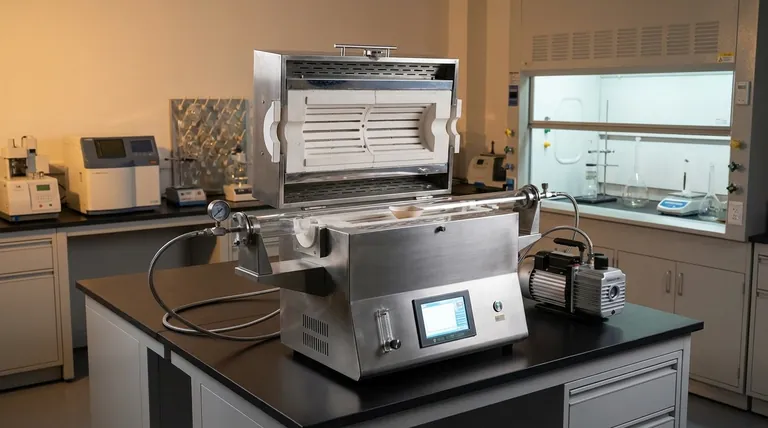
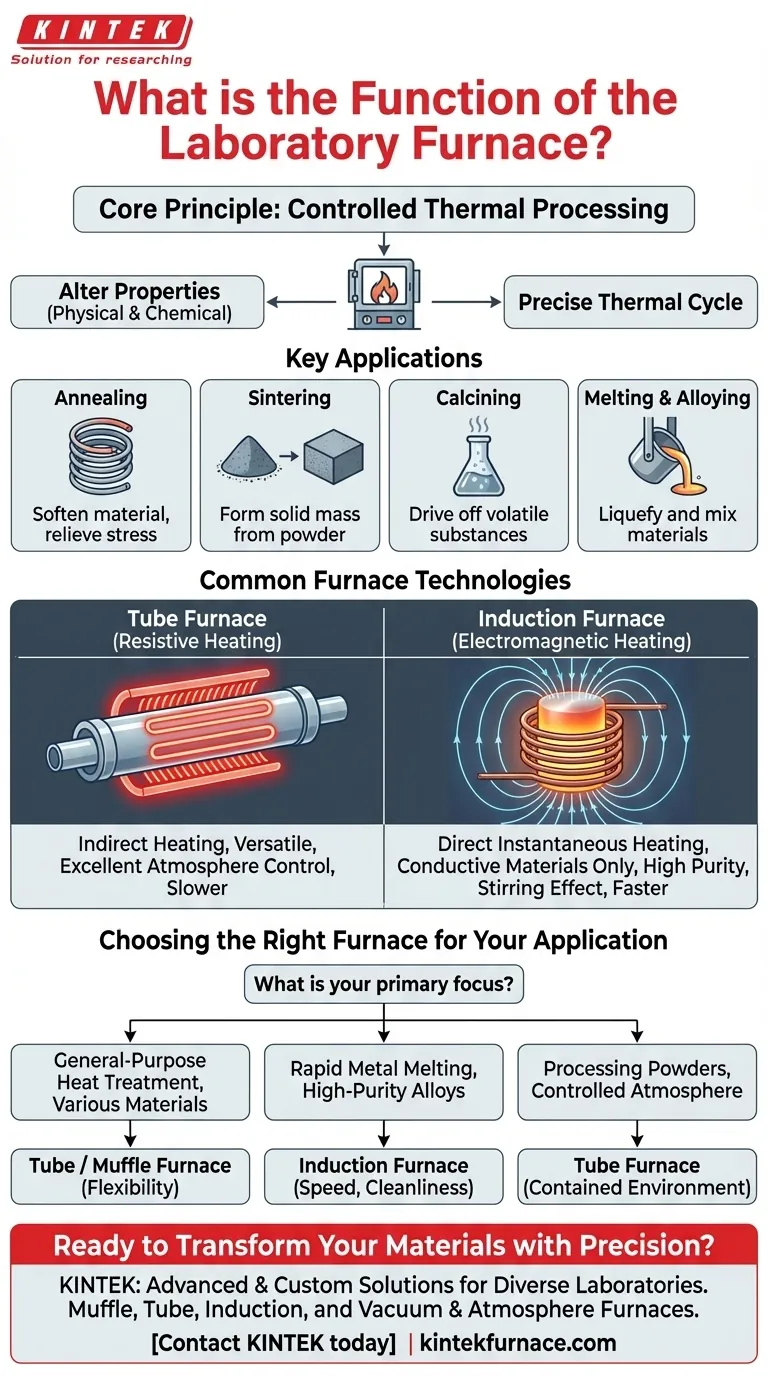
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a device designed for controlled, high-temperature heating. Its primary function is to alter the physical or chemical properties of a material by subjecting it to a precise thermal cycle, with applications including heat treatment, sintering, calcining, annealing, and melting.
