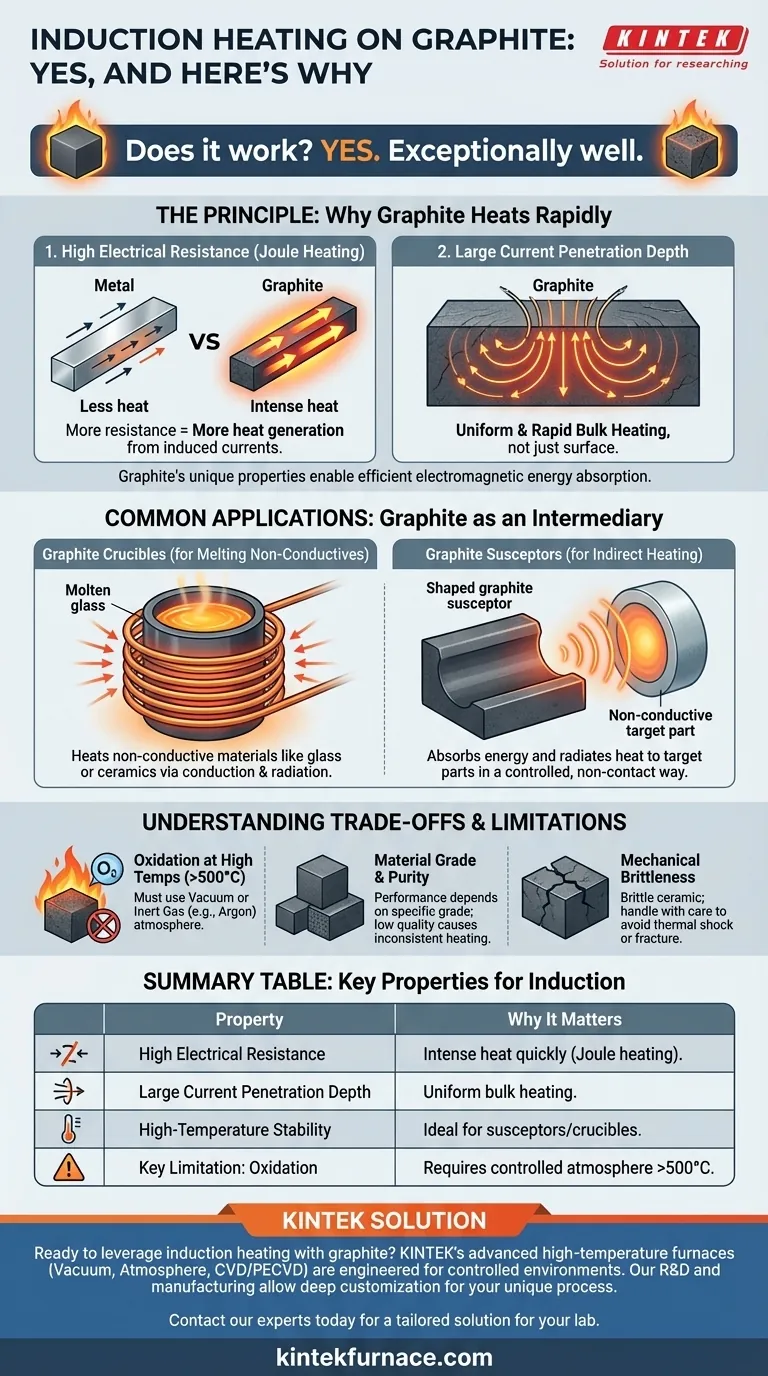
Yes, induction heating works exceptionally well on graphite. Unlike metals that are chosen for their high conductivity, graphite's higher electrical resistance makes it an ideal candidate for induction. This property allows it to absorb electromagnetic energy and convert it into heat with remarkable speed and efficiency.
