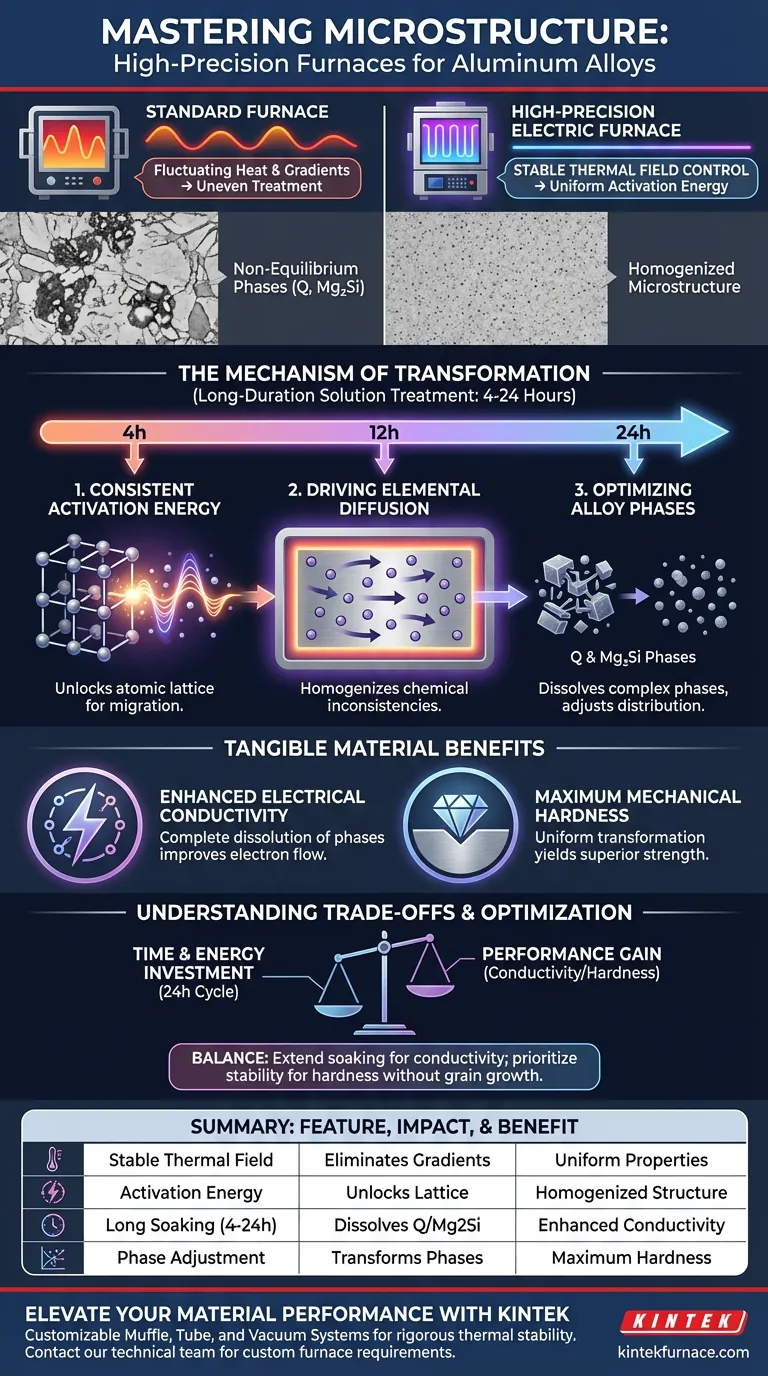
High-precision electric furnaces facilitate microstructural transformation by maintaining a highly stable thermal field that provides consistent activation energy to the material. This controlled environment drives the diffusion of elements across multi-phase microstructures, allowing non-equilibrium primary phases to effectively adjust their elemental distribution over long durations.
By ensuring uniform activation energy over extended periods (4 to 24 hours), these furnaces drive the dissolution of complex phases like Q and Mg2Si. This precise control directly correlates to tangible improvements in both material conductivity and hardness.
The Mechanism of Microstructural Change
Achieving Thermal Stability
The core advantage of a high-precision electric furnace is its ability to maintain stable thermal field control. Unlike standard furnaces which may fluctuate, high-precision units eliminate temperature gradients that could lead to uneven treatment.
