In short, rotary kilns are used in a wide range of environmental applications, most notably for the thermal destruction of hazardous waste, remediation of contaminated soil, recovery of valuable materials from waste streams, and the creation of products used for purification, such as activated carbon.
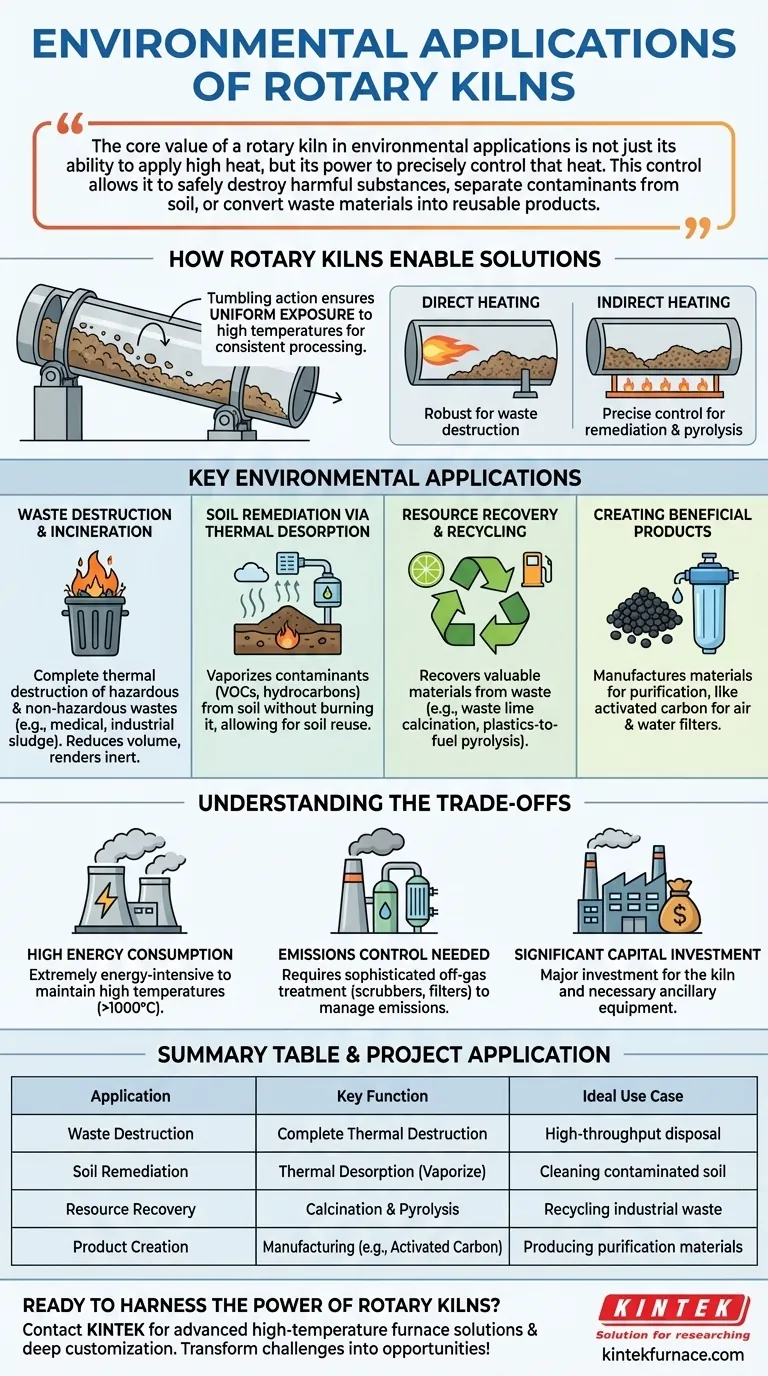
The core value of a rotary kiln in environmental applications is not just its ability to apply high heat, but its power to precisely control that heat. This control allows it to safely destroy harmful substances, separate contaminants from soil, or convert waste materials into reusable products.

