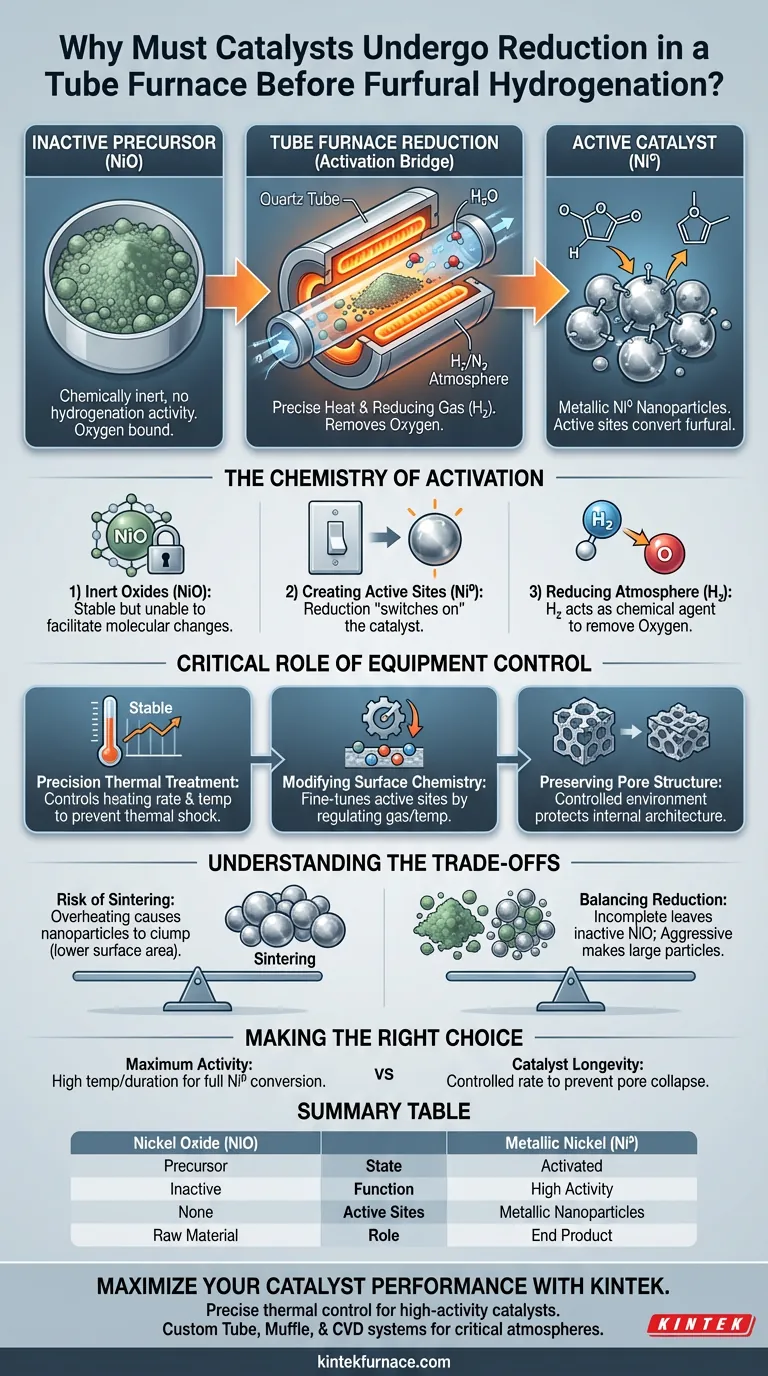
Catalyst reduction is a mandatory activation step because the active components in nickel-based catalysts are synthesized and stored as inactive oxides. To make the catalyst functional, you must chemically strip the oxygen atoms from the nickel oxide (NiO) to create metallic nickel (Ni⁰) nanoparticles.
Core Insight: The tube furnace is not merely a heating device; it is a chemical reactor that facilitates a phase change. It transforms the catalyst from a stable, inert precursor (NiO) into a reactive metallic state (Ni⁰) capable of driving the furfural hydrogenation reaction.
The Chemistry of Activation
The Inert Nature of Oxides
Nickel-based catalysts are typically prepared in the form of nickel oxide (NiO).
While NiO is stable and easy to handle during preparation, it possesses no hydrogenation activity. It is chemically unable to interact with furfural to facilitate the necessary molecular changes.
Creating Active Sites
The reduction process is the mechanism used to "switch on" the catalyst.
