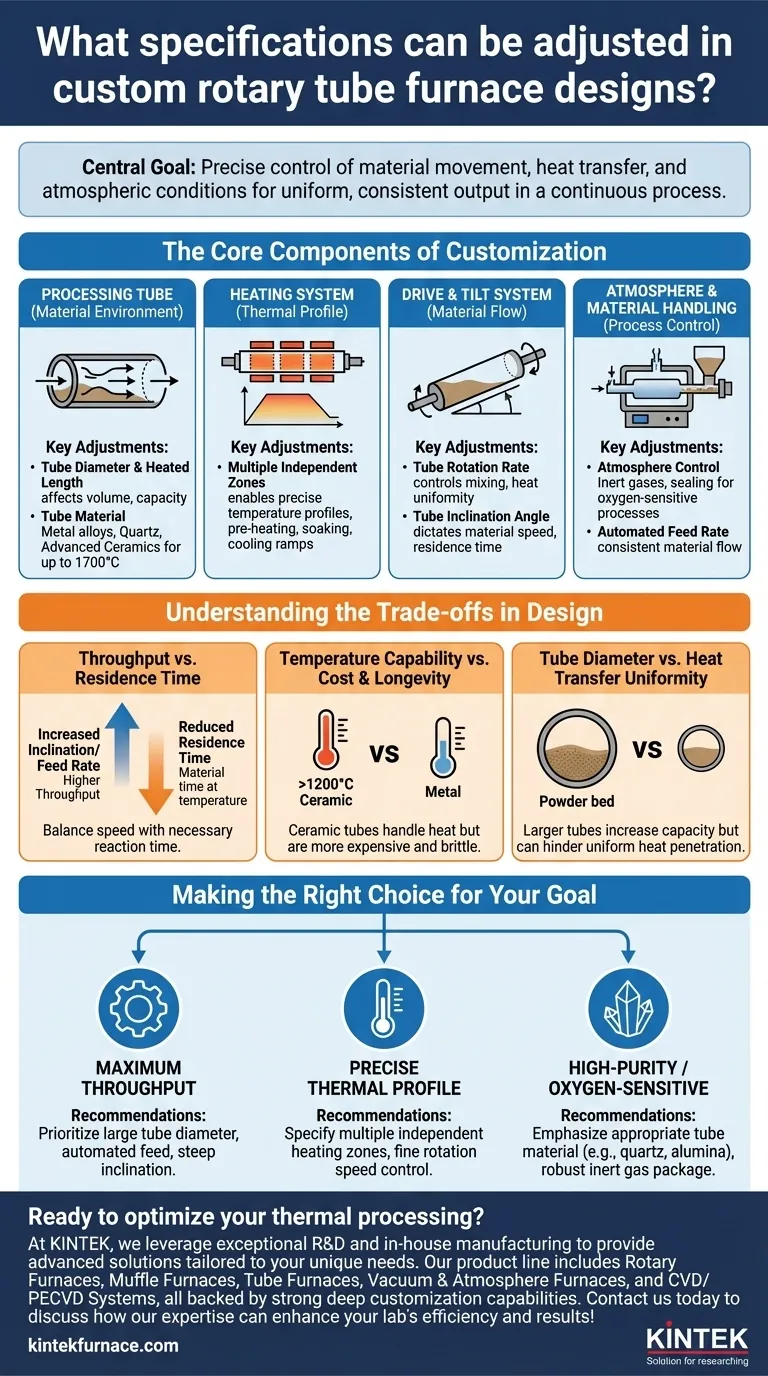
Nearly every critical parameter of a rotary tube furnace can be customized to match a specific thermal processing application. The core specifications you can adjust include the maximum operating temperature, the physical dimensions of the tube (diameter and length), the tube's rotation speed and inclination angle, the number of heating zones, and the system for controlling the internal atmosphere and material feed rate.
Customizing a rotary furnace is not about selecting individual features, but about designing a dynamic system. The central goal is to precisely control the relationship between material movement, heat transfer, and atmospheric conditions to produce a highly uniform and consistent output in a continuous process.
