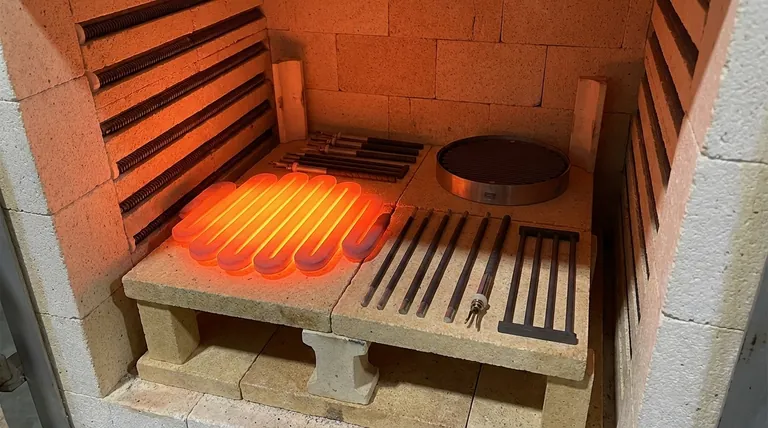
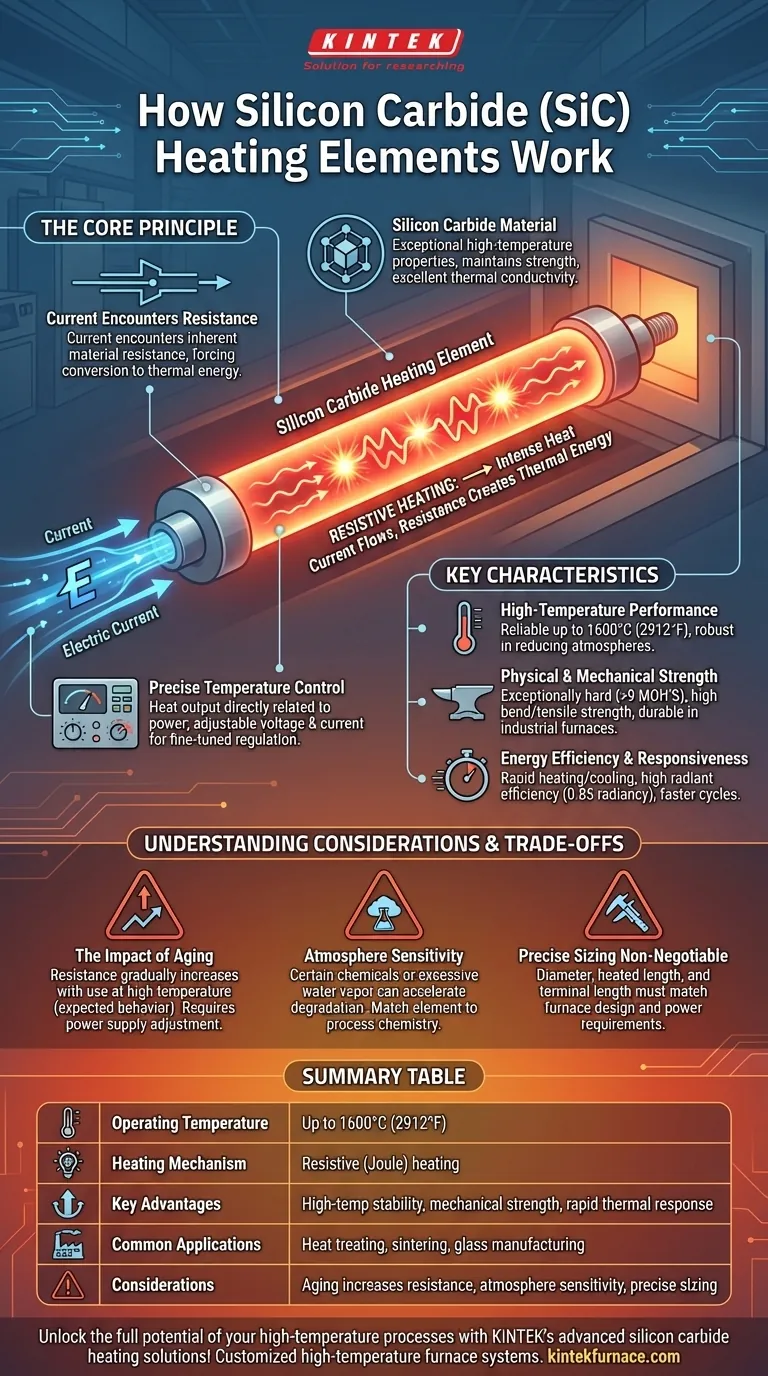
At its core, a silicon carbide (SiC) heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat. When an electric current is passed through the element, the material’s inherent electrical resistance causes it to heat up intensely—a principle known as resistive or Joule heating. This heat is then radiated outward at very high temperatures to heat a furnace, kiln, or other industrial process. The element's temperature can be precisely controlled by adjusting the voltage and current supplied to it.
