In the tool and die industry, furnace brazing is used to construct and repair high-performance cutting tools, molds, and dies. The process involves joining segments of different materials, such as a carbide cutting tip to a steel body, inside a controlled-atmosphere furnace to create a single, robust component with superior hardness and wear resistance.
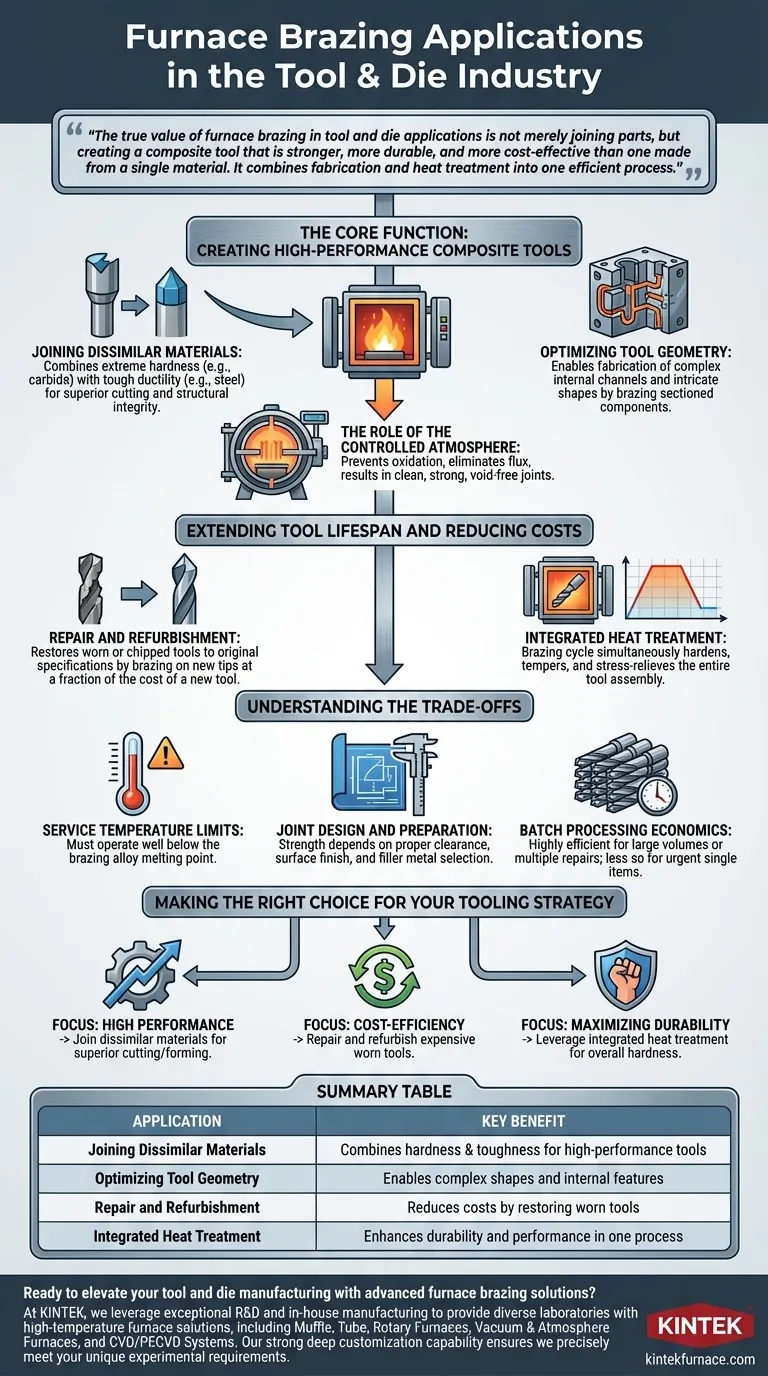
The true value of furnace brazing in tool and die applications is not merely joining parts, but creating a composite tool that is stronger, more durable, and more cost-effective than one made from a single material. It combines fabrication and heat treatment into one efficient process.