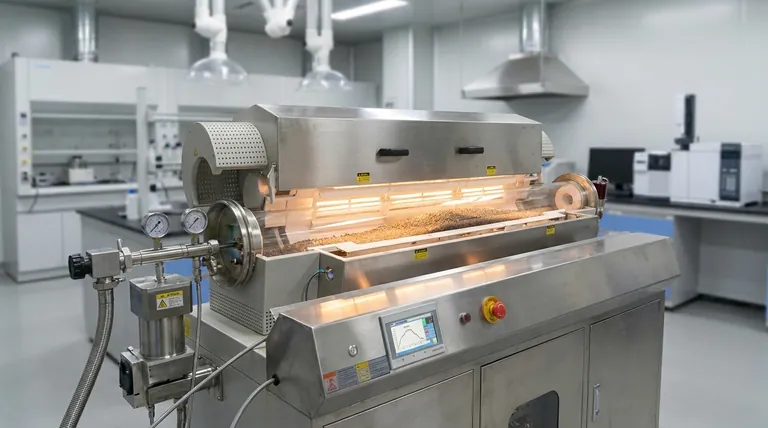

The Core Components of Customization
A rotary tube furnace is an integrated system. Understanding how its main components can be tailored is the key to designing an effective process.
The Processing Tube: Your Material's Environment
The tube itself is the heart of the furnace. Its specifications directly impact throughput, material compatibility, and process integrity. Key adjustments include tube diameter and heated length, which together define the furnace's volume and capacity.
The tube material is also a critical choice. Options range from metal alloys for lower-temperature applications to quartz or advanced ceramics (like alumina) for high-temperature or high-purity processes up to 1700°C.
The Heating System: Defining the Thermal Profile
Modern rotary furnaces are not limited to a single temperature. They can be designed with multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube.
This allows you to create a precise temperature profile, enabling complex processes that may require a pre-heating stage, a specific soaking time at a peak temperature, and a controlled cooling ramp, all within a single continuous operation.
The Drive & Tilt System: Controlling Material Flow
The furnace's ability to mix and transport material is governed by two mechanical adjustments.
The tube rotation rate controls the tumbling and mixing of the powder or granules. A faster speed ensures greater uniformity and heat exposure for each particle.
The tube inclination angle dictates the speed at which material travels from the inlet to the outlet. A steeper angle increases throughput but reduces the residence time—the total time the material spends inside the heated zone.
Atmosphere & Material Handling
For processes sensitive to oxygen, furnaces can be equipped with comprehensive atmosphere control packages. This includes sealed inlets and outlets and precision gas flow systems for blanketing the material with inert gases like nitrogen or argon.
Furthermore, feed rate can be automated with integrated hoppers and feeders, ensuring a consistent flow of material into the furnace, which is essential for stable, continuous operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Design
Every design choice involves a trade-off. Objectively balancing these factors is crucial for developing a successful and cost-effective process.
Throughput vs. Residence Time
Increasing the tube's inclination angle or feed rate will boost your throughput. However, this directly reduces the residence time. You must ensure the material still has enough time at temperature to undergo the desired chemical reaction or physical change.
Temperature Capability vs. Cost & Longevity
Achieving temperatures above 1100-1200°C typically requires a shift from metal alloy tubes to more expensive ceramic tubes. While these materials can handle extreme heat, they can be more brittle and may have a shorter operational lifespan depending on the thermal cycling.
Tube Diameter vs. Heat Transfer Uniformity
A larger tube diameter significantly increases the volume and potential throughput of the furnace. However, it can also create a thicker powder bed depth, making it harder for heat to penetrate uniformly to the center of the material load, even with rotation. This may require slower processing to ensure complete treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal specifications are entirely dependent on your primary processing objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: Prioritize a large tube diameter, an automated feed system, and a design that allows for a steep, adjustable inclination angle.
- If your primary focus is achieving a precise thermal profile: Specify a furnace with multiple independent heating zones and fine control over the tube rotation speed to manage residence time.
- If your primary focus is processing high-purity or oxygen-sensitive materials: Emphasize the selection of an appropriate tube material (e.g., quartz or alumina) and a robust inert gas package with superior sealing.
Ultimately, a well-specified custom rotary furnace transforms a complex thermal process into a reliable and repeatable operation.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Key Adjustments | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 1700°C with material choices | Defines heat tolerance and reaction capabilities |
| Tube Dimensions (Diameter, Length) | Custom sizes for volume and capacity | Affects throughput and powder bed depth |
| Rotation Speed and Inclination Angle | Adjustable rates and angles | Controls material mixing, residence time, and flow |
| Number of Heating Zones | Multiple independent zones | Enables precise temperature profiles for complex processes |
| Atmosphere Control | Inert gas systems and sealing | Ensures purity and prevents oxidation in sensitive materials |
| Material Feed Rate | Automated hoppers and feeders | Maintains consistent input for stable continuous operation |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing with a custom rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on maximizing throughput, achieving precise thermal profiles, or handling high-purity materials, we can design a furnace that precisely meets your experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















