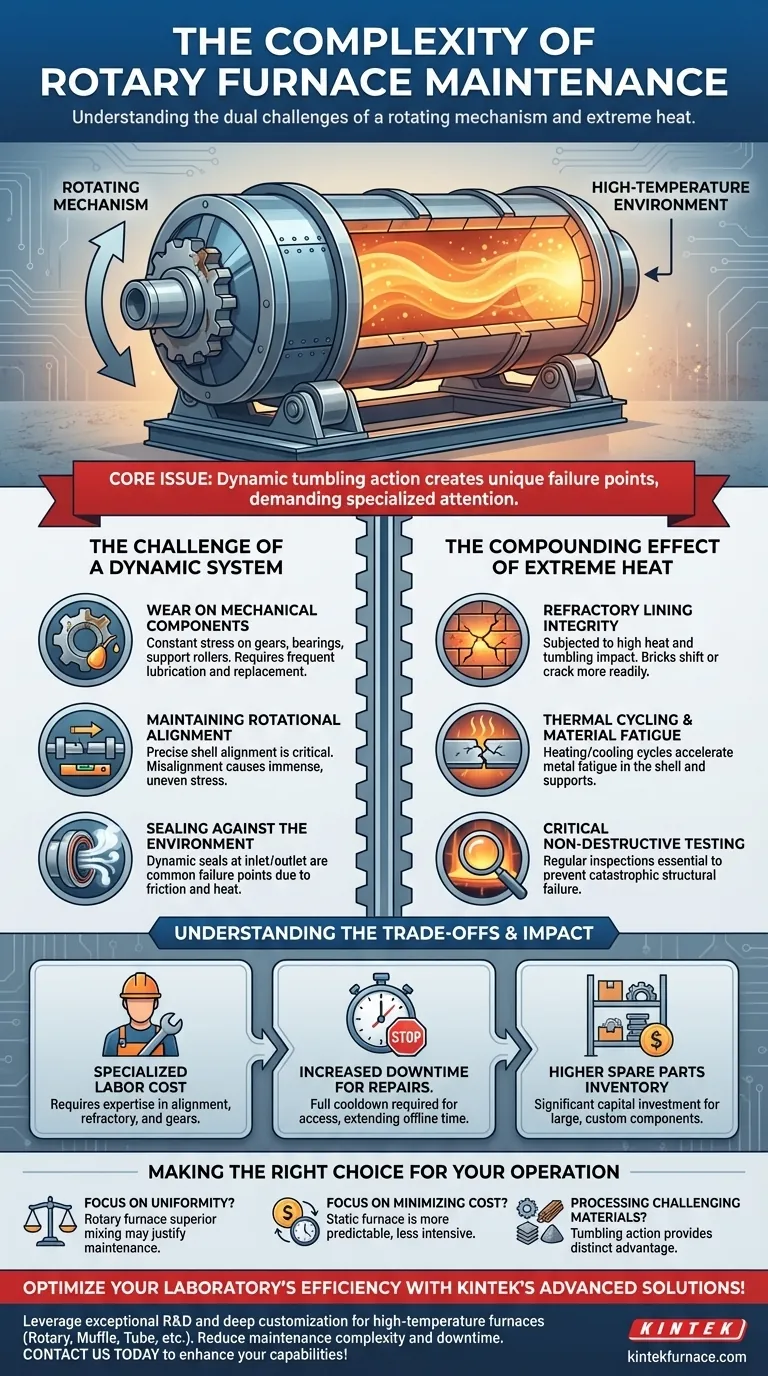
In short, rotary furnace maintenance is more complex due to two fundamental factors: its rotating mechanism and the relentless high-temperature environment it operates in. Unlike static furnaces, the combination of constant motion and extreme heat creates unique failure points that demand more frequent attention and specialized technical skills to address.
The core issue is that the very design feature providing a rotary furnace's advantage—its dynamic, tumbling action—is also the primary source of its increased maintenance complexity and cost.
