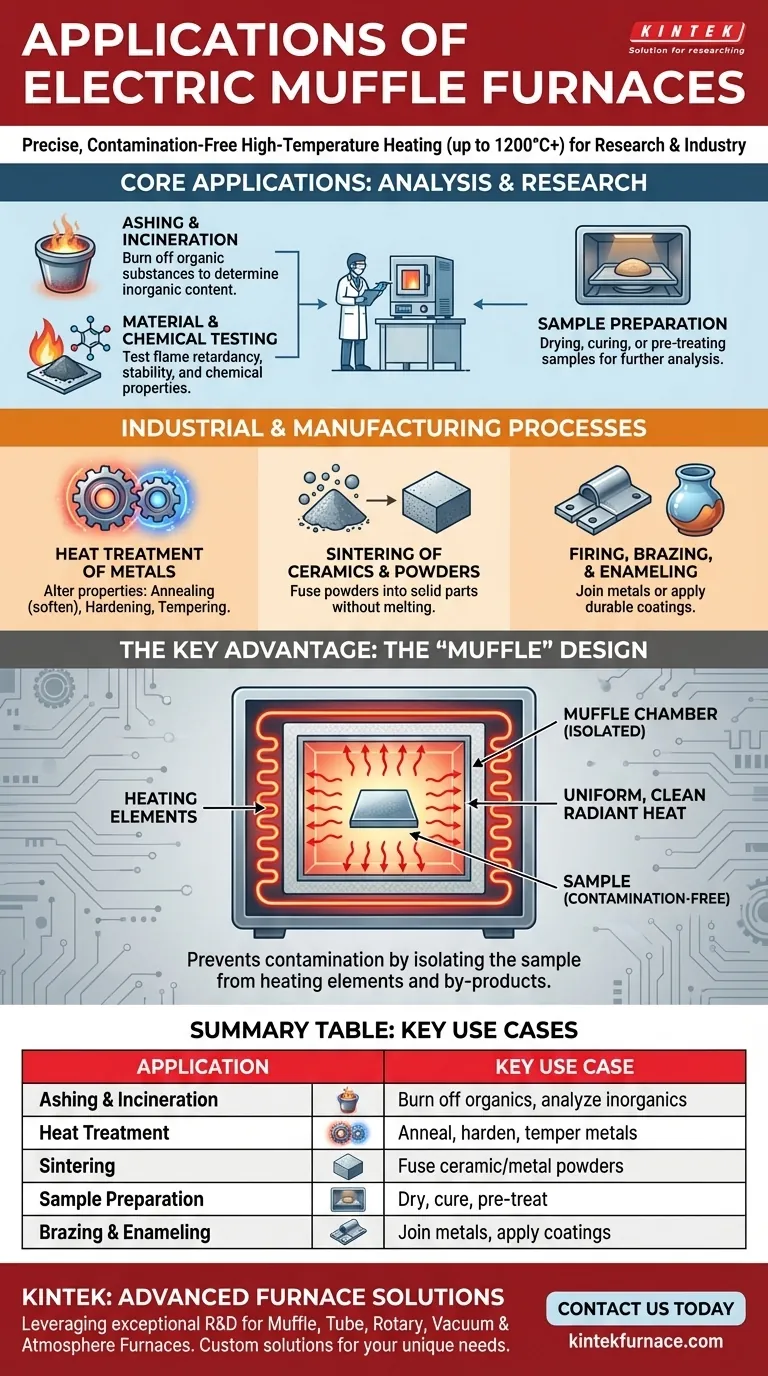
At its core, an electric muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for transforming materials in a controlled environment. Its applications span from industrial manufacturing and metallurgy to analytical chemistry and quality control, making it a versatile tool for any process requiring uniform, clean heat up to 1200°C (2200°F) or higher.
The fundamental purpose of a muffle furnace is not just to get hot, but to provide a contamination-free heating chamber. Its key design feature—the "muffle"—isolates the sample from the heating elements, ensuring the material's properties are altered only by heat, not by chemical by-products of combustion or electrical interference.

Core Applications in Analysis and Research
A muffle furnace is a cornerstone of many laboratories due to its precision and reliability in preparing and testing samples.
