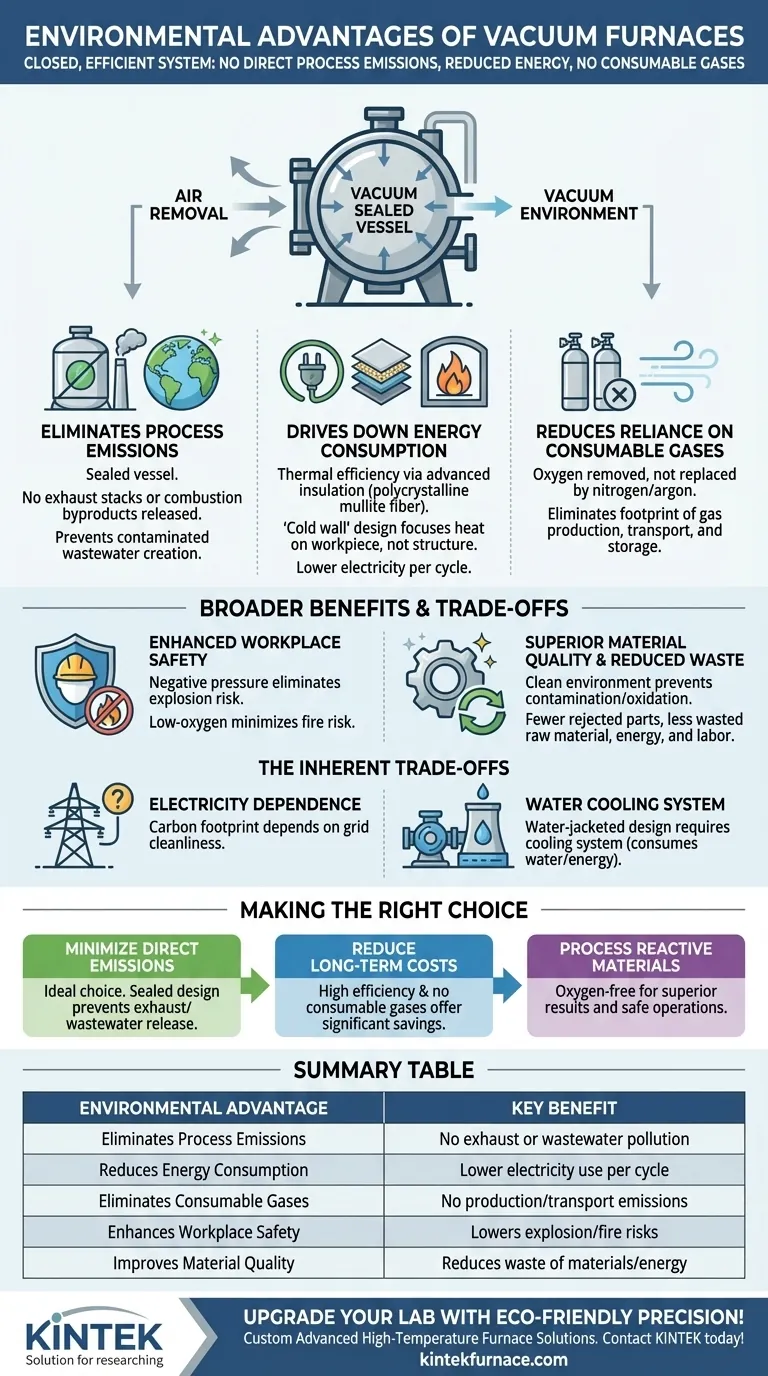
From a technical standpoint, the primary environmental advantages of vacuum furnaces stem from their inherent design as a closed and highly efficient system. By removing the atmosphere rather than replacing it, they eliminate direct process emissions, dramatically reduce energy consumption through advanced insulation, and negate the need for the production and transport of consumable process gases.
