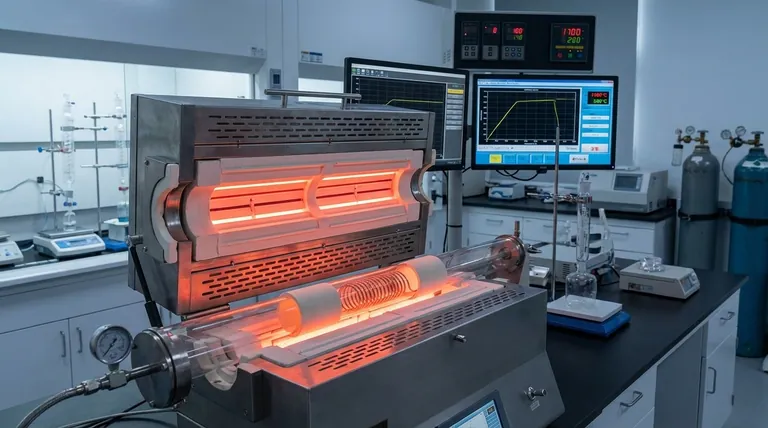
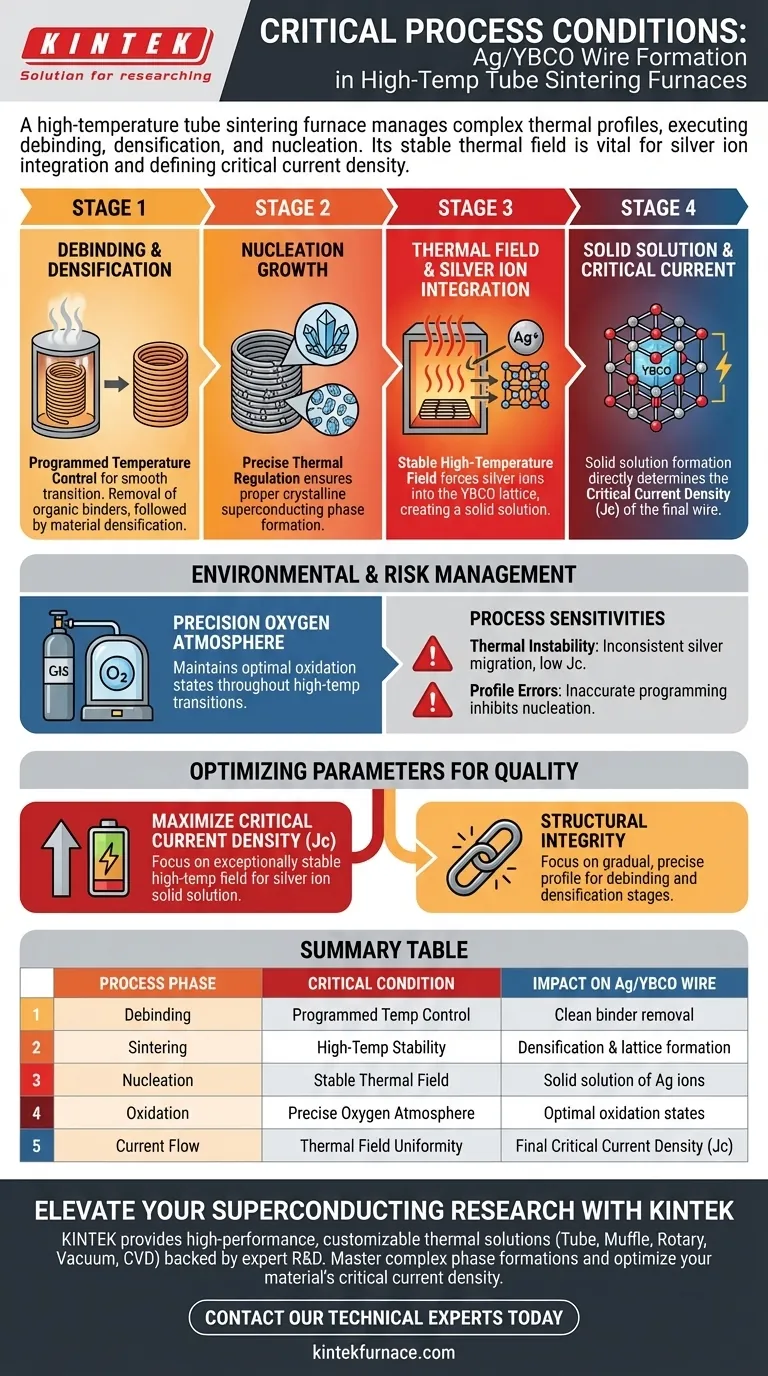
A high-temperature tube sintering furnace provides the precise environmental control required to execute complex heat treatment profiles for Ag/YBCO wires. This equipment manages the critical stages of debinding, densification sintering, and nucleation growth. Most importantly, it generates the stable thermal field necessary for silver ions to integrate into the lattice structure.
