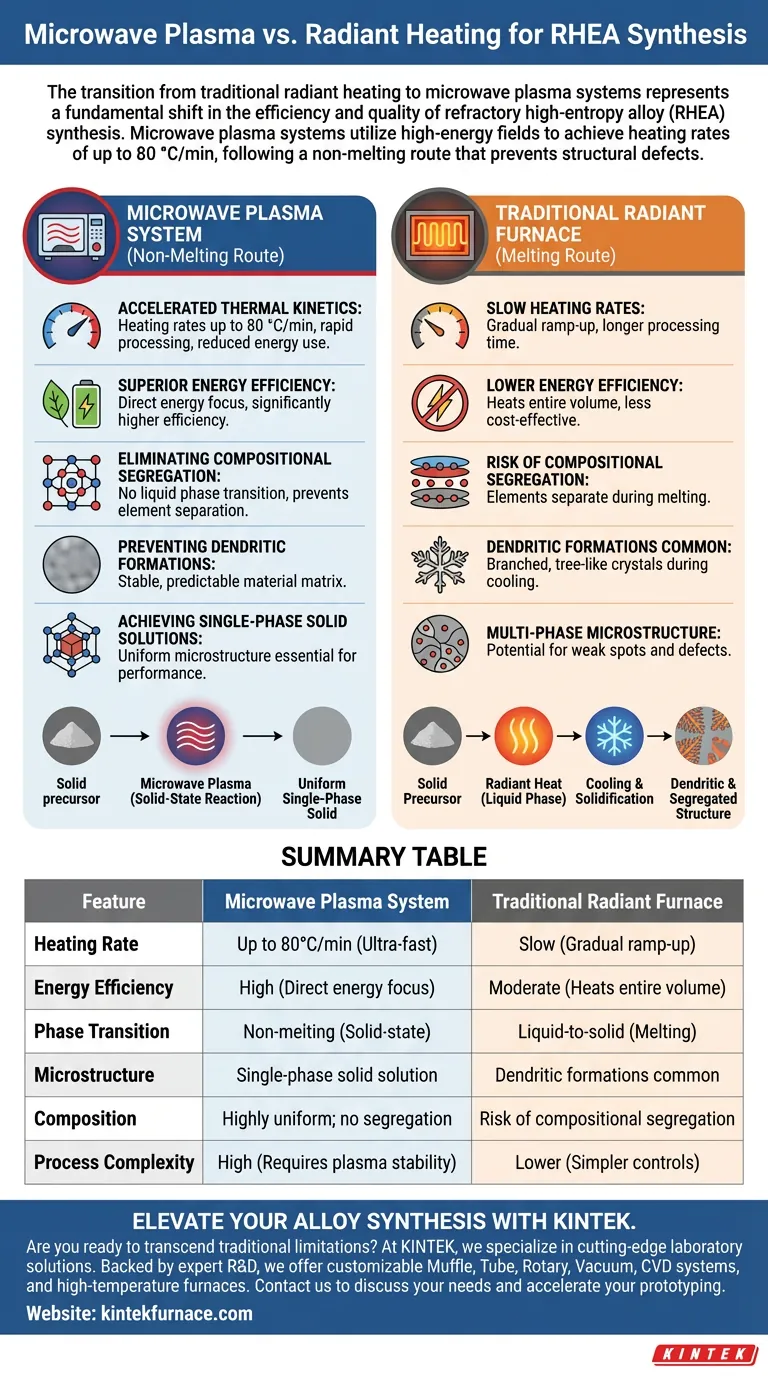
The transition from traditional radiant heating to microwave plasma systems represents a fundamental shift in the efficiency and quality of refractory high-entropy alloy (RHEA) synthesis. While traditional furnaces rely on slow, external heat transfer, microwave plasma systems utilize high-energy fields to achieve heating rates of up to 80 °C/min. This method follows a non-melting route, which inherently prevents the structural defects and chemical imbalances that often plague conventional melting processes.
Core Takeaway: Microwave plasma systems outperform traditional radiant furnaces by providing faster heating and higher energy efficiency, while simultaneously ensuring a uniform, single-phase microstructure by avoiding the liquid-to-solid phase transition entirely.

