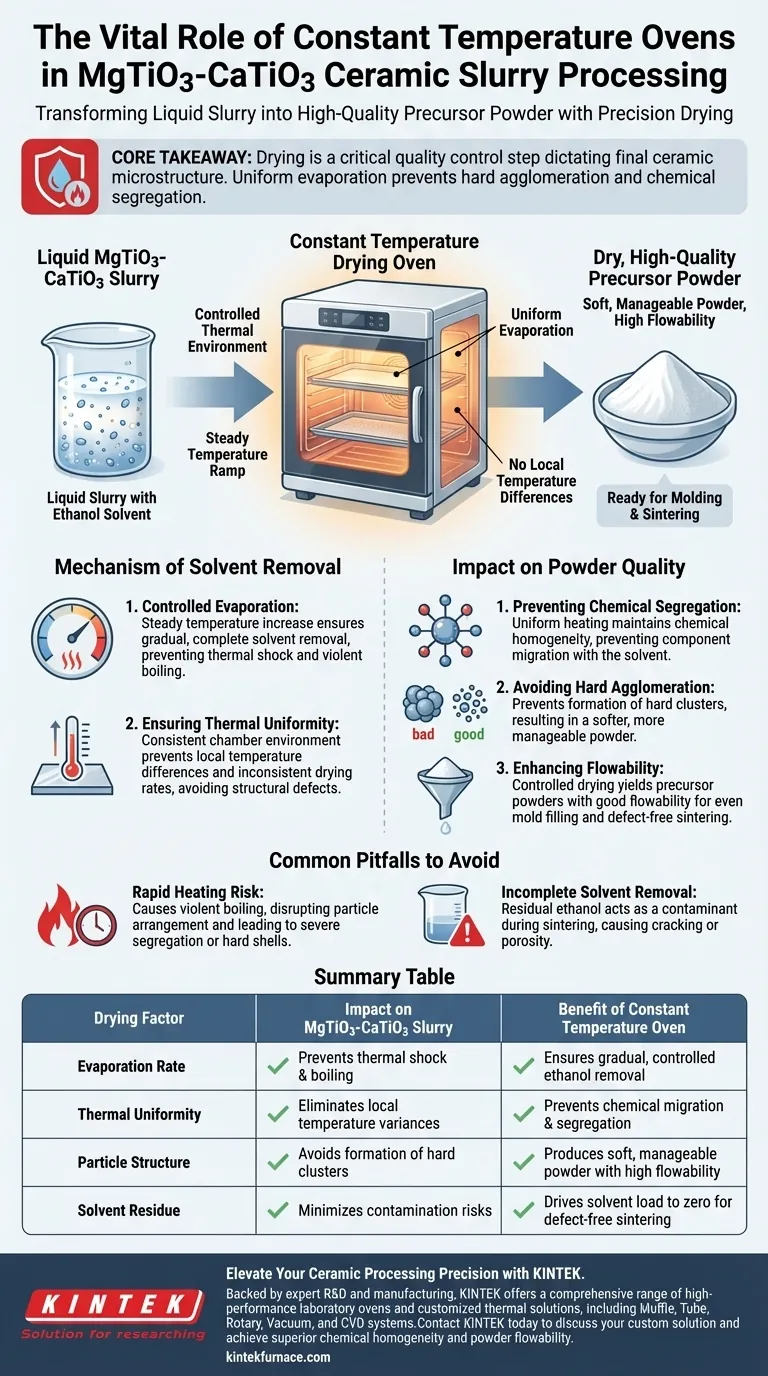
The contribution of a constant temperature drying oven to processing MgTiO3-CaTiO3 ceramic slurry is the precise removal of the ethanol solvent without degrading the material's structure. By providing a uniform thermal environment and steadily increasing the temperature, the oven transforms the liquid slurry into a dry, high-quality precursor powder suitable for subsequent manufacturing steps.
Core Takeaway The drying phase is not merely about removing liquid; it is a critical quality control step that dictates the final ceramic's microstructure. A constant temperature oven ensures uniform evaporation to prevent hard agglomeration and chemical segregation, ensuring the powder flows correctly during molding and sintering.

The Mechanism of Solvent Removal
Controlled Evaporation of Ethanol
The primary function of the oven in this specific process is the removal of the ethanol solvent used during ball milling.
