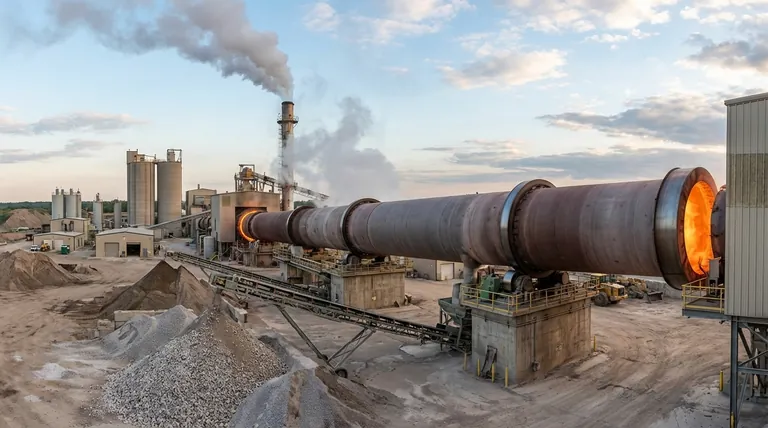
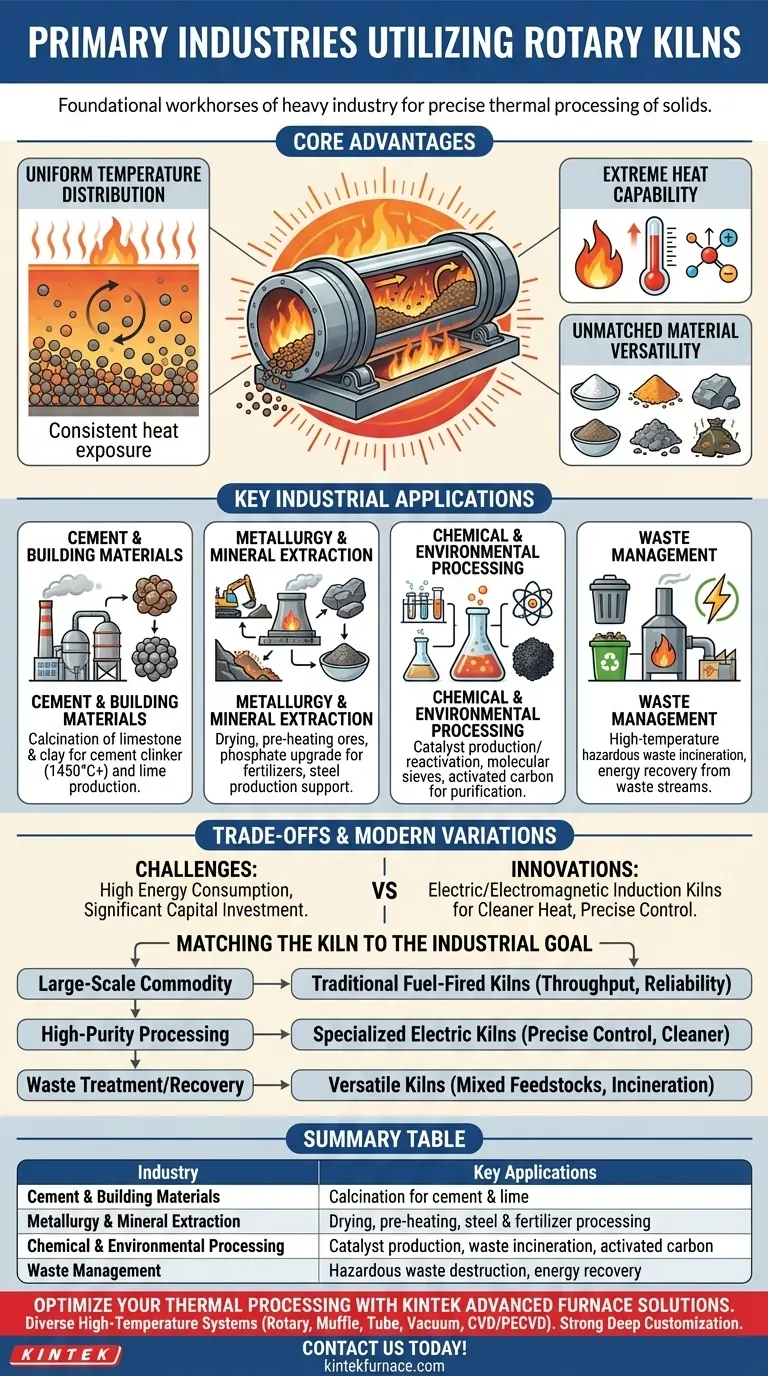
At their core, rotary kilns are the foundational workhorses of heavy industry, most prominently utilized in cement production, mineral processing, metallurgy, and large-scale waste management. Their application extends into specialized fields like chemical manufacturing and environmental remediation, where precise thermal processing of solid materials is critical.
