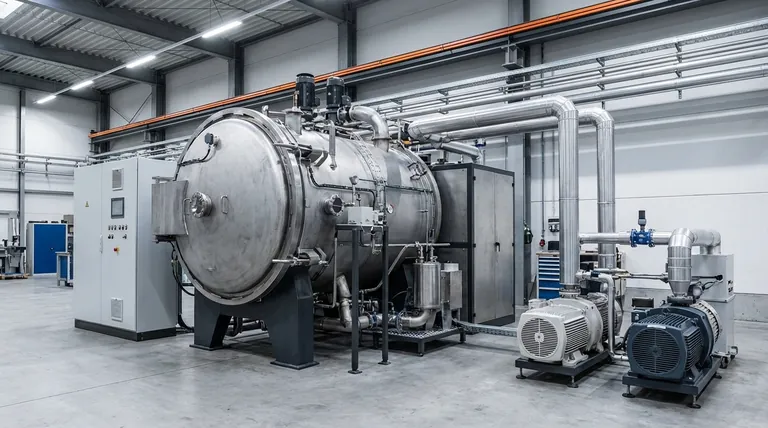

The Core Structural and Thermal System
This is the physical body of the furnace, responsible for containing the process, maintaining structural integrity, and managing heat loss.
Furnace Shell and Door
The furnace shell is the primary pressure vessel. Material choice is a foundational decision. A full carbon steel shell is the most cost-effective option, while an all stainless steel shell offers superior corrosion resistance and cleanliness. A common compromise is a carbon steel shell with an inner stainless steel liner, balancing cost and process purity.
The furnace door provides access and must create a perfect vacuum seal. Designs include hinge rotary doors for smaller furnaces or trolley translating doors for larger units. Locking mechanisms can be manual for simplicity or automatic for improved safety and process consistency.
Thermal Insulation
Effective insulation is crucial for reaching temperatures up to 3000°C while protecting the furnace shell. The insulation package is typically made of graphite felt.
Options range from basic soft graphite felt to more durable rigid composite felt. Rigid felt offers better structural integrity and a longer service life but comes at a higher initial cost.
The Heart of the Process: The Heating System
This system generates the immense energy required for graphitization. The design choice here fundamentally defines the furnace's operational characteristics.
Heating Method
Two primary methods are used. Resistance heating is common, using electrical current passed through graphite heating elements. It offers excellent temperature uniformity.
Alternatively, medium frequency induction heating uses electromagnetic fields to heat the graphite susceptor or the charge directly. This method can offer very rapid heating rates.
Heater and Muffle Materials
The heaters and the protective muffle that surrounds the workload are made from high-purity graphite. The grade of graphite is a critical factor in furnace performance and lifespan.
Imported isostatic graphite represents the highest quality, offering exceptional purity, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. Lower-cost alternatives include three-high graphite or fine-grain graphite, which provide good performance for less demanding applications.
Achieving Purity: The Vacuum and Gas System
This dual-purpose system is responsible for first removing atmospheric contaminants and then introducing a controlled, inert gas environment.
The Vacuum System
This is not just a single part but an integrated system of vacuum pumps (e.g., rotary vane and roots pumps), valves, pipes, and vacuum gauges. The design and selection of this system requires specialized knowledge to achieve the required vacuum levels efficiently and reliably.
The Process Gas System
Once a vacuum is achieved, an inert gas like Argon is introduced. This system includes mass flow controllers or volume flow meters to precisely regulate the gas flow, along with manual or automatic valves to control the backfilling and purging processes.
Command and Control: The Brain of the Furnace
This collection of instruments monitors and controls all process parameters, ensuring a safe and repeatable cycle.
Temperature Measurement and Control
Given the extreme temperatures, direct contact measurement is impossible. Infrared optical pyrometers are used to measure the temperature of the workload or heating elements remotely. This data feeds into temperature control instruments that regulate power to the heaters.
Automation and Interface
Modern furnaces use a Man-Machine Interface (HMI), often a touchscreen computer, for centralized control and monitoring. This interface integrates with the electrical control components and recorders that log process data for quality assurance. The level of automation can range from basic safety interlocks to fully automatic, recipe-driven process cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of components is a balancing act. Understanding these compromises is key to specifying a furnace that meets your technical and financial goals.
Performance vs. Cost
This is the most common trade-off. An all stainless steel shell with isostatic graphite heaters will deliver the highest purity and longest life but carries the highest price tag. A carbon steel furnace with standard graphite is cheaper but may introduce impurities and require more frequent maintenance of the heating elements.
Durability vs. Ease of Maintenance
Rigid composite felt insulation is highly durable and resistant to gas erosion but can be more difficult and expensive to replace than soft felt. Similarly, a complex, fully automated system is highly repeatable but may require more specialized maintenance than a simpler, manually operated one.
Automation vs. Manual Control
Automatic locking doors, gas valves, and vacuum systems reduce the chance of operator error and ensure process consistency. Manual components lower the initial cost and complexity but place a greater responsibility on the operator to follow procedures correctly.
Selecting Components for Your Application
Your final component selection should be driven entirely by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance for R&D or advanced materials: Prioritize an all-stainless or inner-stainless shell, imported isostatic graphite heaters, and a fully automated control system with precise mass flow controllers.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective industrial production: A carbon steel shell with an inner liner, high-quality domestic graphite, and a robust, semi-automated control system often provides the best balance of capital cost and operational reliability.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital expenditure for general-purpose applications: A full carbon steel shell, standard graphite elements, and manual control systems for the vacuum and gas will be the most economical choice, but be prepared for potentially higher long-term maintenance costs and limitations on ultimate purity.
Ultimately, understanding how each component contributes to the final goal empowers you to specify a furnace that is a tool, not a liability.
Summary Table:
| Component Category | Key Options & Trade-offs |
|---|---|
| Structural & Thermal System | Shell: Carbon Steel (cost-effective) vs. Stainless Steel (high purity). Insulation: Soft Graphite Felt vs. Rigid Composite Felt (durability). |
| Heating System | Method: Resistance Heating (uniformity) vs. Induction Heating (speed). Material: Imported Isostatic Graphite (performance) vs. Standard Graphite (cost). |
| Vacuum & Gas System | Vacuum Pumps & Gauges; Process Gas Controls: Manual Valves (cost) vs. Automatic Mass Flow Controllers (precision). |
| Control System | Interface: Basic Controls vs. Automated HMI with Data Logging (repeatability). Temperature Measurement: Infrared Optical Pyrometers. |
Ready to build a vacuum graphitizing furnace tailored to your specific needs?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether your priority is maximum purity for R&D, high-volume industrial production, or optimizing capital expenditure, our product line—including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today for a solution that balances performance, durability, and cost.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity



















