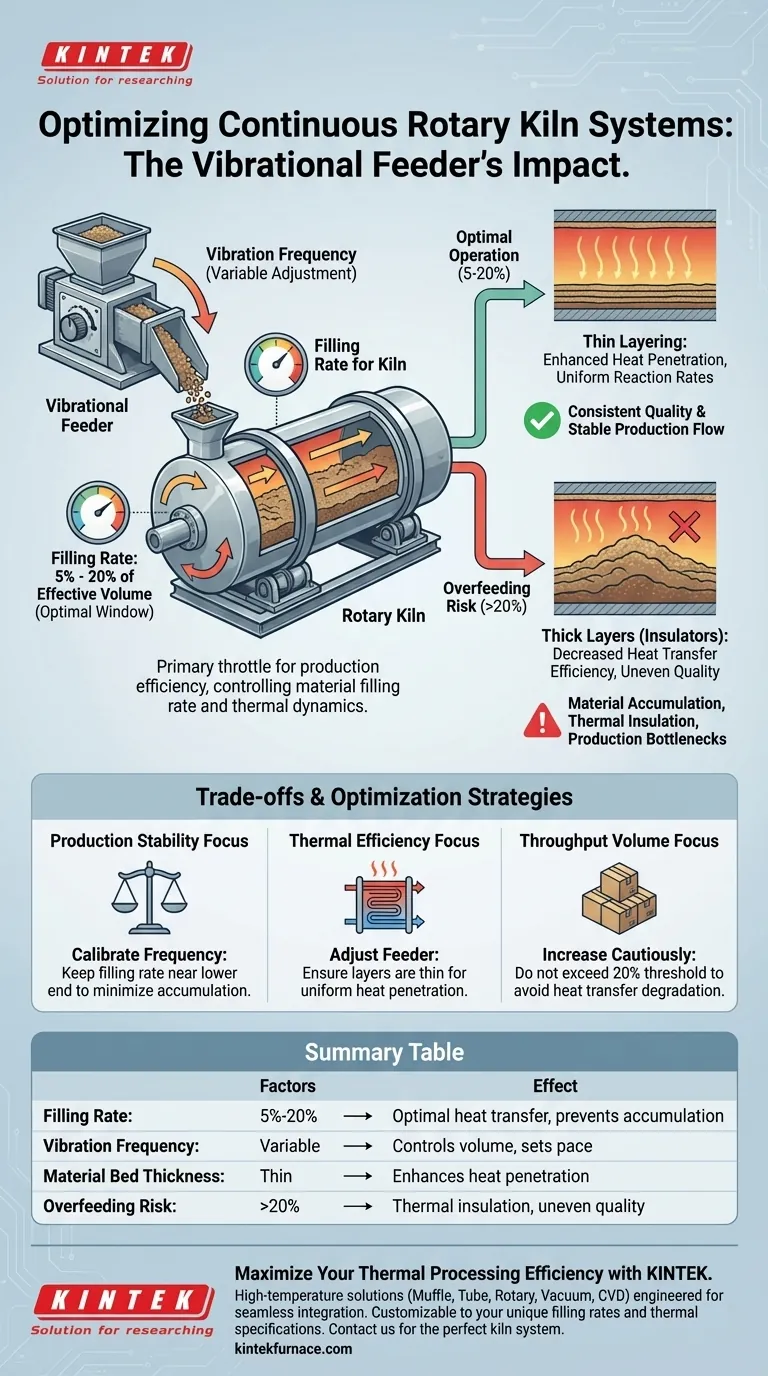
The specifications of a vibrational feeder serve as the primary throttle for production efficiency, directly dictating the material filling rate and thermal dynamics within a continuous rotary kiln system. By precisely adjusting the vibration frequency, the feeder controls the volume of raw material entering the kiln, which is the deciding factor in maintaining a stable, continuous production line.
A vibrational feeder determines the kiln’s filling rate, which must typically be maintained between 5% and 20% of the effective volume to ensure efficiency. Operating within this range prevents material accumulation and ensures optimal heat transfer, directly influencing the consistency and quality of the final product.

Regulating Material Flow and Filling Rates
The Role of Vibration Frequency
The vibrational feeder does not simply move material; it sets the pace of the entire system.
