Argon is the inert gas most commonly used in gloveboxes and Schlenk lines for highly sensitive experiments. While nitrogen is a less expensive and frequent alternative, argon is strictly preferred when there is any risk of the "inert" gas reacting with the experimental materials, which can occur with certain metals or at high temperatures.
The choice between argon and nitrogen is a critical decision in air-sensitive chemistry, balancing cost against chemical purity. While nitrogen is a cost-effective workhorse, argon provides a superior level of inertness, acting as essential insurance for highly reactive or high-temperature experiments.

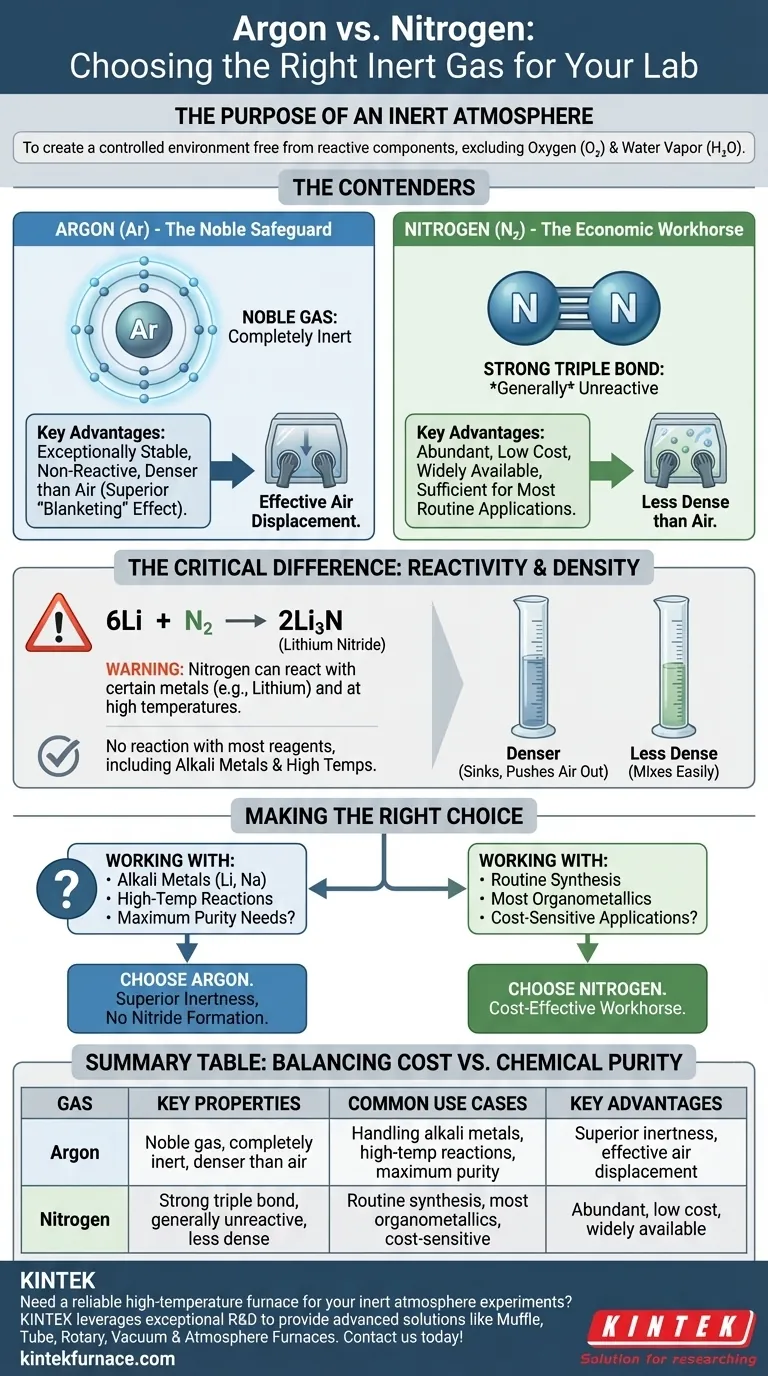
The Purpose of an Inert Atmosphere
The primary function of a glovebox or Schlenk line is to create a controlled environment free from reactive atmospheric components. The main culprits you are trying to exclude are oxygen (O₂) and water vapor (H₂O), which can readily decompose sensitive reagents and catalysts.
An inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen, is used to displace the air and maintain a positive pressure, preventing any atmospheric leaks into the system.
Comparing the Contenders: Argon vs. Nitrogen
While both are used to create an inert atmosphere, their chemical and physical properties dictate when one is a better choice than the other.
Nitrogen: The Economic Workhorse
Nitrogen (N₂) makes up about 78% of the air we breathe and is therefore abundant and inexpensive.
The N₂ molecule is characterized by a very strong triple bond between its two nitrogen atoms. This bond requires a significant amount of energy to break, which is why nitrogen is generally unreactive and suitable for a wide range of chemical applications.
Argon: The Noble Safeguard
Argon (Ar) is a noble gas. This means its atoms have a completely filled outer electron shell, making it exceptionally stable and non-reactive.
Under virtually all laboratory conditions, argon will not form chemical bonds or react with your reagents. This fundamental chemical inertness is its greatest strength.
The Critical Difference: Reactivity
The term "inert" is relative. While nitrogen is mostly unreactive, it is not completely inert.
Under specific conditions, nitrogen can react with certain metals to form metal nitrides. The most common example in synthetic chemistry involves lithium metal, which readily reacts with N₂ gas even at room temperature to form lithium nitride (Li₃N).
6Li + N₂ → 2Li₃N
This unwanted side reaction can consume your reagent and introduce impurities. Similar reactions can occur with other alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, or during syntheses conducted at high temperatures. Argon, as a noble gas, does not have this liability.
A Practical Consideration: Gas Density
A key physical difference is density. Argon is about 40% denser than air, while nitrogen is slightly less dense than air.
This means argon is more effective at displacing air from a container, as it will "sink" and push the lighter air up and out. This "blanketing" effect makes it superior for purging glassware on a Schlenk line and maintaining a stable atmosphere inside a glovebox, as it settles at the bottom rather than mixing easily.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gas requires balancing absolute safety with practical constraints.
Cost: The Primary Driver
The most significant advantage of nitrogen is its low cost. Argon is substantially more expensive than nitrogen.
For laboratories running many gloveboxes or performing large-scale synthesis, this cost difference can be a major factor. For this reason, nitrogen is often the default choice for any work where its potential reactivity is not a concern.
Purity and Supply
Both gases are commercially available in very high purity grades (e.g., 99.999%). The key difference often lies in the supply method.
Large-scale nitrogen users may have on-site generators or large liquid nitrogen dewars that provide a continuous supply of gas from boil-off, further reducing its operational cost. Argon is almost always supplied in high-pressure gas cylinders, which require regular replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Your decision should be based on the specific chemistry you are performing.
- If your primary focus is routine synthesis, purification, or handling most organometallics: Use nitrogen. It is sufficiently inert for the vast majority of applications and offers significant cost savings.
- If your primary focus is working with lithium, other alkali metals, or performing high-temperature reactions: Use argon. Its superior inertness is non-negotiable and protects your experiment from the formation of unwanted metal nitrides.
- If your primary focus is maximum certainty and eliminating all variables: Use argon. The higher cost is a small price to pay for the insurance that your inert gas is truly inert.
Ultimately, understanding the subtle reactivity of nitrogen is what separates routine practice from precise and deliberate experimental design.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Key Properties | Common Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon | Noble gas, completely inert, denser than air | Handling alkali metals, high-temperature reactions, maximum purity needs | Superior inertness, effective air displacement, no nitride formation |
| Nitrogen | Strong triple bond, generally unreactive, less dense than air | Routine synthesis, most organometallics, cost-sensitive applications | Abundant, low cost, widely available |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace for your inert atmosphere experiments? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