Silicon carbide elements are valued not just for their ability to generate heat, but for their unique combination of high-temperature stability, mechanical strength, and rapid thermal response. This makes them a dependable and efficient solution for the most demanding industrial heating applications.

The Core Principle: Resistive Heating
Resistive heating is the fundamental mechanism behind every SiC element. Understanding how this principle is leveraged through the specific properties of silicon carbide is key to appreciating its value.
How Current Creates Heat
When electricity flows through any material, it encounters resistance. This opposition to the current's flow forces the electrical energy to be converted into thermal energy, or heat.
SiC elements are designed to have a specific resistance that maximizes this effect, allowing them to generate significant heat efficiently and controllably.
The Role of Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide is the material of choice for its exceptional properties at extreme temperatures. Unlike common metals that would quickly melt or degrade, SiC maintains its strength and structure.
It possesses excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to distribute heat evenly and respond quickly to changes in power. This combination of high-temperature resilience and thermal performance is what sets it apart.
Precise Temperature Control
The heat output of an SiC element is a direct function of the power applied to it.
By using sophisticated power controllers (typically SCRs or thyristors), operators can precisely adjust the voltage and current. This enables fine-tuned temperature regulation, which is critical for sensitive processes like heat treating, sintering, and glass manufacturing.
Key Characteristics of SiC Elements
The practical advantages of SiC elements stem directly from their physical and electrical characteristics. These features make them a go-to solution for high-performance industrial furnaces.
High-Temperature Performance
SiC elements can operate reliably at furnace temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). They are particularly robust and exhibit high strength in reducing atmospheres, offering an advantage over other materials like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) in certain chemical environments.
Physical and Mechanical Strength
These elements are exceptionally hard (over 9 MOH'S) and possess high bend and tensile strength. This physical robustness makes them durable and resistant to the mechanical stresses present within a large industrial furnace, contributing to a long service life.
Energy Efficiency and Responsiveness
SiC elements heat and cool rapidly, enabling faster process cycles and reducing wasted energy during furnace heat-up. Their high radiant efficiency (a radiancy of 0.85) ensures that the heat they generate is transferred effectively to the product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, SiC elements are not a universal solution. Understanding their operational characteristics is crucial for successful implementation and longevity.
The Impact of Aging
The most critical consideration for SiC elements is aging. Over time and with use at high temperatures, the electrical resistance of an element gradually and irreversibly increases.
This is a normal and expected behavior. However, the power supply system must be capable of providing progressively higher voltage to maintain the required power output and furnace temperature. Failure to account for this is a common cause of performance issues.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
While strong, the lifespan and performance of SiC elements can be affected by the furnace atmosphere. Certain chemicals or excessive water vapor can react with the silicon carbide at high temperatures, accelerating degradation. The choice of element type must always account for the process chemistry.
Precise Sizing is Non-Negotiable
SiC elements are not interchangeable commodities. Each element must be carefully specified for its diameter, heated length, and terminal length to match the furnace's design and power requirements. Incorrect sizing leads to uneven heating, premature failure, and inefficient operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element requires matching its capabilities to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature and process purity: SiC is an excellent choice due to its high-temperature capability and clean, electric heat that introduces no contaminants from combustion.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and speed: The rapid heating and cooling cycles of SiC elements allow for faster throughput and reduced energy costs, making them ideal for dynamic production environments.
- If your primary focus is durability in a demanding environment: The high mechanical strength and long service life of SiC elements ensure reliable operation in heavy industrial furnaces and kilns.
By understanding these principles, you can effectively leverage the power and reliability of silicon carbide for your high-temperature processes.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1600°C (2912°F) |
| Heating Mechanism | Resistive (Joule) heating |
| Key Advantages | High-temperature stability, mechanical strength, rapid thermal response |
| Common Applications | Heat treating, sintering, glass manufacturing |
| Considerations | Aging increases resistance, atmosphere sensitivity, precise sizing required |
Unlock the full potential of your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced silicon carbide heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with customized high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heating applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















