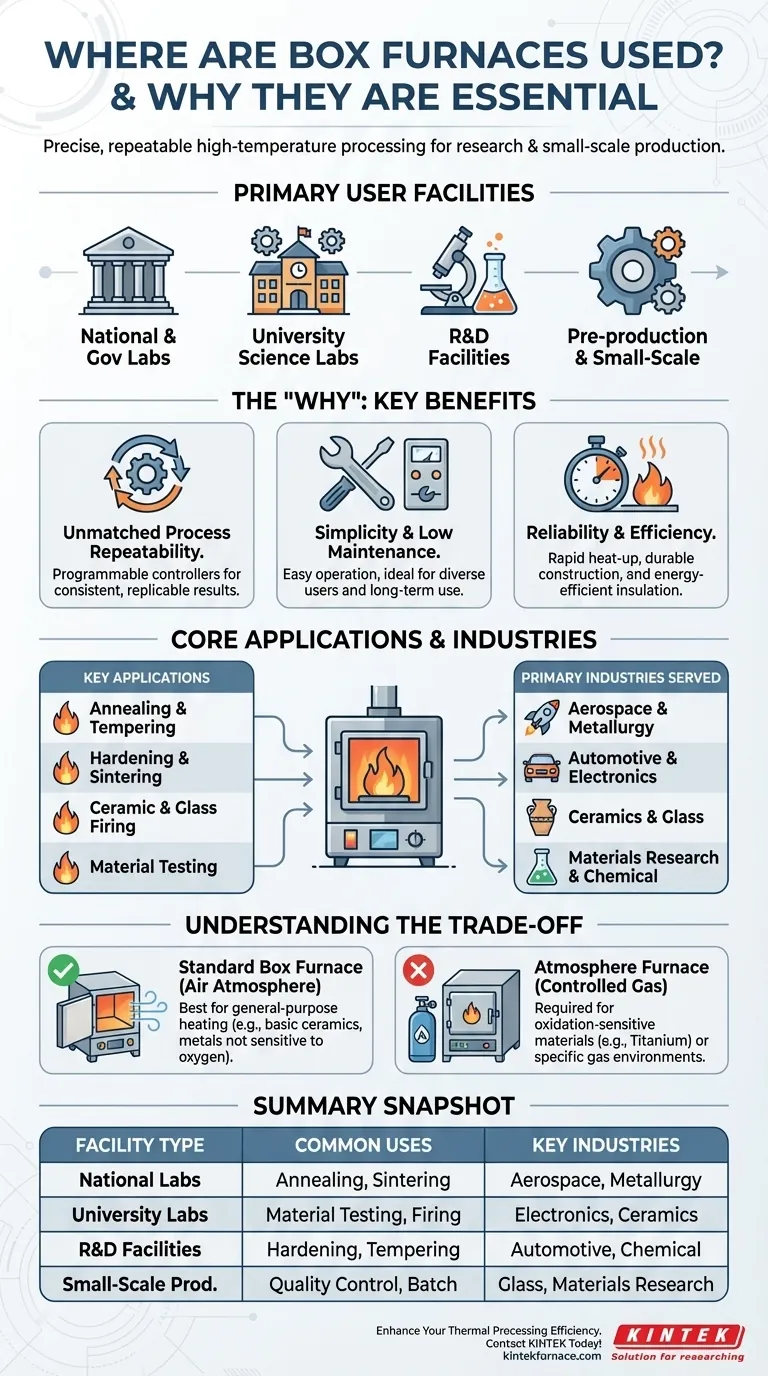
In short, box furnaces are staples in any setting that requires precise, repeatable high-temperature processing on a small to medium scale. They are commonly found in national laboratories, government and private research facilities, university science labs, pre-production manufacturing tests, and small-scale production environments. Their versatility makes them essential in industries ranging from aerospace and metallurgy to ceramics and materials research.
A box furnace is the go-to thermal processing tool for its reliability, versatility, and operational simplicity. While not suited for every specialized industrial process, its ability to precisely control heat for a wide range of common applications makes it an indispensable asset in both laboratory research and small-scale production.

