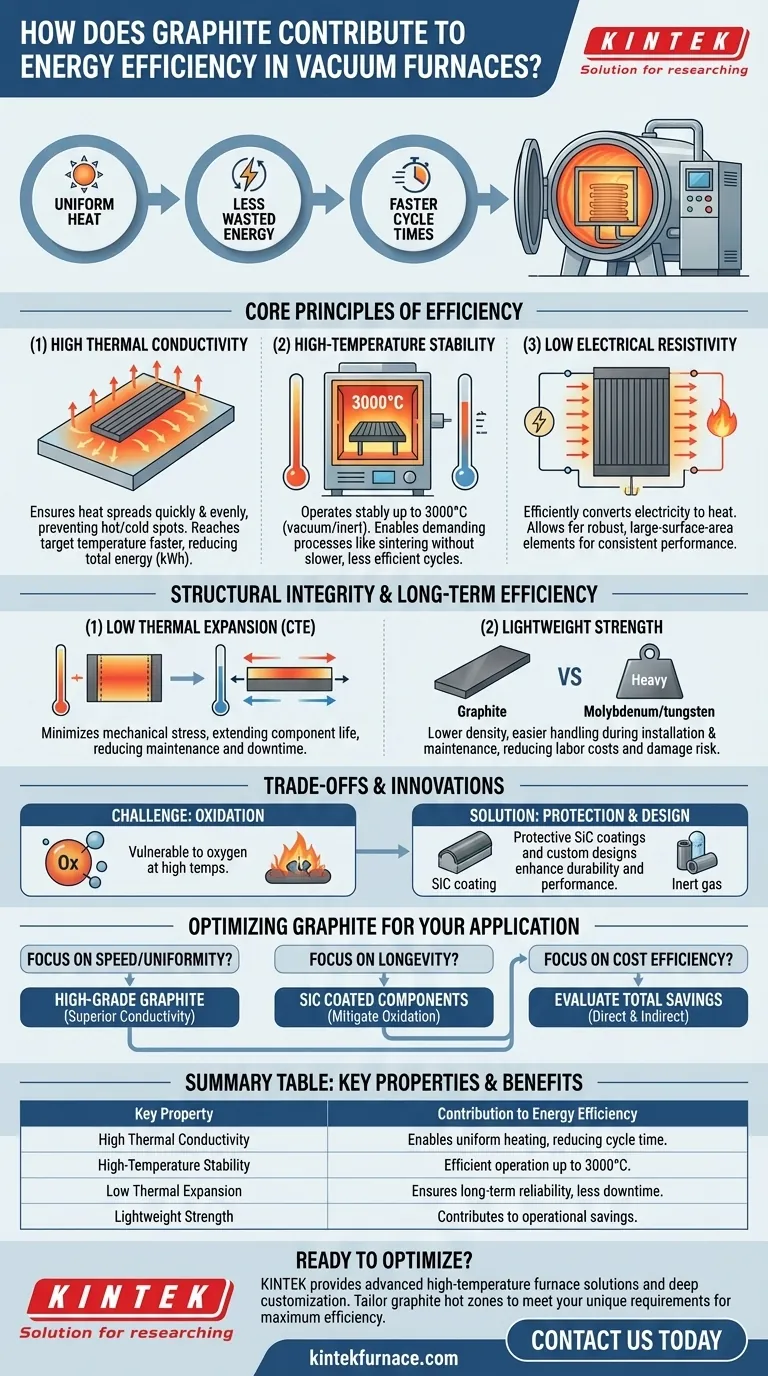
Graphite's contribution to vacuum furnace energy efficiency is multifaceted, stemming from its exceptional ability to conduct heat uniformly, withstand extreme temperatures, and maintain structural integrity. This unique combination allows furnaces to reach and maintain stable process temperatures with less wasted energy and faster cycle times.
While often chosen for its ability to handle intense heat, graphite's most significant impact on energy efficiency lies in its thermal conductivity. By ensuring heat is distributed evenly, it eliminates the need to expend extra energy compensating for hot and cold spots within the furnace.

The Core Principles of Graphite-Driven Efficiency
To understand graphite's role, we must look at how its fundamental properties translate directly into lower energy consumption during furnace operation.