The widespread adoption of rotary kilns is not an accident; it stems from their unique and powerful ability to apply consistent, extremely high temperatures to a vast range of materials, making them an indispensable and versatile tool for thermal transformation.

The Core Function: Why Rotary Kilns Dominate Thermal Processing
To understand why so many industries rely on this technology, you must first understand its three fundamental advantages. These principles explain its presence in factories and processing plants worldwide.
Uniform Temperature Distribution
The continuous, slow rotation of the kiln cylinder ensures that the material inside tumbles and mixes thoroughly. This action guarantees that every particle is exposed to the heat source evenly, resulting in a highly consistent and uniform final product.
Extreme Heat Capability
Rotary kilns are engineered to achieve and sustain the extremely high temperatures required for chemical reactions like calcination, sintering, and oxidation. This capability is essential for physically and chemically transforming raw materials into valuable products.
Unmatched Material Versatility
Few technologies can handle such a wide array of materials. Rotary kilns can process everything from fine powders and granular solids to mineral ores, agricultural feed, and heterogeneous waste streams, making them a flexible solution for diverse industrial needs.
A Breakdown of Key Industrial Applications
The core advantages of the rotary kiln translate directly into its use across several primary industrial sectors.
Cement and Building Materials
This is the most iconic application. Rotary kilns are used to heat a mixture of limestone and clay to over 1450°C, a process called calcination, which creates the small, glass-hard nodules known as "clinker." This clinker is then ground to produce Portland cement. The technology is also used for lime manufacturing.
Metallurgy and Mineral Extraction
In metallurgy, kilns perform critical tasks like drying and pre-heating ores before they enter a smelter. They are also used to upgrade phosphate ores for fertilizers, calcine refractory materials, and assist in steel production by processing inputs and byproducts.
Chemical and Environmental Processing
The chemical industry uses rotary kilns for producing and reactivating catalysts, roasting chemical molecular sieves, and manufacturing activated carbon for air and water purification. In waste management, they serve as high-temperature incinerators to safely destroy hazardous materials or as a method for converting waste into energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Modern Variations
While incredibly effective, the traditional rotary kiln is not without its challenges. Understanding these limitations provides context for the technology's evolution.
High Energy Consumption
Heating a massive, rotating steel drum to thousands of degrees Celsius is an energy-intensive process. This makes fuel or electricity costs a significant operational consideration for any facility using them.
Significant Capital Investment
Rotary kilns are massive pieces of industrial equipment that require a large physical footprint, robust foundations, and significant upfront capital to install. They represent a major, long-term investment for any operation.
The Rise of Specialized Kilns
To address the need for greater efficiency and precision, modern variations have emerged. Electric and electromagnetic induction kilns offer cleaner heat and more precise temperature control, making them ideal for high-purity applications in the chemical and advanced materials sectors, albeit often at a smaller scale.
Matching the Kiln to the Industrial Goal
The choice and configuration of a rotary kiln are dictated entirely by the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commodity production (like cement or lime): Traditional, large-capacity fuel-fired kilns remain the standard due to their unmatched throughput and proven reliability.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical or materials processing: Specialized electric or electromagnetic kilns offer superior temperature control and a cleaner processing environment, preventing contamination from combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is waste treatment or resource recovery: The kiln's inherent versatility in handling mixed and variable feedstocks makes it the ideal technology for incineration, pyrolysis, and materials valorization.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln’s enduring relevance comes from its mastery over the fundamental industrial process of thermal transformation.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Cement & Building Materials | Calcination of limestone and clay for cement and lime production |
| Metallurgy & Mineral Extraction | Drying, pre-heating ores, and processing for steel and fertilizers |
| Chemical & Environmental Processing | Catalyst production, waste incineration, and activated carbon manufacturing |
| Waste Management | Hazardous waste destruction and energy recovery from waste streams |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing with advanced furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs in industries like cement, metallurgy, and waste management. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained



















