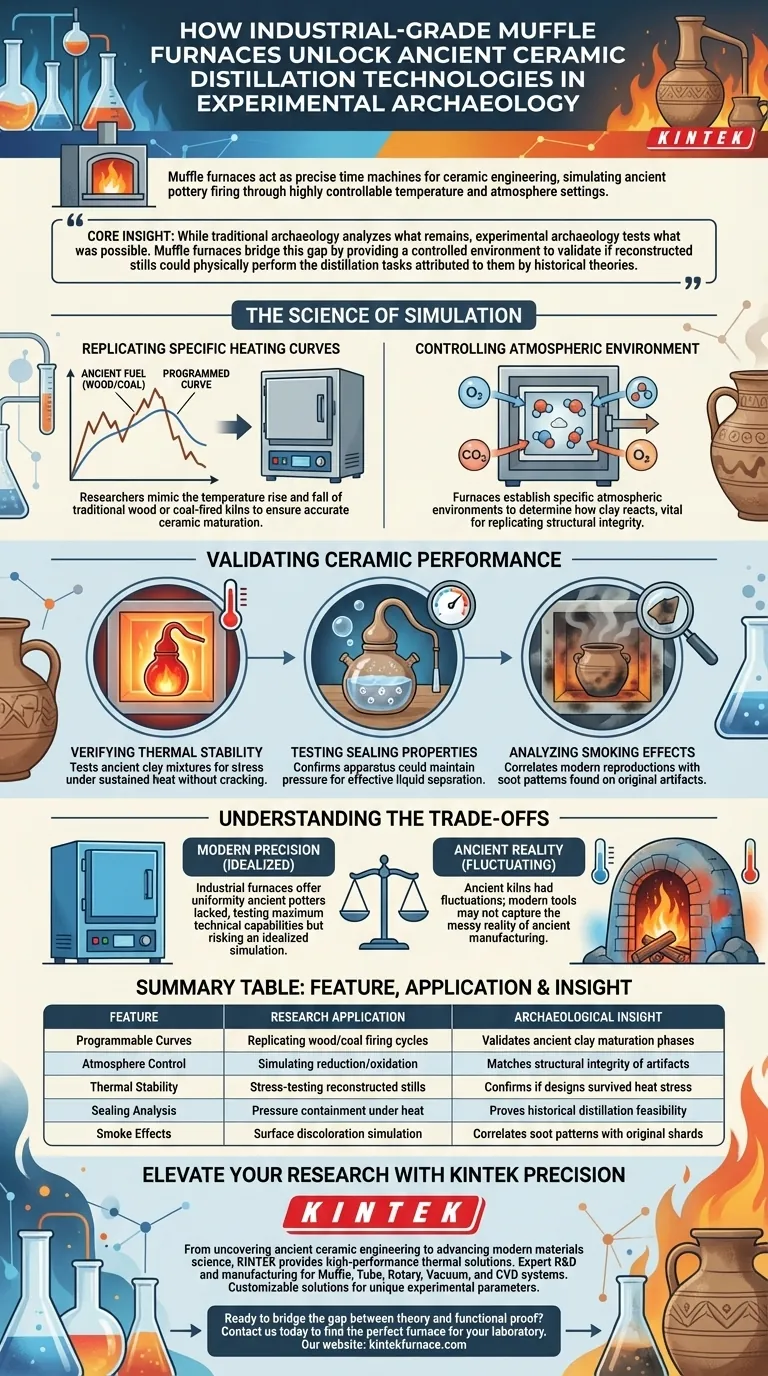
Industrial-grade muffle furnaces act as precise time machines for ceramic engineering. They are utilized in experimental archaeology to rigorously simulate ancient pottery firing processes through highly controllable temperature settings. By replicating specific heating curves and atmospheric conditions, researchers can subject reconstructed ceramic distillation apparatuses to exact tests, verifying their thermal stability, sealing efficiency, and reaction to smoke.
Core Insight While traditional archaeology analyzes what remains, experimental archaeology tests what was possible. Muffle furnaces bridge this gap by providing a controlled environment to validate if reconstructed stills could physically perform the distillation tasks attributed to them by historical theories.

The Science of Simulation
To understand how ancient civilizations managed complex chemical processes, researchers must do more than observe shards; they must recreate the process.
