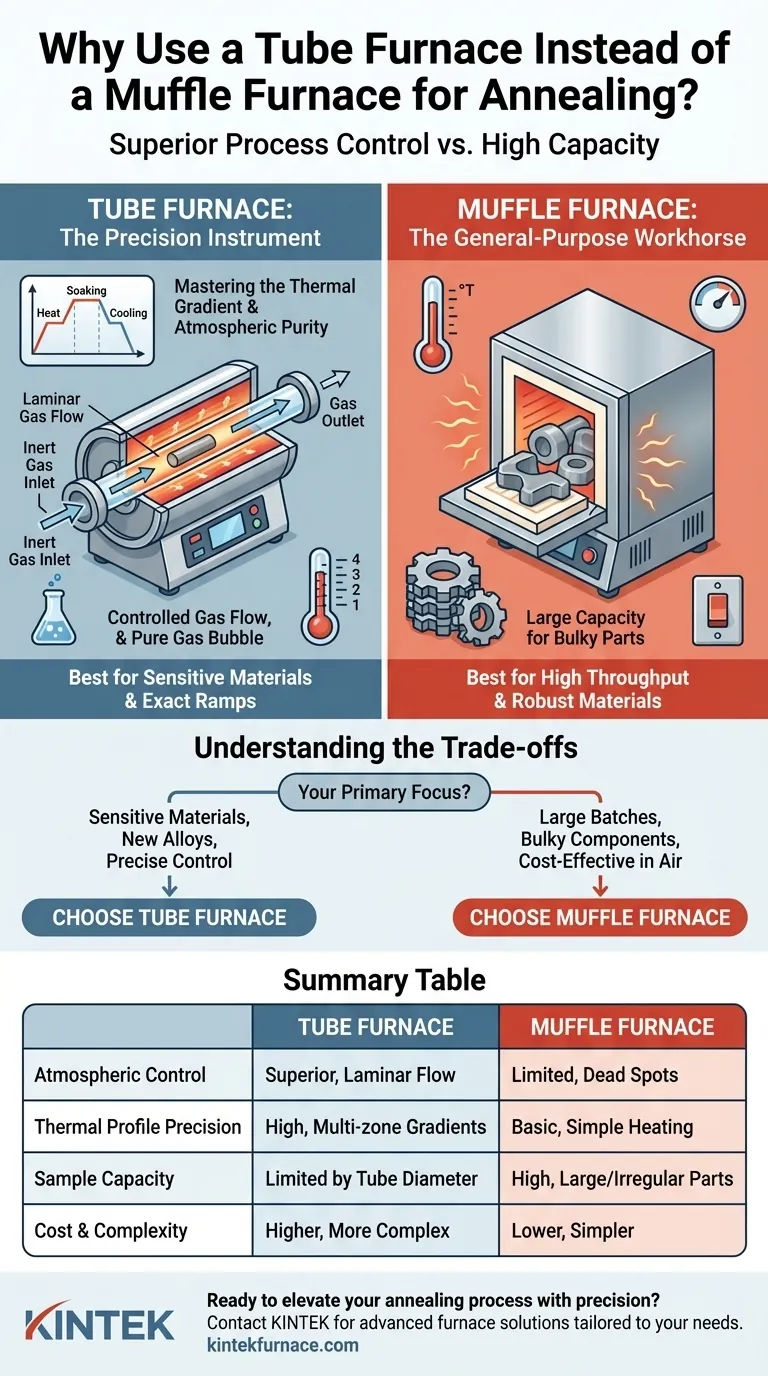
The primary reason to use a tube furnace over a muffle furnace for annealing is superior process control. While both can heat a sample, a tube furnace provides unparalleled precision over the two most critical variables in modern material processing: the thermal profile and the atmospheric environment. This precision is not just a minor feature; it is fundamental to achieving specific material properties in sensitive applications.
The decision between a tube and muffle furnace for annealing hinges on your material's sensitivity. Muffle furnaces are workhorses for general-purpose heating, but tube furnaces are precision instruments essential for processes where exact temperature ramps and atmospheric purity are non-negotiable.

Why Furnace Geometry Dictates Control
The core difference between these two furnace types is not their ability to generate heat, but how they contain and apply it. This distinction in physical design directly impacts the level of control you can achieve.
The Advantage of a Confined Volume
A tube furnace heats a sample within a narrow, cylindrical tube. This small, defined volume is much easier to heat uniformly and to purge of unwanted atmospheric gases like oxygen.
