Beyond simple containers, specialized quartz tubes serve as critical, non-negotiable components in demanding industrial and scientific environments. Their applications range from acting as reaction chambers in high-temperature furnaces and holding silicon wafers during semiconductor fabrication to serving as protective sheaths for sensitive instruments in corrosive atmospheres.
The specialized role of quartz tubes is not accidental. It is a direct result of their unique combination of extreme thermal resistance, high chemical purity, and excellent optical clarity, making them indispensable in processes where nearly any other material would fail.

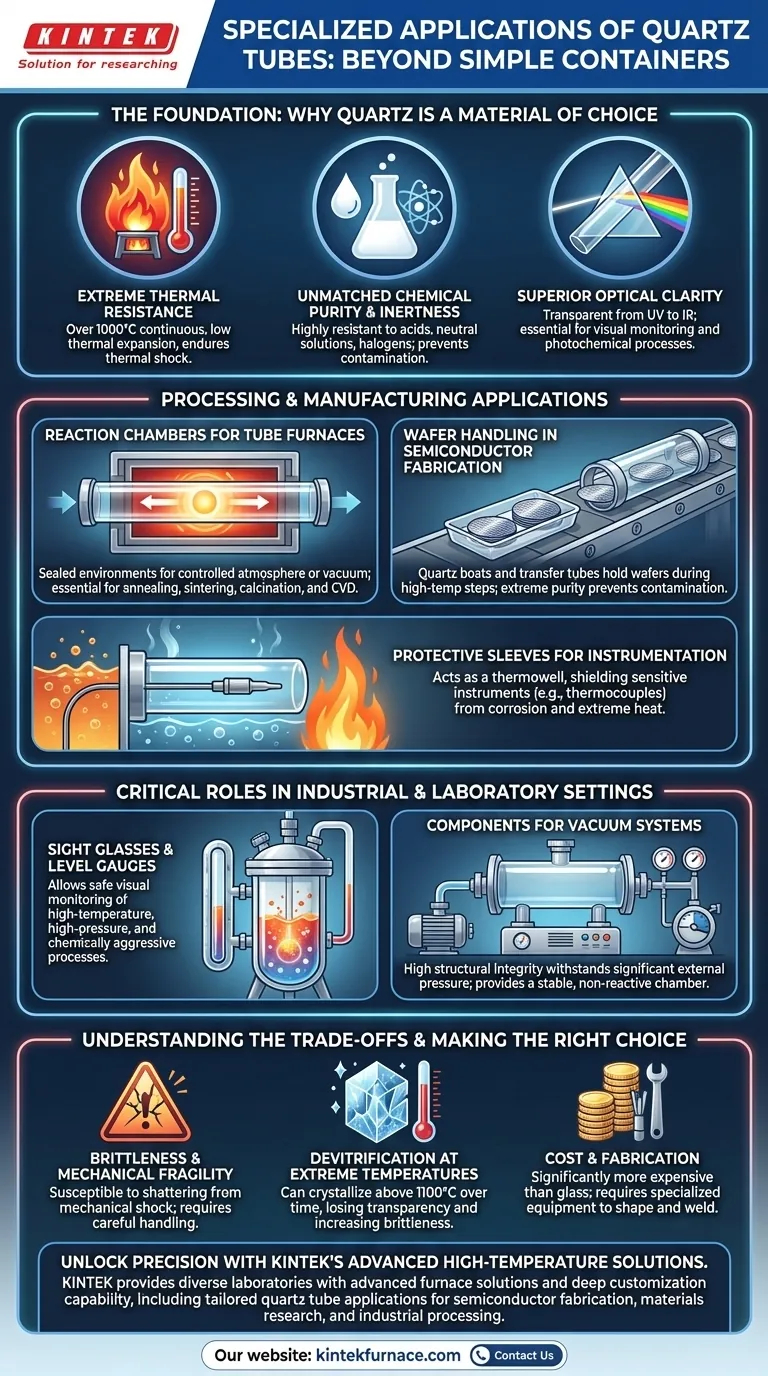
The Foundation: Why Quartz is a Material of Choice
The utility of quartz tubes in specialized roles stems from a few core material properties. Understanding these is key to understanding their applications.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
Quartz can withstand continuous operating temperatures well over 1000°C and has exceptionally low thermal expansion. This allows it to endure rapid temperature changes (thermal shock) that would shatter other materials like standard glass.