The environmental benefits of a vacuum furnace are not add-on features; they are a direct consequence of its core design. A sealed, highly insulated chamber inherently prevents the release of process byproducts and minimizes the energy wasted during heat treatment.

How Vacuum Furnaces Minimize Environmental Impact
The environmental performance of a vacuum furnace is rooted in its fundamental operating principle: creating a controlled environment by removing air and contaminants. This approach yields several key advantages over traditional atmosphere-based furnaces.
Eliminating Process Emissions
A vacuum furnace is a sealed vessel. During a cycle, air and other gases are pumped out, and the process is conducted in a near-complete vacuum.
This closed-loop design means there are no exhaust stacks releasing combustion byproducts or process gases into the atmosphere. Similarly, it prevents the creation of contaminated wastewater that would require treatment.
Driving Down Energy Consumption
Modern vacuum furnaces are engineered for thermal efficiency. They use high-quality insulation materials, such as polycrystalline mullite fiber, which allow for rapid heating while minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment.
Features like double-layer furnace shells and water-jacketed "cold wall" designs further ensure that energy is focused on the workpiece, not wasted heating the furnace structure or the workshop. This directly translates to lower electricity consumption per cycle.
Reducing Reliance on Consumable Gases
Many conventional heat-treating processes require a constant flow of prepared atmospheres, such as nitrogen, argon, or endothermic gas, to protect parts from oxidation.
Vacuum furnaces achieve this protection by simply removing the oxygen. This eliminates the significant environmental footprint associated with producing, compressing, transporting, and storing these industrial gases.
Understanding the Broader Benefits and Trade-offs
The advantages of vacuum technology extend beyond direct environmental metrics, but it's crucial to understand the complete picture, including the associated trade-offs.
Enhanced Workplace Safety
Safety and environmental concerns are often linked. Vacuum furnaces operate at negative pressure, which eliminates the risk of explosion common to pressurized vessels.
The low-oxygen environment also minimizes the risk of fire, making the workplace safer and reducing the potential for environmental incidents.
Superior Material Quality and Reduced Waste
The exceptionally clean environment inside a vacuum furnace prevents contamination and oxidation, leading to a superior surface finish and improved material properties.
This higher quality and consistency result in fewer rejected parts. Reducing scrap directly translates to less wasted raw material, energy, and labor—a significant, if indirect, environmental benefit.
The Inherent Trade-offs
No technology is without its considerations. While highly efficient in operation, the primary energy source for a vacuum furnace is electricity. Its total carbon footprint is therefore dependent on the cleanliness of the electrical grid providing its power.
Furthermore, the water-jacketed cold wall design requires a cooling system. While often a closed-loop circuit, this system consumes both water and the energy needed to pump it, which must be factored into any complete environmental assessment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing the right heat-treating technology requires balancing performance goals with environmental and operational costs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing direct emissions: A vacuum furnace is an ideal choice, as its sealed design inherently prevents the release of exhaust gases and process-related wastewater.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operating costs: The high energy efficiency and elimination of consumable process gases can lead to significant savings that offset a potentially higher initial investment.
- If you are processing highly reactive or sensitive materials: The clean, oxygen-free environment not only provides superior results but also aligns with best practices for safe and environmentally sound operations.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic decision that aligns process excellence with environmental responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Eliminates Process Emissions | No exhaust gases or wastewater released, reducing air and water pollution |
| Reduces Energy Consumption | Advanced insulation and efficient design lower electricity use per cycle |
| Eliminates Consumable Gases | No need for nitrogen or argon, cutting production and transport emissions |
| Enhances Workplace Safety | Lowers explosion and fire risks, preventing environmental incidents |
| Improves Material Quality | Reduces part rejections, minimizing waste of raw materials and energy |
Upgrade your lab with eco-friendly precision! KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, designed to cut your environmental footprint while boosting efficiency. Our deep customization ensures a perfect fit for your unique needs. Contact us today to learn how our expertise can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density



