The furnace’s primary value lies in its ability to create a stable high-temperature environment that forces silver ions to form a solid solution within the YBCO lattice. This specific microstructural change is the direct determinant of the wire's critical current density.

Orchestrating the Phase Formation
To transform raw materials into a superconductor, the furnace must manage a multi-stage thermal evolution.
Managing Complex Heat Treatment Profiles
The furnace utilizes programmed temperature control to execute intricate heating schedules.
This capability allows the system to seamlessly transition between distinct processing phases without thermal shock.
Enabling Debinding and Densification
The first critical stage handled by the furnace is debinding, where organic binders are removed from the wire matrix.
Following this, the furnace raises temperatures to facilitate densification sintering, compacting the material structure.
Controlling Nucleation Growth
The final phase involves the nucleation growth of the superconducting phase.
precise thermal regulation during this stage is essential to ensure the proper crystalline structure forms throughout the wire.
The Critical Role of the Thermal Field
The furnace does not simply heat the material; it creates a specific thermodynamic environment that alters the wire's chemistry.
Facilitating Silver Ion Integration
The furnace provides a stable high-temperature thermal field.
This stability is physically necessary for silver ions to mobilize and enter the YBCO lattice.
Forming the Solid Solution
Once the silver ions enter the lattice, they form a solid solution.
This chemical integration is vital, as it directly determines the critical current density of the final product.
Environmental Control
Beyond temperature, the chemical atmosphere within the tube is a defining factor in success.
Precision Oxygen Atmosphere
The furnace maintains precise oxygen atmosphere control throughout the sintering process.
This ensures the oxidation state of the materials remains optimal during the high-temperature transitions.
Understanding Process Sensitivities
While the furnace enables these processes, the complexity of the treatment brings inherent risks that must be managed.
The Impact of Thermal Instability
If the thermal field lacks stability, the migration of silver ions into the lattice will be inconsistent.
This failure to form a uniform solid solution will result in wires with unpredictable or low critical current density.
Profile Programming Errors
The heat treatment profiles are described as complex for a reason.
Inaccurate programming during the debinding or densification stages can permanently inhibit the proper nucleation of the superconducting phase.
Optimizing Process Parameters for Wire Quality
Achieving high-performance Ag/YBCO wires requires strictly aligning the furnace's capabilities with the material's chemical requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximizing critical current density: Ensure the furnace maintains an exceptionally stable high-temperature field to maximize the formation of the silver ion solid solution.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Verify that the programmed temperature control offers a gradual and precise profile for the debinding and densification stages.
The high-temperature tube sintering furnace is the decisive tool that governs the microstructural evolution from raw powder to a high-capacity superconductor.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Critical Condition Provided | Impact on Ag/YBCO Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Debinding | Programmed Temp Control | Clean removal of organic binders without damage |
| Sintering | High-Temp Stability | Material densification and lattice formation |
| Nucleation | Stable Thermal Field | Solid solution formation of silver ions in lattice |
| Oxidation | Precise Oxygen Atmosphere | Optimal oxidation states for superconductivity |
| Current Flow | Thermal Field Uniformity | Determines the final Critical Current Density (Jc) |
Elevate Your Superconducting Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when engineering Ag/YBCO wires. KINTEK provides the high-performance thermal solutions required to master complex phase formations. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific sintering profiles and atmospheric requirements.
Ready to optimize your material’s critical current density?
Contact our technical experts today to discuss how our lab high-temp furnaces can bring unmatched stability to your research.
Visual Guide
References
- Xingyi Zhang, Youhe Zhou. Ag/YBCO superconducting round wires fabricated by bimaterial 3D printing. DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-7301425/v1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for long-term heat treatment of FeTeSe crystals? Achieve High Crystallinity & Uniformity
- What is the primary benefit of horizontal tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Thermal Uniformity for Your Materials
- What is the function of a Tube Furnace in the preparation of WSe2 thin films? Master Precise Atomic Deposition
- What role does a tube furnace play in the carbonization of porous carbon? Master Precise Thermal Control
- Why is a tantalum tube encapsulated in a vacuum quartz tube? Prevent Oxidation & Embrittlement in High-Temp Calcination
- What advantages does a continuous flow tube reactor provide for CO2 hydrogenation? Optimize Catalyst Evaluation
- Why are high-temperature tube furnaces essential for perovskite catalysts? Precision Shaping & Crystallization
- What are the limitations of stainless steel tube furnaces? Overcome Temperature and Contamination Issues



















