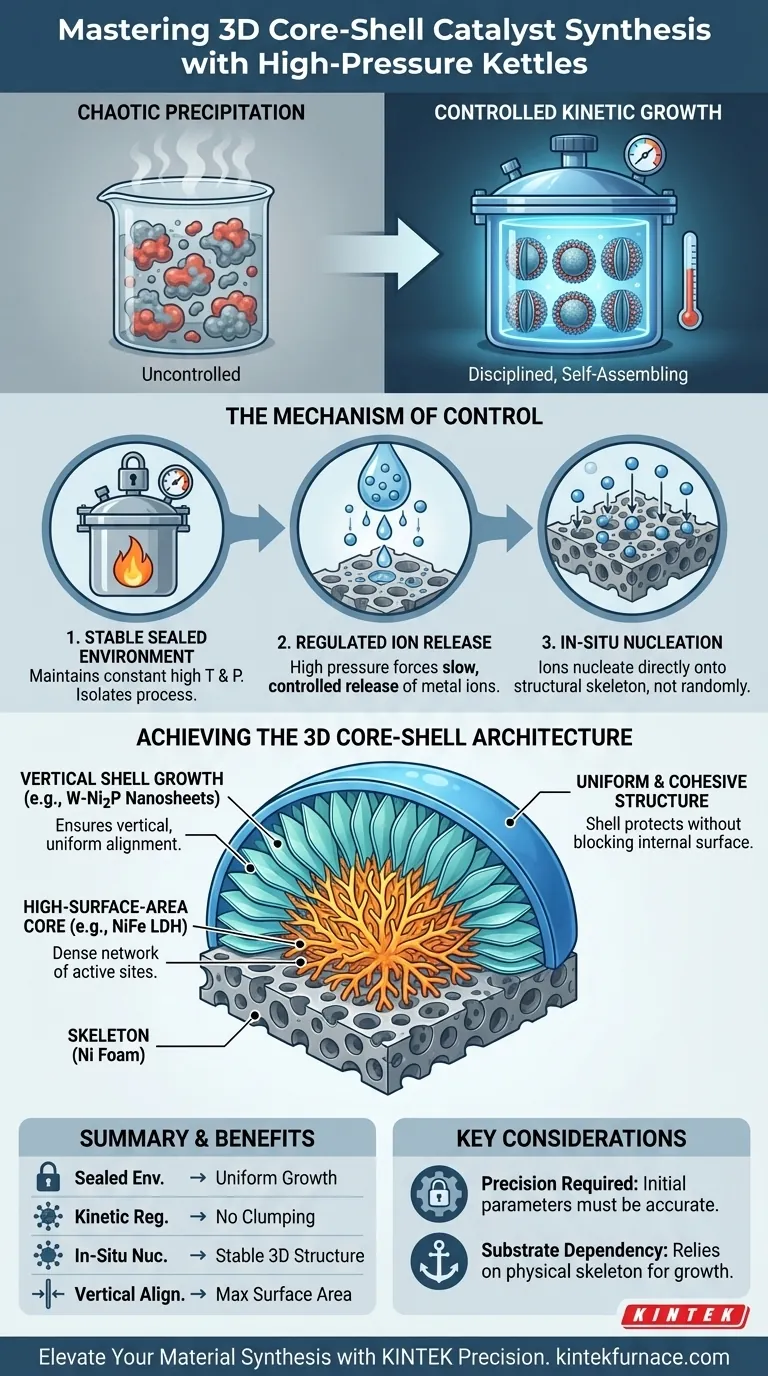
A high-pressure reaction kettle functions as a precision containment vessel that facilitates 3D core-shell formation by maintaining a constant, sealed hydrothermal environment. This specific combination of high temperature and high pressure forces the slow, controlled release of metal ions, enabling them to nucleate directly onto a structural skeleton rather than precipitating randomly.
The core value of the high-pressure kettle is its ability to replace chaotic chemical precipitation with controlled kinetic growth. By strictly regulating the reaction environment, it ensures that complex structures—like vertically aligned nanosheets—can grow uniformly around a central core.

The Mechanism of Control
Creating a Stable Hydrothermal Environment
The reaction kettle provides a sealed ecosystem that isolates the chemical process from external variables. It maintains a constant state of high temperature and pressure throughout the synthesis duration. This stability is the foundational requirement for growing complex, multi-layered structures.