The Core Function: A Versatile Workhorse for Thermal Processing
A box furnace, at its core, is a highly insulated chamber designed to achieve uniform high temperatures for processing materials. Its strength lies in its straightforward design and its ability to execute a wide variety of thermal profiles with high precision.
Key Applications: From Metals to Ceramics
Facilities use box furnaces for a range of foundational thermal processes. These are not niche applications but rather the building blocks of materials science and light manufacturing.
Common uses include:
- Annealing: Softening metals or glass to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility.
- Hardening & Tempering: Heat-treating steel parts to increase hardness and then tempering them to improve toughness.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials, such as ceramics or metal powders, into a solid mass using heat without melting them.
- Ceramic & Glass Firing: Firing clay, glazes, and glass in both laboratory and art studio settings.
- Material Testing: Performing experimental melting, heat treatment, and analysis in R&D environments.
Primary Industries Served
The versatility of these applications means box furnaces are found across numerous high-tech and traditional sectors.
This includes aerospace, automotive, electronics, metallurgy, ceramics, glass production, and the chemical industry. They are particularly vital in materials research and development, which underpins innovation in all these fields.
Why These Facilities Choose Box Furnaces
The widespread adoption of box furnaces is not accidental. It stems from a specific combination of features that makes them the ideal choice for research, testing, and small-batch production.
Unmatched Process Repeatability
Scientific research and quality control demand consistency. Box furnaces are engineered with fully programmable controllers that allow for precise management of heating rates, soak times, and cooling rates.
This process repeatability ensures that an experiment run today can be perfectly replicated tomorrow, which is a non-negotiable requirement for national labs and R&D facilities.
Simplicity and Low Maintenance
Compared to more complex industrial furnaces, a box furnace is valued for its simple operation and low maintenance costs.
This makes it an ideal tool for university laboratories, where many different students and researchers with varying levels of experience may need to use the equipment.
Designed for Reliability and Efficiency
These furnaces are built for long-term, demanding use. They typically use premium components and a sturdy construction to ensure reliability.
Modern designs also feature rapid heat-up and response times, dense load capability, and insulation that reduces external surface temperatures, making them safer and more efficient for a laboratory environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Box Furnace vs. Specialized Equipment
While incredibly versatile, a box furnace is not the solution for every thermal processing need. Understanding its primary limitation is key to selecting the right equipment.
The Standard: General-Purpose Heating
A standard box furnace operates by heating materials in the presence of ambient air. It is the perfect tool for any process where the material is not negatively affected by oxygen at high temperatures.
This covers a vast range of "basic scenarios" like a majority of ceramic firing, basic metal heat treatments, and general sample heating.
The Limitation: Atmosphere Control
The critical limitation of a standard box furnace is its lack of atmosphere control.
For materials that are sensitive to oxidation, such as titanium alloys, or for processes that require a specific gas environment (e.g., a reducing atmosphere for certain types of sintering), a standard box furnace is unsuitable. These applications demand a specialized atmosphere furnace, which is designed to contain a controlled, inert, or reactive gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on the materials you are processing and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The box furnace offers the process repeatability and versatility needed for experimentation with various materials in a standard air atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or pre-production manufacturing: Its reliability, dense load capability, and simple operation make it ideal for proving a process or running limited batches.
- If your primary focus is education or general lab work: The low maintenance, safety features, and ease of use of a box furnace are its greatest assets in a university or general testing environment.
- If your primary focus is processing oxidation-sensitive materials: You must look beyond a standard box furnace to a specialized atmosphere furnace that provides a controlled gas environment.
Ultimately, the box furnace's strength lies in its ability to deliver reliable and precise heat treatment for the widest range of common applications, making it a foundational tool in modern science and industry.
Summary Table:
| Facility Type | Common Uses | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| National Labs | Annealing, Sintering | Aerospace, Metallurgy |
| University Labs | Material Testing, Firing | Electronics, Ceramics |
| R&D Facilities | Hardening, Tempering | Automotive, Chemical |
| Small-Scale Production | Quality Control, Batch Processing | Glass Production, Materials Research |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace for your lab or production? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to enhance your thermal processing efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