Replicating Specific Heating Curves
Modern muffle furnaces allow for the programming of exact heating curves.
Researchers use this to mimic the temperature rise and fall that would occur in a traditional wood or coal-fired kiln.
This ensures the ceramic body matures exactly as it would have in antiquity, providing an accurate baseline for testing.
Controlling the Atmospheric Environment
Beyond heat, the chemical composition of the air inside the kiln is critical.
Furnaces allow researchers to establish specific atmospheric environments.
This control determines how the clay reacts, which is vital for replicating the structural integrity of ancient vessels.
Validating Ceramic Performance
Once the firing environment is established, the focus shifts to testing the physical capabilities of the reconstructed distillation apparatus.
Verifying Thermal Stability
Distillation requires sustained heat, often causing stress on ceramic materials.
Researchers use these furnaces to verify the thermal stability of the reconstruction.
This tests whether the ancient clay mixtures and designs could withstand the operational temperatures required for distillation without cracking or failing.
Testing Sealing Properties
For distillation to work, vapor must be contained.
The furnaces allow for the testing of sealing properties under heat.
This confirms if the apparatus could maintain the necessary pressure and containment to separate liquids effectively.
Analyzing Smoking Effects
The visual and physical impact of the firing process leaves clues.
Researchers observe the smoking effects on the ceramics during simulation.
These effects help correlate modern reproductions with the soot patterns or discoloration found on original archaeological artifacts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While modern technology offers precision, it presents specific challenges when studying the past.
The Problem of "Too Much" Control
Industrial furnaces provide a level of uniformity that ancient potters never possessed.
Ancient kilns had temperature fluctuations and "cold spots" that modern muffle furnaces eliminate.
Therefore, while these tools are excellent for testing the maximum technical capabilities of a design, they may simulate an idealized version of the process rather than the messy reality of ancient manufacturing.
Applying Modern Tech to Ancient Mysteries
The goal of using these furnaces is to move from theoretical models to functional proof.
- If your primary focus is Process Verification: Use the furnace to establish precise heating curves that mimic the thermal ramp-up of ancient fuel sources.
- If your primary focus is Artifact Analysis: Focus on the atmospheric controls to verify if the sealing and thermal stability of your reconstruction match historical fragments.
By simulating the actual operational levels of these devices, researchers confirm the technical sophistication of ancient distillation processes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Research Application | Archaeological Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Programmable Curves | Replicating wood/coal firing cycles | Validates ancient clay maturation phases |
| Atmosphere Control | Simulating reduction/oxidation | Matches structural integrity of artifacts |
| Thermal Stability | Stress-testing reconstructed stills | Confirms if designs survived heat stress |
| Sealing Analysis | Pressure containment under heat | Proves historical distillation feasibility |
| Smoke Effects | Surface discoloration simulation | Correlates soot patterns with original shards |
Elevate Your Research with KINTEK Precision
From uncovering the secrets of ancient ceramic engineering to advancing modern materials science, KINTEK provides the high-performance thermal solutions you need. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you require standard lab high-temp furnaces or fully customizable solutions tailored to unique experimental parameters, our equipment ensures the precision, stability, and control your project demands.
Ready to bridge the gap between theory and functional proof? Contact us today to consult with our experts and find the perfect furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Mona Bagheri Ghaleh, Carmela Vaccaro. Exploring Early Distillation Hypotheses: Investigating Unique Pottery from Tepe Sagzabad on the Central Iranian Plateau (Iron Age). DOI: 10.4236/ad.2025.131002
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature of the muffle furnace? It's a critical design choice.
- How does a high-temperature box furnace contribute to the sintering of doped zirconate ceramics? Achieve 94% Density
- What is the application of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab
- What is the difference between batch furnace and continuous furnace? Flexibility vs. High-Volume Efficiency
- What conditions does a muffle furnace provide for ceramic bricks? Precision Heat for Hedenbergite Synthesis
- What types of facilities typically use box furnaces? Essential for Labs and Small-Scale Production
- How does a box-type high-temperature furnace influence K439B superalloy? Precision Control for γ' Phase Morphology
- What are the specific applications of box type electric furnaces in metallurgy? Essential for Heat Treatment and Material Synthesis



