Regulating Metal Ion Release
One of the most critical functions of this environment is the modulation of chemical kinetics. The high-pressure conditions cause metal ions to be released slowly into the solution. This prevents the rapid, uncontrolled crashing out of materials that often leads to amorphous or clumpy products.
Facilitating In-Situ Nucleation
Because the ions are released gradually, they are forced to nucleate in-situ along the provided substrate (specifically the nickel foam skeleton mentioned in your context). This direct attachment to the skeleton is what anchors the 3D structure, providing a stable base for subsequent layers to grow.
Achieving the 3D Core-Shell Architecture
Forming the High-Surface-Area Core
The hydrothermal environment specifically fosters the growth of the initial core material, such as NiFe LDH (Layered Double Hydroxide). The conditions within the kettle are tuned to maximize the specific surface area of this core, creating a dense network of active sites.
Ensuring Vertical Shell Growth
The sealed environment is essential for the orientation of the outer shell. It drives the W-Ni2P nanosheets (the outer layer) to grow vertically relative to the core. This vertical alignment is difficult to achieve in open or ambient pressure systems.
Guaranteeing Uniformity
Uniformity is the hallmark of a successful core-shell catalyst. The constant pressure ensures that the outer nanosheets cover the core evenly. This results in a cohesive structure where the shell protects or enhances the core without blocking access to the internal surface area.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Constraint of the "Sealed" System
The "sealed" nature of the kettle is both its greatest strength and a notable limitation. Once the reaction begins, the environment is closed; you cannot easily adjust temperature or pressure dynamically. This means the initial parameters must be calculated with extreme precision to ensure the "slow release" mechanism functions correctly.
Substrate Dependency
This synthesis method relies heavily on the presence of a physical skeleton, such as nickel foam. The mechanism described is one of supported growth (nucleating along the skeleton). It may not be as effective for synthesizing free-standing core-shell particles that lack a foundational support structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximizing active surface area: Prioritize this method to ensure the inner core develops the high specific surface area required for catalytic efficiency.
- If your primary focus is structural durability and access: Use this approach to guarantee the outer nanosheets grow vertically and uniformly, preventing agglomeration that could block active sites.
By leveraging the constant pressure of the reaction kettle, you transform a chaotic chemical mixture into a disciplined, self-assembling architectural process.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism Feature | Function in Catalyst Synthesis | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed Environment | Maintains constant high temperature and pressure | Ensures uniform growth across all surfaces |
| Kinetic Regulation | Modulates slow release of metal ions | Prevents random precipitation and clumping |
| In-Situ Nucleation | Direct attachment to nickel foam skeletons | Creates stable, anchored 3D architectures |
| Vertical Alignment | Drives nanosheet growth perpendicular to core | Maximizes specific surface area and active sites |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Ready to achieve unmatched uniformity in your 3D core-shell catalysts? KINTEK provides state-of-the-art high-pressure reaction systems designed for the rigorous demands of hydrothermal synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique research needs.
Don't settle for chaotic precipitation—master your kinetic growth today.
Contact Our Technical Experts Now
Visual Guide
References
- Yu Gao, Xiaoteng Liu. In situ growth of three-dimensional walnut-like nanostructures of W-Ni2P@NiFe LDH/NF as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for water decomposition. DOI: 10.1007/s42114-024-01176-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles essential for the synthesis of Ni3In2Se2? | Precision Material Purity
- What is the function of the laboratory furnace? Master Material Transformation with Precision Heating
- What is the role of High-Strength Graphite Molds in Al-Ti-Zr sintering? Mastering Vacuum Hot Pressing Performance
- How does a high-precision heating stage contribute to the drying and crystallization of FAPbBr3 nanosheets?
- What is the technical purpose of double-sealing raw materials in vacuum quartz tubes? Expert Synthesis Guide
- What is the function of a vacuum system in PLD? Ensure High-Density, Pure Electrolyte Thin Films
- What are some specialized applications of quartz tubes? Essential for High-Temperature and High-Purity Processes
- Why are high-temperature ceramic crucibles used for chalcopyrite? Ensure Purity in Ore Thermal Treatment



