Ashing and Incineration
Ashing is the process of burning off all organic substances in a sample to leave behind only the inorganic components, or ash.
This is critical in analytical chemistry, pharmaceutical quality control, and environmental testing to determine the mineral or non-combustible content of a material.
Material and Chemical Property Testing
Researchers use muffle furnaces to subject materials to extreme heat and observe the results.
This includes testing the flame retardancy of aerospace components, assessing the stability of pharmaceutical drugs at high temperatures, and identifying the fundamental chemical properties of new compounds.
Sample Preparation
In many analytical workflows, samples must be dried, cured, or pre-treated at a specific high temperature before further analysis can occur. A muffle furnace provides the stable environment needed for this crucial preparation step.
Industrial and Manufacturing Processes
Beyond the lab, muffle furnaces are workhorses in specialized industrial settings for shaping and strengthening materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals
In metallurgy, heat treatment is used to alter the molecular structure of metals to change their physical properties like hardness and ductility.
Common processes performed in a muffle furnace include:
- Annealing: Softening a metal to make it easier to work with.
- Hardening: Heating and then rapidly cooling steel to increase its hardness.
- Tempering: Reducing the brittleness of hardened steel.
Sintering of Ceramics and Powders
Sintering is a process that uses heat to fuse powders—like ceramics or metals—into a solid, coherent mass without melting them completely. This is a fundamental step in creating many advanced ceramic parts and metallic components.
Firing, Brazing, and Enameling
The furnace's high, uniform heat is ideal for firing ceramic glazes, creating durable enamel coatings on metal, and brazing—a process that joins two pieces of metal using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature.
The Key Advantage: The "Muffle" Design
The furnace's name reveals its most important feature. Understanding this principle is key to understanding its applications.
What is the "Muffle"?
The muffle is a separate, insulated inner chamber that contains the sample. The heating elements are positioned on the outside of this chamber.
Preventing Contamination
Because the heating elements never make direct contact with the sample or its immediate atmosphere, there is no risk of contamination. This is absolutely critical for chemical analysis, pharmaceutical work, and electronics, where even trace impurities can ruin a result.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
The enclosed muffle chamber radiates heat evenly from all sides, creating a highly uniform temperature zone. This ensures that the entire sample is processed consistently, which is essential for reliable heat treatment and repeatable experiments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with specific limitations.
Limited by Chamber Size
Most muffle furnaces are designed for benchtop or small-scale industrial use. They are ideal for processing samples or small parts, not for large-volume manufacturing.
Operates in an Air Atmosphere
A standard muffle furnace heats materials in the presence of oxygen. For processes that require an inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum to prevent oxidation, a specialized and more expensive furnace is necessary.
Energy and Time Considerations
Reaching temperatures of 1000°C or more requires significant electrical power and time. The heating and cooling cycles can be lengthy, which must be factored into any workflow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right tool, you must match the furnace's capabilities to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (like ashing): You need a furnace that offers exceptionally precise temperature control and a certified-clean chamber to guarantee sample purity.
- If your primary focus is metallurgy or material science (like heat treating): Look for a furnace with programmable temperature profiles to control heating and cooling rates, as this dictates the final properties of the material.
- If your primary focus is general lab research or small-scale firing: A durable, easy-to-use benchtop model with excellent temperature uniformity is the most practical and versatile choice.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when your process demands pure, uniform heat, completely isolated from outside influence.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use Case |
|---|---|
| Ashing & Incineration | Burn off organic material to analyze inorganic content |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening, and tempering of metals |
| Sintering | Fuse ceramic or metal powders into solid parts |
| Sample Preparation | Dry, cure, or pre-treat materials before analysis |
| Brazing & Enameling | Join metals or apply durable coatings with high heat |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a high-temperature furnace?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions for diverse laboratories. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs precisely.
Whether you require contamination-free heating for analysis, programmable profiles for metallurgy, or uniform sintering for ceramics, we can deliver a furnace tailored to your goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can drive your research and quality control forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the thermal treatment process of chalcopyrite ore?
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation



