Efficiency and Speed Advantages
Accelerated Thermal Kinetics
Microwave plasma systems can reach target temperatures far faster than traditional furnaces, boasting heating rates as high as 80 °C/min. This rapid heating reduces the overall processing time and minimizes the energy required to maintain high temperatures.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Unlike radiant heating, which must heat the entire furnace volume and insulation, microwave plasma focuses energy more directly. This results in significantly higher energy efficiency, making it a more sustainable and cost-effective option for synthesizing complex alloys.
The Non-Melting Advantage in Microstructure
Eliminating Compositional Segregation
Because the microwave plasma process follows a non-melting route, the materials do not transition through a liquid phase. This prevents compositional segregation, where different elements settle or separate based on their melting points or densities.
Preventing Dendritic Formations
Traditional melting methods often result in the formation of dendritic structures (branched, tree-like crystals) during cooling. The solid-state or non-melting nature of microwave plasma synthesis bypasses this phase, leading to a more stable and predictable material matrix.
Achieving Single-Phase Solid Solutions
The precision of the plasma environment allows for the production of single-phase solid solution alloys. This results in a highly uniform microstructure, which is essential for the mechanical performance and thermal stability of refractory high-entropy alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Control Complexity
While microwave plasma is highly efficient, it requires precise control over plasma stability and gas composition. Unlike the simpler "set and forget" nature of some radiant furnaces, plasma systems demand sophisticated monitoring to ensure uniform energy distribution across the sample.
Scale and Geometry Limitations
Traditional radiant furnaces are often easier to scale for very large bulk components or high-volume batches. Microwave plasma systems may face challenges regarding field uniformity when processing exceptionally large or irregularly shaped parts, potentially leading to localized "hot spots."
Strategic Implementation for Alloy Development
Successful synthesis of high-performance RHEAs requires matching the heating technology to your specific structural requirements.
- If your primary focus is microstructural uniformity: Microwave plasma is the superior choice because it bypasses the melting phase that typically triggers chemical imbalances.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping and throughput: The 80 °C/min heating rate allows for significantly faster experimental cycles compared to the slow ramp-up times of radiant furnaces.
- If your primary focus is eliminating casting defects: Utilize the non-melting route of plasma systems to prevent the formation of weak dendritic structures.
By leveraging the non-melting pathway of microwave plasma, engineers can produce refractory alloys with a level of structural integrity that traditional radiant furnaces simply cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Microwave Plasma System | Traditional Radiant Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | Up to 80°C/min (Ultra-fast) | Slow (Gradual ramp-up) |
| Energy Efficiency | High (Direct energy focus) | Moderate (Heats entire volume) |
| Phase Transition | Non-melting (Solid-state) | Liquid-to-solid (Melting) |
| Microstructure | Single-phase solid solution | Dendritic formations common |
| Composition | Highly uniform; no segregation | Risk of compositional segregation |
| Process Complexity | High (Requires plasma stability) | Lower (Simpler controls) |
Elevate Your Alloy Synthesis with KINTEK
Are you ready to transcend the limitations of traditional melting? At KINTEK, we specialize in cutting-edge laboratory solutions designed for the next generation of material science. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as specialized high-temperature furnaces—all customizable to your unique research needs.
Whether you are developing refractory high-entropy alloys or advanced ceramics, our precision heating technology ensures superior microstructural uniformity and energy efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and see how our tailored systems can accelerate your prototyping and production cycles.
Visual Guide
References
- Bria Storr, Shane A. Catledge. High entropy alloy MoNbTaVW synthesized by metal-oxide reduction in a microwave plasma. DOI: 10.1063/5.0192076
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages do MPCVD-grown diamond coatings offer for cutting tools? Unlock Unmatched Tool Performance
- What are the key advantages of the MPCVD method? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Scalability
- What is the basic principle of operation for the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system? Unlock High-Purity Material Growth
- What does MPCVD stand for and what is its primary use? Discover High-Quality Diamond Growth Solutions
- What effect does the sample base position have in an MPCVD device? Master Plasma Control for Optimal Deposition
- What is the significance of stable discharge plasma in MPCVD? The Key to High-Quality Diamond Synthesis
- What are the advantages of MPCVD over traditional CVD methods? Achieve Superior Film Purity and Quality
- What are the limitations of MPCVD? Balancing High Performance with Substrate Sensitivity and Cost



















