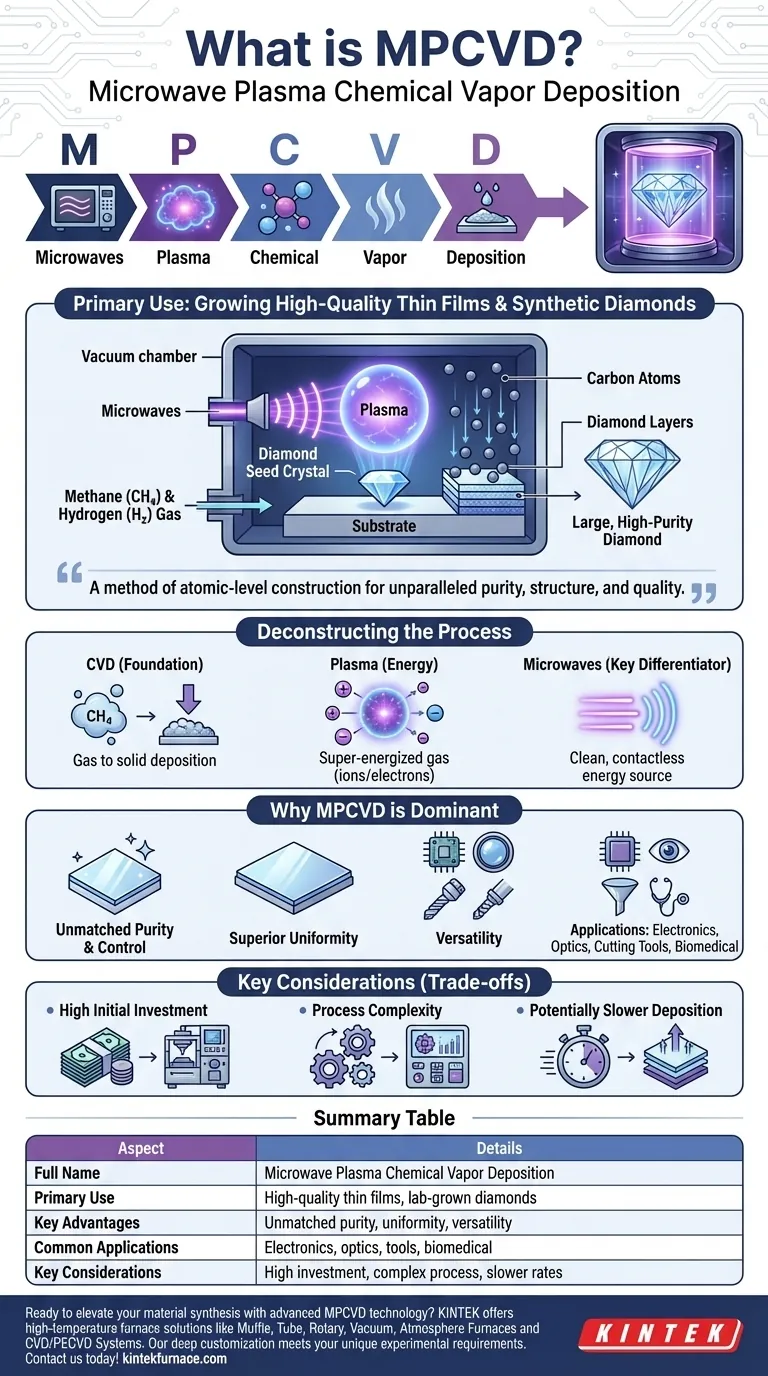
At its core, MPCVD stands for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition. It is a highly advanced manufacturing process used to grow exceptionally high-quality thin films and synthetic materials, most notably lab-grown diamonds, on a substrate. The technique uses microwave energy to create a plasma environment where gases are broken down and reformed into a solid crystalline structure.
MPCVD is not just a coating technique; it is a method of atomic-level construction. By using microwave-generated plasma, it allows for the precise, layer-by-layer growth of materials like diamond, offering unparalleled control over purity, structure, and quality.

Deconstructing the MPCVD Process
To truly understand MPCVD, it helps to break down each component of its name. The process is a sophisticated evolution of a more fundamental technology.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Foundation
The parent technology is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In any CVD process, precursor gases are introduced into a chamber where they react and deposit a solid material onto a heated surface, or substrate.