In contrast, a muffle furnace heats a large, box-like chamber. While this allows for larger samples, the sheer volume makes achieving perfect thermal uniformity and rapid atmospheric changes significantly more challenging.
Precision in Atmospheric Management
The annealing process often requires a specific atmosphere—such as a vacuum or an inert gas like argon—to prevent oxidation or induce desired chemical changes.
A tube furnace is uniquely suited for this. Its cylindrical shape with a clear inlet and outlet allows for a consistent, laminar flow of gas over the sample. This ensures the entire sample is exposed to the pure, intended atmosphere. Muffle furnaces with gas ports can introduce inert gas, but their large, open chambers often struggle with dead spots and inefficient purging, compromising atmospheric purity.
Mastering the Thermal Gradient
Annealing is defined by its heating, soaking, and cooling phases. The rate of these temperature changes is critical.
The design of a tube furnace, particularly multi-zone models, allows for precise, programmable control over temperature gradients along the length of the tube. This enables you to execute complex thermal profiles with high repeatability, which is crucial for research and the production of advanced materials.
Muffle Furnaces: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A tube furnace is not always the superior choice. The muffle furnace remains a vital tool when its specific advantages align with the process goals.
When Capacity Matters Most
The most obvious advantage of a muffle furnace is its size. It can accommodate large, bulky, or irregularly shaped parts that simply would not fit inside a process tube.
For applications like annealing large batches of standard components where ultimate precision is secondary to throughput, the muffle furnace is the more practical and efficient option.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
If your annealing process is straightforward—such as heating a robust material in air to a single setpoint—a muffle furnace is the simpler and more cost-effective solution. They are excellent for general heat-treating tasks that do not involve sensitive materials or complex atmospheric requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires an objective look at the compromises inherent in each design. There is no single "best" furnace, only the best furnace for a specific task.
Control vs. Throughput
This is the central trade-off. Tube furnaces offer elite process control for a very small sample volume. Muffle furnaces provide high throughput and capacity at the expense of that fine control.
Cost and Complexity
The precision of a tube furnace comes at a price. Models with advanced gas handling systems and multi-zone temperature programming are significantly more expensive and complex to operate than a standard muffle furnace.
Sample Limitations
The defining constraint of a tube furnace is the diameter of its process tube. Your sample must physically fit, which excludes a wide range of industrial parts and components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Annealing Goal
Your decision ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials or developing new alloys: Choose a tube furnace for its unmatched control over atmosphere and temperature gradients.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating large batches or bulky components in air: A muffle furnace provides the necessary capacity and cost-effectiveness for the job.
- If your primary focus is annealing in an inert atmosphere with less stringent purity requirements: A muffle furnace with a gas port is a viable compromise, but a tube furnace will always offer superior atmospheric control.
By understanding that the choice is fundamentally about precision versus capacity, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific material science objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Control | Superior, with laminar gas flow for purity | Limited, prone to dead spots and inefficient purging |
| Thermal Profile Precision | High, with programmable multi-zone gradients | Basic, suitable for simple heating tasks |
| Sample Capacity | Limited by tube diameter, small volumes | High, accommodates large or irregular parts |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher cost, more complex operation | Lower cost, simpler to use |
| Best For | Sensitive materials, exact annealing processes | General-purpose heating, high-throughput tasks |
Ready to elevate your annealing process with precision? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by deep customization capabilities. Whether you're working with sensitive materials or require high throughput, our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results in your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of pre-treating sapphire substrates in a tube furnace? Optimize Your Epitaxial Growth Foundation
- Can horizontal tube furnaces support controlled atmosphere experiments? Unlock precise material processing
- What factors should be considered when choosing tube furnace cracking? Optimize Your Thermal Decomposition Process
- What role does a tube furnace play in the one-step pyrolysis of Fe-BN-C catalysts? Precision Synthesis Explained
- What role do sealed quartz or glass tubes play in the synthesis of ternary copper sulfides? Mastering Micro-Reactors
- How do vacuum tubes work for dummies? The Simple Analogy to Understand Electronic Control
- What are the different designs of High Temperature Tube Furnaces? Choose the Right Design for Your Lab
- What distinguishes a compact tube furnace from other types? Ideal for Small-Scale Lab Precision



