Graphite is not just compatible with induction heating; it is a strategic material used to solve specific challenges. Its ability to heat rapidly makes it a go-to choice for high-temperature applications, often serving as a heating element (a susceptor or crucible) to heat other, non-conductive materials.

The Principle: Why Graphite Heats via Induction
Induction heating works by inducing electrical eddy currents within a material. The material's resistance to the flow of these currents is what generates heat (a phenomenon known as Joule heating). Graphite's properties are uniquely suited for this process.
It's All About Electrical Conductivity
The fundamental requirement for induction heating is that the material must be an electrical conductor. While often associated with metals, this principle also applies to other conductive materials like graphite, certain semiconductors, and even plasma.
High Resistance Is the Key
While metals like copper have very low electrical resistance, graphite has a significantly higher resistance. This means that for the same amount of induced current, graphite will generate far more heat. This high-resistance characteristic is precisely why it heats so quickly and effectively.
Large Current Penetration Depth
The combination of graphite's electrical properties results in a large current penetration depth. In practical terms, this means the induced currents are not just confined to the surface but are generated throughout a larger volume of the material. This leads to more uniform and rapid bulk heating compared to many metals.
Common Applications for Induction-Heated Graphite
Because it heats so well, graphite is often used as an intermediary to heat other things. This makes it a critical tool in manufacturing and material processing.
Graphite Crucibles
When you need to melt non-conductive materials like glass or certain ceramics, you cannot heat them directly with induction. Instead, you can place them inside a graphite crucible. The induction coil heats the crucible, which then transfers its heat to the material inside via conduction and radiation.
Graphite Susceptors
A susceptor is any material that "suspects" (absorbs) electromagnetic energy and converts it to heat. In many processes, a precisely shaped piece of graphite is used as a susceptor. It is placed near a non-conductive part, and when the induction field is activated, the susceptor heats up and radiates thermal energy to heat the target part in a controlled, non-contact way.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, using graphite in induction heating is not without its challenges. Understanding these limitations is crucial for successful implementation.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
Graphite's most significant drawback is its tendency to oxidize (burn) in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures, typically starting around 500°C (932°F). For high-temperature or long-duration processes, graphite components must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent them from degrading.
Material Grade and Purity Matter
The term "graphite" covers a wide range of materials with different densities, purities, and grain structures. The performance of a graphite crucible or susceptor in an induction field is directly tied to its specific grade. Using an incorrect or low-quality grade can lead to inconsistent heating or premature failure.
Mechanical Brittleness
Unlike metals, graphite is a brittle ceramic material. It cannot be bent or deformed without fracturing. This requires careful mechanical design and handling to avoid thermal shock or physical impact, which can cause cracking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right approach depends entirely on what you are trying to heat.
- If your primary focus is melting or heating non-conductive powders and liquids: Use a graphite crucible, which will act as the primary heating container.
- If your primary focus is heating a specific, non-conductive solid part: Design a graphite susceptor shaped to radiate heat efficiently onto your target component.
- If your primary focus is using graphite as the final component: You must account for its mechanical brittleness and its need for an inert atmosphere at high temperatures.
By understanding graphite's unique electrical properties and practical limitations, you can leverage it as a powerful and efficient tool for demanding induction heating tasks.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Induction Heating |
|---|---|
| High Electrical Resistance | Generates intense heat quickly from induced currents (Joule heating). |
| Large Current Penetration Depth | Enables uniform bulk heating, not just surface heating. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Withstands extreme temperatures, ideal for use as a susceptor or crucible. |
| Key Limitation: Oxidation | Requires a vacuum or inert atmosphere (e.g., argon) above 500°C (932°F). |
Ready to leverage the power of induction heating with graphite?
KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces, including our Vacuum & Atmosphere and CVD/PECVD systems, are engineered to create the perfect controlled environment for your graphite-based processes. Our strong in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities allow for deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're using graphite crucibles for melting or custom susceptors for precise thermal processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can provide a tailored solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?



