Introducing Plasma: The "P" in MPCVD
Plasma is the fourth state of matter, created when a gas is super-energized to the point that its atoms are broken into charged ions and electrons. In the MPCVD process, this plasma provides the intense energy needed to efficiently break down the precursor gases into their fundamental, reactive components (e.g., carbon atoms).
The Role of Microwaves: The "M" in MPCVD
The "Microwave" aspect is the key differentiator. Microwaves are used as a clean and highly controllable energy source to generate and sustain the plasma. This method avoids direct contact with heating filaments, which prevents contamination and allows for the creation of exceptionally pure materials.
Putting It All Together: From Gas to Crystal
In a typical MPCVD diamond growth process:
- A vacuum chamber is set up with a small diamond "seed" crystal as the substrate.
- A precise mixture of gases, typically methane (a source of carbon) and hydrogen, is introduced.
- Microwaves are used to ignite the gases into a stable ball of plasma above the seed crystal.
- The plasma breaks down the methane, freeing carbon atoms that then rain down and attach to the diamond seed, replicating its crystal structure.
- Over time, these atoms build up layer by layer, growing a much larger, high-purity diamond.
Why MPCVD Is a Dominant Technique
MPCVD is valued across multiple high-tech industries because it delivers results that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
Unmatched Purity and Control
Because microwaves provide energy without physical contact, the risk of impurities entering the film is drastically reduced. This allows for the growth of films, particularly diamonds, with exceptional clarity and structural integrity.
Superior Uniformity
The process enables the deposition of large, highly uniform films over a wide surface area. This is critical for applications like semiconductor wafers or coating large optical lenses, where consistency is paramount.
Versatility Across Industries
The precision of MPCVD has led to its adoption in a range of fields:
- Electronics: Creating diamond-based semiconductors that can operate at higher temperatures and frequencies.
- Optics: Producing durable, anti-reflective coatings for lenses and windows.
- Cutting Tools: Applying ultra-hard diamond coatings to extend tool life and performance.
- Biomedical: Developing biocompatible coatings for medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, MPCVD is not a universal solution. Its precision comes with specific considerations.
High Initial Investment
MPCVD reactors are complex, sophisticated pieces of equipment. The initial capital cost for setting up an MPCVD system is significant compared to simpler deposition methods.
Process Complexity
Achieving high-quality results requires precise control over numerous variables, including gas pressure, temperature, gas mixture, and microwave power. Operating these systems effectively demands a high level of expertise.
Potentially Slower Deposition Rates
The focus on controlled, layer-by-layer growth means that MPCVD can sometimes be a slower process than bulk deposition techniques. The trade-off is one of speed versus ultimate quality and purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding when to leverage MPCVD depends entirely on your end goal and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is the highest-purity gem-quality diamonds or advanced semiconductors: MPCVD is the industry standard, offering unparalleled control over the final material's properties.
- If your primary focus is creating durable coatings for industrial tools or optics: MPCVD provides a superior, uniform, and long-lasting film that justifies the investment for high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is rapid, cost-effective coating without extreme purity demands: Simpler, faster, and less expensive deposition methods may be more suitable for your needs.
Ultimately, MPCVD represents a fundamental shift from simply coating a surface to precisely engineering a new material from the atom up.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition |
| Primary Use | Growing high-quality thin films and synthetic materials, especially lab-grown diamonds |
| Key Advantages | Unmatched purity, superior uniformity, versatility across industries |
| Common Applications | Electronics (diamond semiconductors), optics (coatings), cutting tools, biomedical implants |
| Key Considerations | High initial investment, process complexity, potentially slower deposition rates |
Ready to elevate your material synthesis with advanced MPCVD technology? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for growing high-purity diamonds and thin films. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What are the operational benefits of using a CVD Tube Furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What is the process for synthesizing transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) using CVD tube furnaces? Master High-Quality Thin Film Growth
- What are the practical applications of gate media prepared by CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Advanced Electronics and More
- What are the advantages of CVD tube furnace sintering systems? Achieve Superior Material Control and Purity
- What are the key design features of a CVD Tube Furnace? Optimize Your Material Synthesis with Precision



