This stability is non-negotiable for microstructural transformation. It ensures that every part of the alloy receives the exact thermal input required for change.
Consistent Activation Energy
Microstructural changes require a specific energy threshold to occur. High-precision furnaces provide consistent activation energy throughout the entire heating cycle.
This continuous supply of energy "unlocks" the atomic lattice. It allows elements to break free from their initial positions and migrate to where they are needed for structural reinforcement.
Driving Elemental Diffusion
Once activated, the primary mechanism of change is diffusion. The furnace promotes the diffusion of elements throughout the alloy’s multi-phase microstructures.
This movement homogenizes the material. It smoothes out chemical inconsistencies that naturally occur during the casting process.
Optimizing Alloy Phases
Adjusting Non-Equilibrium Phases
As-cast aluminum alloys often contain non-equilibrium primary phases. These are unstable structures that negatively impact the material's mechanical properties.
Long-duration solution treatment allows these phases to adjust their elemental distribution. The furnace holds the material in a state where these phases can dissolve or transform into more stable, beneficial configurations.
Targeting Copper and Silicon Phases
This process is particularly critical for alloys containing copper and silicon. Specifically, it targets complex structures such as Q phases or Mg2Si phases.
Without precise heat, these phases may remain coarse or unevenly distributed. Proper thermal treatment ensures they are refined and integrated correctly into the matrix.
The Role of Soaking Time
Transformation is not instantaneous. Effective treatment requires precise control over soaking times, typically ranging from 4 to 24 hours.
This extended duration provides the necessary window for slow-moving diffusion processes to complete. It ensures the material reaches its maximum potential for conductivity and strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Cost of Precision
While high-precision treatment maximizes material properties, it requires significant time investment. Committing to a 24-hour soaking cycle increases energy consumption and reduces throughput compared to rapid treatments.
Balancing Hardness and Efficiency
There is a point of diminishing returns. While extending soaking time generally improves hardness performance, operators must determine if the marginal gain justifies the extended furnace occupancy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the benefits of high-precision solution treatment, align your furnace settings with your specific material performance targets.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize the upper limits of soaking time (closer to 24 hours) to ensure the complete dissolution and diffusion of Q and Mg2Si phases.
- If your primary focus is Hardness: Focus on the stability of the thermal field to ensure uniform transformation of non-equilibrium phases without inducing grain growth.
Precision in thermal control is the defining factor in converting raw aluminum alloys into high-performance engineering materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Microstructure | Material Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Stable Thermal Field | Eliminates temperature gradients | Uniform material properties |
| Activation Energy | Unlocks atomic lattice for migration | Homogenized chemical structure |
| Long Soaking (4-24h) | Dissolves Q and Mg2Si phases | Enhanced electrical conductivity |
| Phase Adjustment | Transforms non-equilibrium phases | Maximum mechanical hardness |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precision in thermal control is the difference between a standard alloy and a high-performance engineering material. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems specifically designed to maintain the rigorous thermal stability required for long-duration solution treatments.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet the unique diffusion and phase-transformation needs of your aluminum-based alloys. Whether you are targeting peak electrical conductivity or maximum structural hardness, KINTEK’s advanced laboratory furnaces ensure consistent results every cycle.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process? Contact our technical team today to discuss your custom furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Compositional Design, Microstructure, and Thermal Processing of Aluminum-Based Complex Concentrated Alloys. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15010088
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What electrical safety checks should be performed before operating a benchtop furnace? Ensure Safe Operation and Prevent Hazards
- What types of heat transfer occur in a box-type resistance furnace? Master Radiation and Convection for Optimal Heating
- Why is controlled heat treatment in a muffle furnace necessary for calcined clay? Achieve Optimal Pozzolanic Activity
- What are some common uses of muffle furnaces in material testing? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Accurate Results
- Why is chamber size an important consideration when selecting a muffle furnace? Optimize Your Lab's Efficiency and Results
- What are the standard features of box furnaces? Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How does a high-temperature electric furnace contribute to the melting process of radiation shielding glass?
- What role does a high-temperature electric furnace play in Cr:Al2O3 synthesis? Master Lattice Integration at 1400°C.



