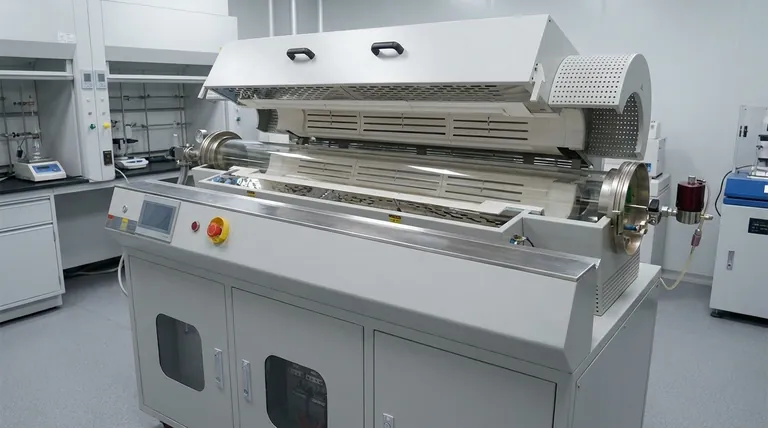

The Challenge of a Dynamic System
The primary distinction of a rotary furnace is its movement. This mechanical action, while essential for uniform material processing, introduces several points of potential failure not present in static systems.
Wear on Mechanical Components
A rotary furnace relies on a complex system of gears, bearings, support rollers, and a drive motor to function. These components are under constant mechanical stress.
This continuous movement inevitably leads to wear and tear, requiring regular lubrication, monitoring, and eventual replacement. A failure in the drive system or a seized bearing can bring the entire operation to a halt.
Maintaining Rotational Alignment
The entire furnace shell, which can be massive, must rotate perfectly on its axis. Even minor misalignment can cause immense, uneven stress on the support structures, the shell itself, and the drive train.
Re-establishing and maintaining this alignment is a precision task that requires specialized tools and expertise, far beyond the scope of general maintenance.
Sealing Against the Environment
Crucially, the furnace must be sealed at both the inlet and outlet ends to maintain its internal atmosphere and prevent heat loss. These seals must function perfectly while one part (the furnace shell) is rotating and the other (the feed and discharge chutes) is stationary.
These dynamic seals are common failure points, subject to wear from both friction and high temperatures. A compromised seal can lead to reduced efficiency, process contamination, and safety hazards.
The Compounding Effect of Extreme Heat
The high-temperature environment inside the furnace exacerbates the mechanical challenges and introduces its own set of problems, particularly concerning material integrity.
Refractory Lining Integrity
The internal refractory lining that protects the steel shell is subjected not only to high heat but also to the constant tumbling and impact of the material being processed.
This mechanical stress from rotation can cause bricks to shift or crack far more readily than in a static furnace. Repairing this lining is a time-consuming process that requires a full cooldown and specialized masonry skills.
Thermal Cycling and Material Fatigue
The combination of heat, mechanical load, and rotation accelerates metal fatigue in the furnace's steel shell and support components.
Cooling and heating cycles, which cause materials to expand and contract, add another layer of stress. This makes regular, non-destructive testing and inspection critical to prevent catastrophic structural failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use a rotary furnace comes with a clear understanding that its superior processing capabilities are balanced by a higher operational cost and maintenance burden.
The Cost of Specialized Labor
Maintaining a rotary furnace is not a job for a general mechanic. It requires specialized expertise in areas like large-scale mechanical alignment, high-temperature refractory work, and industrial gear systems. This expertise is both more expensive and harder to find.
Increased Downtime for Repairs
Even minor inspections or repairs can lead to significant downtime. The furnace must be completely cooled before personnel can safely access internal components, a process that can take days for large units. The complexity of the repairs themselves also extends the time the asset is offline.
Higher Inventory of Spare Parts
The unique mechanical components mean an organization must stock a wider and more expensive range of spare parts. This includes large bearings, custom seals, and drive train components that represent a significant capital investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing a rotary furnace must be a strategic decision based on your specific processing needs, weighed against your capacity for its intensive maintenance requirements.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity and throughput: The superior mixing and heat transfer of a rotary furnace may justify the higher maintenance burden.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost and downtime: A simpler, static furnace will almost always be a more predictable and less resource-intensive choice.
- If you are processing varied or challenging materials: The tumbling action of a rotary furnace provides a distinct advantage that can often outweigh the associated maintenance complexity.
Ultimately, the complexity of rotary furnace maintenance is an inherent trade-off for its advanced processing capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Rotating Mechanism | Wear on gears, bearings, and seals; requires frequent lubrication and alignment |
| High-Temperature Environment | Accelerates refractory lining wear and metal fatigue; demands regular inspections |
| Specialized Labor | Needs expertise in mechanical alignment and refractory work; increases costs |
| Increased Downtime | Repairs require full cooldown, leading to extended operational halts |
| Spare Parts Inventory | Higher need for custom components like seals and bearings, raising capital investment |
Optimize your laboratory's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, reducing maintenance complexity and downtime. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your processing capabilities and operational reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