Unmatched Chemical Purity and Inertness
Fused quartz is one of the purest materials commercially available. It is highly resistant to acids, neutral solutions, and halogens, ensuring that it does not react with or contaminate the substances it contains, which is critical for semiconductor and pharmaceutical work.
Superior Optical Clarity
Quartz is transparent across a wide spectrum, from ultraviolet (UV) to infrared (IR). This property is essential for applications requiring visual monitoring or for processes that use light to initiate a reaction, such as UV water purification or photochemistry.
Specialized Applications in Processing and Manufacturing
In industrial settings, quartz tubes are not just labware; they are integral parts of the manufacturing process itself.
Reaction Chambers for Tube Furnaces
The most common specialized use is as a reaction chamber in a laboratory or industrial tube furnace. When fitted with flanges, a quartz tube can create a sealed environment for a controlled atmosphere or vacuum.
This setup is essential for processes like annealing, sintering, calcination, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where temperature and atmospheric purity are paramount.
Wafer Handling in Semiconductor Fabrication
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on quartz. Quartz boats (carriers) and transfer tubes are used to hold and move silicon wafers during high-temperature etching and deposition steps.
The material's extreme purity prevents contamination of the delicate silicon wafers, which could otherwise ruin an entire batch of microchips.
Protective Sleeves for Instrumentation
In high-temperature environments, sensitive instruments like thermocouples must be shielded from direct contact with corrosive materials or extreme heat.
A quartz tube acts as a protective thermowell, allowing the sensor to accurately measure temperature without being damaged.
Critical Roles in Industrial and Laboratory Settings
Beyond large-scale manufacturing, quartz tubes serve precise functions where visibility and stability are crucial.
Sight Glasses and Level Gauges
In chemical reactors or high-pressure vessels, a quartz tube can serve as a sight glass. Its ability to withstand high temperatures, pressure, and chemical attack while remaining perfectly clear allows operators to safely monitor processes inside.
Components for Vacuum Systems
Quartz tubes possess high structural integrity, making them suitable for use in vacuum systems. They can withstand the significant external pressure without collapsing, providing a stable and non-reactive chamber for vacuum processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptional, quartz is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these is crucial for proper application.
Brittleness and Mechanical Fragility
Like other ceramics, quartz is brittle. While it can handle immense thermal stress, it is susceptible to shattering from mechanical shock or impact. Careful handling is always required.
Devitrification at Extreme Temperatures
When held at very high temperatures (typically above 1100°C) for extended periods, quartz can begin to devitrify, or crystallize. This process causes it to lose its transparency and become more brittle, limiting its long-term operational ceiling.
Cost and Fabrication
Fused quartz is significantly more expensive than borosilicate glass and requires specialized equipment to shape and weld. This higher cost is a key consideration, reserving its use for applications where its unique properties are a strict requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting quartz should be a deliberate decision based on specific process demands.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., semiconductors): The chemical inertness and high purity of quartz are non-negotiable to prevent sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature observation (e.g., furnace sight glasses): The combination of thermal stability and optical clarity makes quartz one of the few viable choices.
- If your primary focus is controlled atmosphere heat treatment (e.g., annealing): A flanged quartz tube is the standard for creating a sealed, non-reactive environment at high temperatures.
By understanding its unique properties and limitations, you can leverage quartz not just as a material, but as a strategic tool for process integrity and control.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Reaction Chambers in Tube Furnaces | High thermal resistance, chemical inertness for annealing, sintering, CVD |
| Wafer Handling in Semiconductor Fabrication | Extreme purity prevents contamination, essential for microchip production |
| Protective Sleeves for Instruments | Shields thermocouples from corrosion and heat, ensuring accurate measurements |
| Sight Glasses and Level Gauges | Optical clarity and durability for monitoring high-temperature processes |
| Components for Vacuum Systems | Structural integrity for stable, non-reactive vacuum environments |
Unlock Precision with KINTEK's Advanced High-Temperature Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in semiconductor fabrication, materials research, or industrial processing, we deliver tailored quartz tube applications that ensure purity, durability, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your processes and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