The specific function of a laboratory furnace is determined by its underlying technology. Choosing the right furnace is not just about reaching a target temperature; it's about selecting the correct heating method—such as resistive or induction—to achieve the desired outcome for your material.

The Core Principle: Controlled Thermal Processing
A laboratory furnace's purpose goes far beyond simple heating. It is an instrument for precisely manipulating material structure at a microscopic level through the controlled application of thermal energy.
What is Thermal Processing?
Thermal processing uses heat to change a material's properties. This can involve relieving internal stresses, driving chemical reactions, or altering a material's crystalline structure to make it harder, softer, or more durable.
Key Applications Explained
- Annealing: This process involves heating a material and allowing it to cool slowly. The primary function is to soften the material, improve its ductility, and relieve internal stresses that may have built up during manufacturing.
- Sintering: This is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder by applying heat below its melting point. It is fundamental in the manufacturing of ceramics and in powder metallurgy.
- Calcining: This high-temperature process is used to heat materials to drive off volatile substances, such as water or carbon dioxide, or to induce a phase transition. It is common in the production of cement and certain catalysts.
- Melting and Alloying: For metals, a furnace can be used to heat a substance past its melting point. This is essential for casting, purification, and creating alloys by mixing different molten metals into a homogenous solution.
Common Furnace Technologies
The method a furnace uses to generate heat dictates its ideal applications, speed, and capabilities. The two most common designs in a laboratory setting are resistive tube furnaces and induction furnaces.
The Tube Furnace (Resistive Heating)
A tube furnace is a versatile workhorse that operates much like a high-powered conventional oven. Heating elements (resistors) outside a ceramic or quartz tube generate heat, which then radiates inward to heat the sample placed inside the tube.
This design allows for excellent atmosphere control, as the tube can be sealed and filled with inert gases or placed under a vacuum to prevent oxidation or contamination.
The Induction Furnace (Electromagnetic Heating)
An induction furnace uses a completely different principle. High-frequency alternating current is passed through a copper coil, creating a powerful magnetic field.
When a conductive material, such as a metal sample, is placed inside the coil, this magnetic field induces electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the sample itself. The material's own resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat from the inside out.
A unique benefit of this method is that the magnetic field also stirs the molten metal, ensuring a perfectly uniform and homogenous mixture when creating alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these technologies involves clear trade-offs in speed, material compatibility, and application focus.
Heating Method and Speed
A tube furnace relies on indirect heating (radiation and convection), which is slower but provides excellent temperature uniformity for processes like annealing.
An induction furnace provides direct, instantaneous heating only within the sample. It is exceptionally fast but can create steep thermal gradients if not properly controlled.
Material Compatibility
The greatest strength of a tube furnace is its versatility. It can heat any material placed inside it, including metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites.
An induction furnace, by its nature, can only heat electrically conductive materials. It is useless for heating most ceramics or other insulators directly.
Purity and Contamination
Because an induction furnace is contactless—only the magnetic field touches the sample—it is an inherently cleaner process. This makes it ideal for creating high-purity alloys where contamination from heating elements is a concern.
A tube furnace offers very good sample protection by isolating it within the work tube, preventing direct contact with the heating elements and ambient air.
Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on your material and your experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment of various materials: A muffle or tube furnace offers the most flexibility for annealing, sintering, or calcining different material types.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting metals or creating high-purity alloys: An induction furnace provides unmatched speed, cleanliness, and the unique benefit of electromagnetic stirring.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or materials in a controlled atmosphere: A tube furnace is the standard choice, as the sealed tube provides a contained and easily managed environment.
Understanding the mechanism behind the heat is the key to achieving precise and repeatable results in your work.
Summary Table:
| Function | Primary Goal | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften material, relieve stress | Metalworking, glass manufacturing |
| Sintering | Form solid mass from powder | Powder metallurgy, ceramics |
| Calcining | Drive off volatile substances | Cement production, catalyst preparation |
| Melting/Alloying | Liquefy and mix materials | Metal casting, alloy creation |
| Technology | Heating Method | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Furnace | Resistive (indirect) | Versatile heat treatment, controlled atmospheres |
| Induction Furnace | Electromagnetic (direct) | Rapid metal melting, high-purity alloys |
Ready to Transform Your Materials with Precision?
Understanding the function of a laboratory furnace is the first step. The next is selecting the right high-temperature solution for your specific needs.
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced furnace solutions. Whether your work requires the versatile atmosphere control of our Muffle and Tube Furnaces, the rapid, clean melting of our Induction Furnaces, or a custom Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnace tailored to your unique process, we have the expertise and technology to support you.
Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you achieve superior and repeatable results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and let our experts guide you to the ideal laboratory furnace solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