High Thermal Conductivity for Uniform Heating
Graphite’s high thermal conductivity is its most critical feature for efficiency. It ensures that heat generated by the elements is spread quickly and evenly throughout the furnace's hot zone.
This uniform temperature distribution prevents hot and cold spots. As a result, the system can reach the desired target temperature across the entire workload without having to "overshoot" or run longer, directly reducing the total energy (kWh) consumed per cycle.
High-Temperature Stability for Demanding Processes
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; it sublimes at extremely high temperatures (around 3600°C). In a vacuum or inert atmosphere, it can operate stably up to 3000°C.
This allows furnaces to run high-temperature processes like sintering and annealing efficiently. Materials that degrade or deform at these temperatures would require slower, less efficient cycles or be entirely unsuitable.
Low Electrical Resistivity for Efficient Heat Generation
Graphite heating elements function by resisting the flow of electricity, which efficiently converts electrical energy into thermal energy.
Its low resistivity allows for the design of robust, large-surface-area heating elements. These elements provide consistent and repeatable heating performance, ensuring that energy is converted into useful heat exactly where it is needed.
Structural Integrity's Impact on Long-Term Efficiency
Beyond immediate thermal performance, graphite's physical properties contribute to operational efficiency and reliability, which reduces long-term energy waste and cost.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
Graphite expands and contracts very little when heated and cooled. This thermal stability is crucial during the rapid temperature cycling common in vacuum furnace operations.
Low expansion minimizes mechanical stress on the heating elements, fixtures, and insulation. This leads to longer component life, reduced maintenance, and less furnace downtime, which is a critical component of overall operational efficiency.
Lightweight Strength for Operational Savings
Compared to refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten, graphite has a much lower density while maintaining excellent strength at high temperatures.
This lightweight nature makes components easier and safer to handle during installation and maintenance. This reduces labor costs and minimizes the risk of damage, contributing to a more economical and efficient operation over the furnace's lifespan.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Innovations
While highly effective, graphite is not without its limitations. Understanding these challenges and the solutions developed to overcome them is key to maximizing its benefits.
The Challenge of Oxidation
Graphite's primary vulnerability is its reaction to oxygen at elevated temperatures. Even small air leaks in a vacuum furnace can cause graphite components to oxidize, leading to material loss and eventual failure.
This necessitates careful furnace maintenance, high-quality vacuum integrity, and the use of inert backfill gases (like argon or nitrogen) during specific parts of the process cycle.
Innovations in Protection and Design
To counter oxidation and enhance performance, modern graphite components often incorporate key innovations.
Protective coatings, such as a thin layer of Silicon Carbide (SiC), can be applied to seal the graphite from reactive atmospheric elements, significantly extending its service life. Furthermore, custom-designed parts tailored to a specific furnace's geometry and process requirements can further enhance temperature uniformity and durability.
Optimizing Graphite for Your Application
Choosing and using graphite components effectively means aligning their properties with your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is process speed and uniformity: Prioritize high-grade graphite with superior thermal conductivity to minimize cycle times and ensure consistent product quality.
- If your primary focus is component longevity and reduced maintenance: Invest in components with protective SiC coatings to mitigate oxidation risk and extend the operational life of your hot zone.
- If your primary focus is overall cost efficiency: Evaluate both the direct energy savings from efficient heating and the indirect operational savings from graphite's durability and lightweight nature.
Ultimately, leveraging graphite effectively is about harnessing its unique thermal and structural properties to achieve faster, more uniform, and more reliable heating cycles.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Contribution to Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|
| High Thermal Conductivity | Enables uniform heating, eliminating hot/cold spots and reducing cycle time. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Allows efficient operation up to 3000°C for demanding processes. |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Minimizes stress during cycling, ensuring long-term reliability and less downtime. |
| Lightweight Strength | Reduces handling costs and risk of damage, contributing to operational savings. |
Ready to optimize your furnace's energy efficiency and performance?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. We can tailor graphite-based hot zones and components to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring maximum thermal uniformity and process efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's capabilities and reduce your operational costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity



