By adjusting the vibration frequency, operators control the precise rate at which raw materials are introduced to the kiln. This frequency is the variable that determines the volume of material present in the kiln at any given moment.
Defining the Optimal Filling Window
Efficiency relies on maintaining a specific filling rate, defined as the percentage of the kiln's effective volume occupied by material.
In specific applications, such as the preparation of bio-calcium oxide, this rate should fall between 5% and 20%. Keeping the volume within these specific bounds is essential for maintaining a continuous, stable production flow.
The Thermal Implications of Feed Rate
Controlling Layer Thickness
The rate at which the feeder supplies material directly impacts the thickness of the material bed inside the kiln.
If the feeder specifications allow for excessive input, the material layers become too thick. Thick layers act as insulators, preventing heat from penetrating evenly through the raw material.
Impact on Heat Transfer Efficiency
The efficiency of a rotary kiln is defined by how well it transfers heat to the material.
Proper control of the feeder prevents the decrease in heat transfer efficiency associated with overly thick material layers. By limiting the layer depth, the feeder ensures that thermal energy is utilized effectively, resulting in consistent reaction rates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Material Accumulation
Pushing the vibrational feeder beyond the optimal frequency to increase throughput creates immediate mechanical risks.
Overfeeding leads to material accumulation, where raw input builds up faster than it can be processed. This disrupts the continuous flow and can cause significant bottlenecks in the production line.
Balancing Volume vs. Quality
There is a direct tension between feed volume and product consistency.
While a higher feed rate increases theoretical output, it compromises product quality by creating thermal inconsistencies. Stability in the production line is prioritized over maximum volume to ensure the final output meets quality standards.
Optimizing Your Feeder Strategy
If your primary focus is Production Stability:
- Calibrate the vibrational frequency to keep the filling rate near the lower end of the 5-20% range to minimize accumulation risks.
If your primary focus is Thermal Efficiency:
- Adjust the feeder to ensure material layers remain thin enough to allow uniform heat penetration, preventing energy waste.
If your primary focus is Throughput Volume:
- Increase the vibration frequency cautiously, ensuring you do not exceed the 20% effective volume threshold where heat transfer degrades.
Precise control of the vibrational feeder is not just about moving material; it is about stabilizing the thermal environment to guarantee a high-quality product.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Recommended Range/Impact | Effect on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Rate | 5% - 20% of Effective Volume | Ensures optimal heat transfer and prevents material accumulation. |
| Vibration Frequency | Variable Adjustment | Directly controls material volume and sets the production pace. |
| Material Bed Thickness | Thin Layering | Enhances heat penetration and ensures uniform reaction rates. |
| Overfeeding Risk | >20% Filling Rate | Leads to thermal insulation, uneven quality, and production bottlenecks. |
Maximize Your Thermal Processing Efficiency with KINTEK
Precise material handling is the foundation of high-performance lab operations. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all engineered to integrate seamlessly with your production requirements.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our furnaces are fully customizable to your unique filling rates and thermal specifications. Whether you are optimizing bio-calcium oxide production or advanced material synthesis, KINTEK ensures your lab achieves superior stability and quality.
Ready to elevate your production standards? Contact our technical experts today to discover the perfect kiln system for your needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Suwanan Chuakham, Apipong Putkham. Scalable production of bio-calcium oxide via thermal decomposition of solid - hatchery waste in a laboratory-scale rotary kiln. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84889-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is maintenance more complex for rotary furnaces? Key Challenges and Solutions
- What environmental applications utilize rotary kilns? Transform Waste into Value with Precision
- How do mixing technologies improve rotary furnace performance? Boost Efficiency & Cut Costs
- What are the primary industries that utilize rotary kilns? Key Applications in Cement, Metallurgy & More
- What types of small parts are commonly processed in rotary retort furnaces? Ideal for Fasteners and Powders
- How do rotary furnaces improve gas diffusion? Achieve Uniform Gas-Solid Reactions for Your Lab
- What specifications can be adjusted in custom rotary tube furnace designs? Tailor for Precision and Efficiency
- What are the advantages of using a rotary reactor for carbonization? Achieve Superior Biochar Quality



