By exposing the material to high temperatures in a tube furnace, the oxygen in the NiO lattice is removed. This converts the oxide into metallic nickel (Ni⁰). These metallic nanoparticles serve as the active sites required to convert furfural into 2-methylfuran.
The Role of the Reducing Atmosphere
Heat alone is insufficient to activate the catalyst.
The tube furnace allows for the introduction of a specific reducing atmosphere, typically a mixture like 5 vol.% H₂/N₂. The hydrogen gas acts as the chemical agent that physically bonds with the oxygen in the catalyst, removing it as water vapor and leaving behind pure metal.
The Critical Role of Equipment Control
Precision Thermal Treatment
A tube furnace provides the precise thermal environment necessary for this chemical transformation.
It allows operators to control the heating rate and constant temperature duration with high accuracy. This control is vital to ensure the reduction is uniform throughout the catalyst bed without subjecting the material to thermal shock.
Modifying Surface Chemistry
Beyond simple reduction, the tube furnace environment allows for the fine-tuning of the catalyst's surface.
By regulating the gas mixture and temperature, you can facilitate the directional removal of oxygen-containing functional groups. This permits a gradient adjustment of the active sites' chemical properties, optimizing them for the specific demands of the furfural reaction.
Preserving Pore Structure
The controlled environment of the tube furnace protects the physical integrity of the catalyst support.
Unlike uncontrolled heating, which might collapse the material's internal architecture, the tube furnace ensures that the pore structure remains intact during the aggressive chemical changes of reduction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Sintering
While high heat is required for reduction, excessive temperature or duration can be detrimental.
Overheating in the tube furnace can cause the newly formed metallic nanoparticles to clump together, a process known as sintering. This drastically reduces the surface area available for the reaction, lowering the catalyst's overall efficiency.
Balancing Reduction Completeness
There is a delicate balance between achieving full reduction and maintaining particle size.
Insufficient reduction leaves inactive oxide (NiO) behind, resulting in poor conversion rates. Conversely, aggressive reduction conditions often lead to larger metal particles, which may alter the selectivity of the reaction or reduce activity per gram of catalyst.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your furfural hydrogenation reaction is successful, apply the reduction step with the following specific goals in mind:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Activity: Ensure the reduction temperature is high enough and the duration long enough to completely convert all NiO to metallic Ni⁰.
- If your primary focus is Catalyst Longevity: Use a controlled heating rate in the tube furnace to prevent thermal shock and pore collapse, ensuring the physical structure supports the active metal sites.
Ultimately, the tube furnace reduction is the bridge between a chemically inert powder and a highly active catalyst capable of complex organic transformations.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Nickel Oxide (NiO) | Metallic Nickel (Ni⁰) |
|---|---|---|
| State | Precursor (Inert Oxide) | Activated Catalyst |
| Function | Inactive; Storage-stable | High Hydrogenation Activity |
| Active Sites | None | Metallic Nanoparticles |
| Role in Furnace | Raw Material | End Product after Reduction |
| Effect on Furfural | No Reaction | Conversion to 2-methylfuran |
Maximize Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the difference between an inert powder and a high-activity catalyst. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to handle critical reduction atmospheres like H₂/N₂ with absolute safety and precision. Whether you need to preserve delicate pore structures or prevent sintering through exact heating rates, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique furfural hydrogenation needs.
Ready to optimize your activation process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your research.
Visual Guide
References
- Ismaila Mudi, Joseph Wood. A Kinetic Model of Furfural Hydrogenation to 2-Methylfuran on Nanoparticles of Nickel Supported on Sulfuric Acid-Modified Biochar Catalyst. DOI: 10.3390/catal14010054
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a dual-zone tube furnace for APCVD of SnSe2? Master Phase Purity & Stoichiometry
- What role does a tube furnace play in the co-pyrolysis of MIPW and COS? Unlock Precise Thermal Waste Transformation
- What is the primary function of a CVD tube furnace in the preparation of Multi-Layer Graphene? Expert Guide
- What conditions does a tube sintering furnace provide for Ag/YBCO wires? Ensure High Critical Current Density
- What is the primary function of a quartz tube diffusion furnace? Optimize PERT Solar Cell Doping Performance
- How does a Vertical Fluidized Bed Furnace ensure reaction stability? Key Mechanisms for Sulfur Oxidation Experiments
- What are the common applications of alumina tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in Materials Processing
- Why is the heat treatment process using a tube furnace essential in the preparation of Mn7Co3Ce1Ox catalysts?



