How Rotary Kilns Enable Environmental Solutions
A rotary kiln is essentially a large, rotating, slightly inclined cylinder. Material is fed into the higher end, and as the kiln turns, the material tumbles and mixes, slowly moving toward the lower end.
This tumbling action is the key. It ensures every particle of the material is uniformly exposed to the high temperatures inside, guaranteeing a consistent and complete thermal process.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Kilns can be heated directly, where a flame is in contact with the material, or indirectly, where the cylinder is heated from the outside.
Indirect heating is often preferred for environmental tasks like soil remediation or waste pyrolysis. It prevents the creation of unwanted combustion byproducts and offers finer control over the material's chemical transformation.
Key Environmental Applications in Detail
The versatility of the rotary kiln's thermal processing capabilities makes it suitable for several distinct environmental objectives.
Waste Destruction & Incineration
Rotary kilns are a workhorse for incinerating both hazardous and non-hazardous wastes. This includes materials like contaminated industrial byproducts, medical waste, and municipal sewage sludge.
The high temperatures and long residence times ensure the complete destruction of organic compounds, reducing waste volume and rendering it inert and safe for disposal.
Soil Remediation via Thermal Desorption
For soils contaminated with hydrocarbons, pesticides, or other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), rotary kilns are used for a process called thermal desorption.
The kiln heats the soil just enough to vaporize the contaminants without burning the soil itself. The contaminated vapor is then captured and treated separately, leaving behind clean, reusable soil.
Resource Recovery and Recycling
Many "waste" streams contain valuable materials that can be recovered.
A prime example is waste lime recovery in paper mills or sugar processing plants. The kiln reheats the lime sludge (calcium carbonate) to convert it back into quicklime (calcium oxide), a process called calcination, allowing it to be reused. Similarly, processes like pyrolysis can convert waste plastics or wood into fuel or chemical feedstocks.
Creating Environmentally Beneficial Products
Rotary kilns are also used to manufacture materials that solve other environmental problems.
This includes producing or reactivating activated carbon, a highly porous material used extensively in air and water purification filters. The kiln's controlled atmosphere is essential for creating the carbon's specific porous structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary kilns are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is critical for proper application.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining temperatures often exceeding 1000°C is extremely energy-intensive. This represents a significant operational cost and has its own environmental footprint that must be managed.
The Need for Emissions Control
Heating and incinerating waste materials inevitably produces off-gases that must be treated before being released into the atmosphere. A complete kiln system requires sophisticated scrubbers, filters, and afterburners to manage air emissions, adding to its complexity and cost.
Significant Capital Investment
Rotary kilns are large, heavy-duty pieces of industrial machinery. The initial capital cost for the kiln and its necessary ancillary equipment is substantial, making it a major investment decision.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice depends entirely on the material you are processing and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is waste destruction: A direct-fired rotary kiln provides a robust, high-throughput solution for the complete thermal destruction of a wide range of organic wastes.
- If your primary focus is soil remediation: An indirect-fired kiln is ideal for thermal desorption, as it allows you to precisely remove contaminants without damaging the soil matrix.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery: The kiln's ability to perform specific chemical transformations like calcination makes it perfect for converting industrial sludges or other waste streams into valuable, reusable products.
Ultimately, mastering these applications comes from seeing the rotary kiln as a versatile thermal reactor, capable of transforming a problem material into a stable or valuable solution.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Destruction & Incineration | Complete thermal destruction of hazardous and non-hazardous wastes | High-throughput disposal of medical or industrial waste |
| Soil Remediation | Thermal desorption to vaporize contaminants from soil | Cleaning soil polluted with hydrocarbons or VOCs |
| Resource Recovery | Calcination and pyrolysis to recover materials like lime or fuels | Recycling waste from paper mills or plastics |
| Product Creation | Manufacturing activated carbon for purification | Producing materials for air and water filters |
Ready to harness the power of rotary kilns for your environmental projects? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on waste destruction, soil remediation, or resource recovery, we can help you achieve efficient and sustainable outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can transform your challenges into opportunities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