Rather than subjecting the slurry to thermal shock, the oven is programmed to steadily increase the temperature. This controlled ramp ensures that the solvent evaporates completely but gradually.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
The "constant temperature" aspect refers to the oven's ability to maintain a consistent environment throughout the chamber.
This prevents local temperature differences within the slurry batch. If one area heats faster than another, it can lead to inconsistent drying rates, which often results in structural defects in the final powder.
Impact on Powder Quality
Preventing Chemical Segregation
Uniform heating is essential for maintaining the chemical homogeneity of the MgTiO3-CaTiO3 mixture.
When drying is uneven, chemical components can migrate with the solvent, leading to uneven chemical distribution. The constant temperature oven locks the chemical distribution in place by ensuring the solvent leaves the matrix uniformly.
Avoiding Hard Agglomeration
One of the most significant risks in drying ceramic slurries is the formation of "hard agglomerates"—clusters of particles that fuse together and are difficult to break down later.
By avoiding rapid, uncontrolled boiling, the oven prevents these hard clusters from forming. This results in a softer, more manageable powder.
Enhancing Flowability
The ultimate goal of the drying process is to prepare the powder for molding and sintering.
The controlled drying process yields precursor powders with good flowability. This characteristic is vital for ensuring the powder fills molds evenly and sinters into a dense, defect-free ceramic component.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Rapid Heating
While it may be tempting to increase temperatures quickly to save time, this approach is detrimental to MgTiO3-CaTiO3 slurries.
Rapid heating can cause the solvent to boil violently. This disrupts the particle arrangement and can lead to severe segregation or the formation of hard shells on the particles, compromising the final ceramic properties.
Incomplete Solvent Removal
Failure to achieve complete evaporation results in residual ethanol within the powder.
Residual solvents can act as contaminants during the sintering phase, potentially causing cracking or porosity in the final ceramic part. The oven's steady thermal profile is designed specifically to drive the solvent load down to zero.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your MgTiO3-CaTiO3 ceramics, you must prioritize process control over processing speed during the drying stage.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Homogeneity: Ensure the oven is calibrated to eliminate cold spots, preventing component migration due to local temperature variances.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency (Molding): Prioritize a steady temperature ramp to prevent hard agglomeration, ensuring the resulting powder flows smoothly into your molds.
Success in ceramic processing depends not just on the materials you mix, but on the precision with which you remove the solvents that helped mix them.
Summary Table:
| Drying Factor | Impact on MgTiO3-CaTiO3 Slurry | Benefit of Constant Temperature Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporation Rate | Prevents thermal shock and boiling | Ensures gradual, controlled ethanol removal |
| Thermal Uniformity | Eliminates local temperature variances | Prevents chemical migration and segregation |
| Particle Structure | Avoids formation of hard clusters | Produces soft, manageable powder with high flowability |
| Solvent Residue | Minimizes contamination risks | Drives solvent load to zero for defect-free sintering |
Elevate Your Ceramic Processing Precision with KINTEK
Don't let inconsistent drying compromise your material integrity. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory ovens and constant temperature drying systems designed to deliver the thermal uniformity required for advanced ceramics like MgTiO3-CaTiO3.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all customizable to meet your unique research or production needs.
Ready to achieve superior chemical homogeneity and powder flowability? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Wega Trisunaryanti, Satriyo Dibyo Sumbogo. Characteristic and Performance of Ni, Pt, and Pd Monometal and Ni-Pd Bimetal onto KOH Activated Carbon for Hydrotreatment of Castor Oil. DOI: 10.22146/ijc.84640
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature annealing furnace play in the preparation of AAO substrates? Enhance Pore Regularity
- What inert gas is commonly used in gloveboxes and Schlenk lines, and why is it preferred over nitrogen in some cases? Discover Argon's Superior Inertness for Sensitive Experiments
- How does a glove box provide environmental control for Mn2AlB2 precursors? Protect Material Purity & Reaction Accuracy
- Why is an environmental laboratory chamber equipped with an optical window required for synthesizing Hafnium Carbide?
- What is the operational mechanism of a smelting reduction furnace (SRF)? Optimize Your HAlMan Metallurgy Process
- What role does a laboratory blast drying oven play in metal powder preparation? Ensure Purity & Prevent Oxidation
- What is the significance of using a high-precision gas mass flow controller for hydrogen flow? | Master Uniform Thermal Reduction
- How do elliptical mirrors function to create a horizontal temperature field in an optical Floating-Zone furnace?



