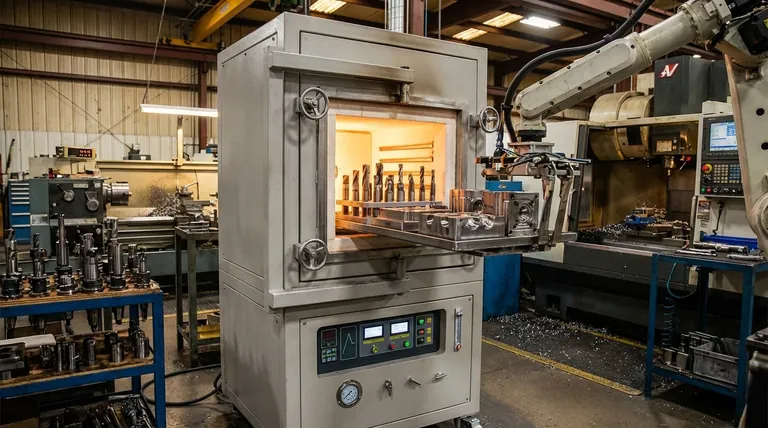

The Core Function: Creating High-Performance Composite Tools
Furnace brazing enables the design of tools that leverage the best properties of multiple materials, which would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to achieve through machining alone.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
The most common application is joining an extremely hard but brittle material (like tungsten carbide) to a tough and ductile material (like tool steel). The carbide provides the wear-resistant cutting or forming surface, while the steel provides the structural integrity and impact resistance for the tool's body.
Optimizing Tool Geometry
Brazing allows for the creation of tools with complex internal channels or intricate shapes. For example, dies for plastic injection molding or metal casting can be fabricated in sections and then brazed together, creating a finished product with features that are difficult to machine.
The Role of the Controlled Atmosphere
Performing the process inside a vacuum or inert gas furnace is critical. This controlled environment prevents oxidation and eliminates the need for corrosive chemical fluxes, resulting in a clean, exceptionally strong, and void-free joint that is ready for use with minimal post-processing.
Extending Tool Lifespan and Reducing Costs
Beyond initial fabrication, furnace brazing is a cornerstone of cost-effective tool management and maintenance, directly impacting manufacturing efficiency.
Repair and Refurbishment
Instead of discarding an expensive die or a large cutting tool when its working surface wears down or chips, the worn section can be removed. A new tip or surface can then be furnace brazed onto the existing tool body, restoring it to its original specifications at a fraction of the cost of a new tool.
Integrated Heat Treatment
The brazing cycle is often designed to double as a heat treatment process. As the assembly is heated to melt the brazing filler metal and then cooled, the entire tool can be simultaneously hardened, tempered, and stress-relieved under precise control. This enhances the overall durability and performance of the final tool.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, furnace brazing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
Service Temperature Limits
A brazed tool cannot be used at temperatures that approach the melting point of the braze filler alloy. The joint will lose strength and fail. The service temperature of the tool must always remain well below the brazing temperature.
Joint Design and Preparation
The strength of a brazed joint is highly dependent on proper engineering. Factors like joint clearance, surface finish, and the selection of the correct filler metal are critical. A poorly designed joint is an inherent weak point, regardless of the quality of the brazing process itself.
Batch Processing Economics
Furnace brazing is a batch process, making it highly efficient for producing many identical tools or processing multiple repairs simultaneously. However, it can be less time-efficient for a single, urgent repair compared to manual methods like torch brazing or welding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Tooling Strategy
Your specific goal will determine how you can best apply furnace brazing to your operations.
- If your primary focus is creating complex or high-performance tools: Use furnace brazing to join dissimilar materials like carbide and steel for superior cutting or forming capabilities.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and sustainability: Implement a furnace brazing program to repair and refurbish expensive worn dies and cutting tools instead of replacing them.
- If your primary focus is maximizing tool durability: Leverage the integrated heat treatment cycle of furnace brazing to enhance the overall hardness and wear resistance of your tool assemblies.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage furnace brazing not just as a joining method, but as a strategic asset for manufacturing excellence.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Joining Dissimilar Materials | Combines hardness and toughness for high-performance tools |
| Optimizing Tool Geometry | Enables complex shapes and internal features |
| Repair and Refurbishment | Reduces costs by restoring worn tools |
| Integrated Heat Treatment | Enhances durability and performance in one process |
Ready to elevate your tool and die manufacturing with advanced furnace brazing solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you achieve stronger, more durable, and cost-effective tools. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance



















