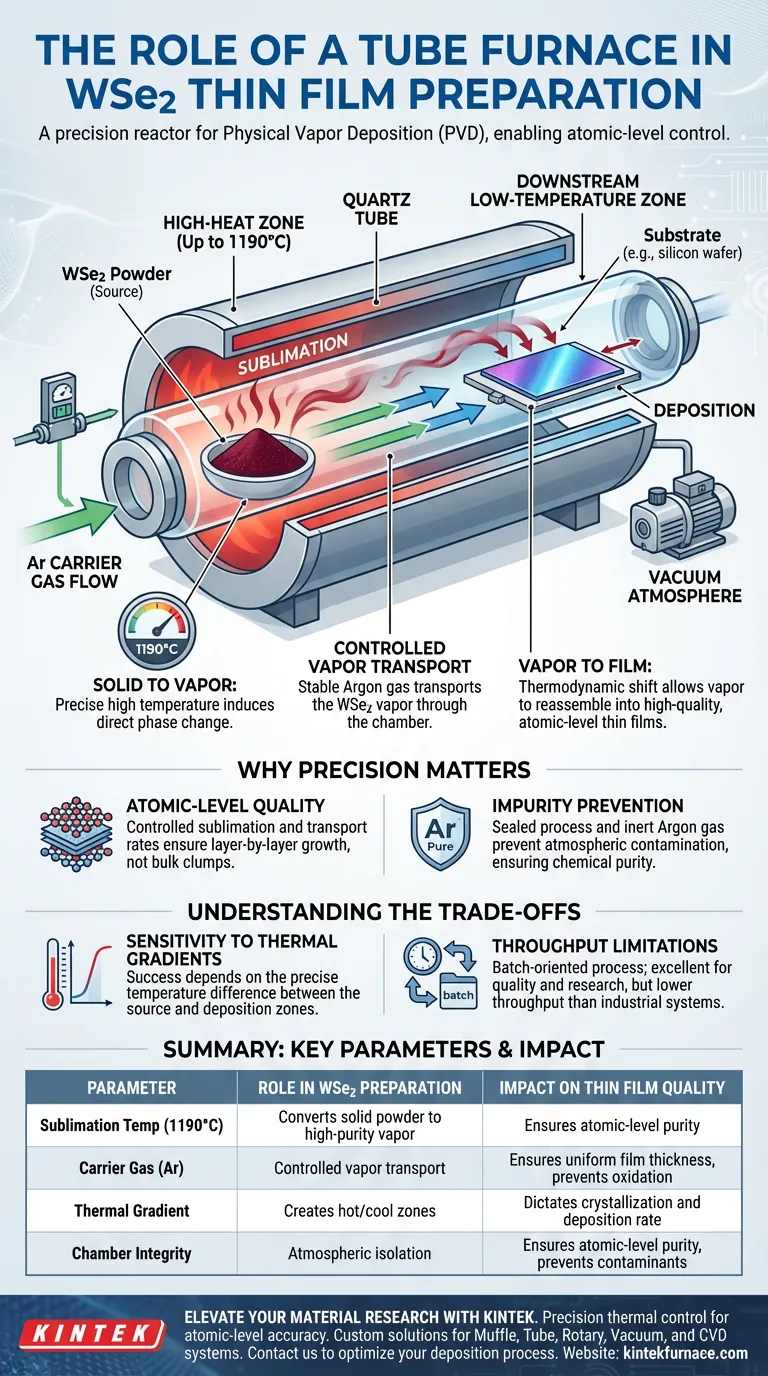
In the preparation of Tungsten Diselenide (WSe2) thin films, the Tube Furnace serves as the critical reaction chamber for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). It provides a precise high-temperature environment, reaching up to 1190°C, to facilitate the sublimation of WSe2 powder. By combining this intense heat with a stable argon carrier gas, the furnace enables the transport of vaporized material to a substrate for controlled growth.
The tube furnace functions as a precision engine for phase change and transport. It converts solid source powder into a gas in a high-heat zone and guides it to a cooler downstream zone, allowing the material to reassemble into high-quality, atomic-level thin films.

The Mechanics of WSe2 Film Growth
To understand the function of the tube furnace, one must look beyond simple heating. It acts as a flow reactor that manages temperature gradients and gas dynamics to achieve atomic precision.
Facilitating Sublimation
The primary role of the furnace is to induce sublimation. WSe2 powder is placed in the central heating zone.
The furnace ramps the temperature up to 1190°C. At this specific thermal point, the solid powder transitions directly into a gas phase, creating the "source vapor" required for deposition.
Controlled Vapor Transport
Once the material is vaporized, it must be moved. The tube furnace utilizes a precise control system to maintain a stable flow of argon carrier gas.
This inert gas picks up the WSe2 vapor and transports it through the tube. The stability of this flow is crucial; turbulence or fluctuation here would result in uneven film thickness.
Downstream Deposition
The actual film formation does not happen in the hottest zone. The furnace is designed to create a downstream low-temperature zone.
As the argon carries the hot vapor into this cooler region, the thermodynamic conditions change. The WSe2 vapor creates a deposit on the target substrate, organizing itself into high-quality, atomic-level thin films.
Why Precision Matters
The difference between a usable semiconductor film and a failed experiment often lies in the furnace's ability to maintain strict environmental controls.
Atomic-Level Quality
The goal of using a tube furnace in PVD is to achieve atomic-level thickness.
By strictly controlling the sublimation rate (via temperature) and the transport rate (via gas flow), the furnace ensures the film grows layer by layer rather than as bulk clumps.
Impurity Prevention
While the primary focus is temperature, the tube furnace also acts as an isolation chamber.
By sealing the process and using an inert carrier gas like argon, the furnace prevents atmospheric contaminants from interacting with the reactive WSe2 vapor. This ensures the resulting film is chemically pure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace is an effective tool for PVD, the process relies heavily on the exact calibration of variables.
Sensitivity to Thermal Gradients
The success of the deposition depends entirely on the temperature difference between the source zone and the deposition zone.
If the downstream zone is too hot, the material will not deposit; if it is too cold, the crystalline structure may form poorly. The furnace creates the gradient, but the user must define the profile perfectly.
Throughput Limitations
Tube furnaces are excellent for high-precision, research-grade materials, but they generally offer lower throughput compared to industrial-scale deposition systems.
The process is batch-oriented. It requires time to ramp up to 1190°C, stabilize, deposit, and cool down, making it ideal for quality over quantity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a tube furnace for WSe2 preparation, your specific research objectives should dictate your parameters.
- If your primary focus is Film Purity: Prioritize the integrity of the vacuum seals and the purity of the Argon gas source to prevent oxidation during the high-temperature phase.
- If your primary focus is Thickness Control: Focus on the precise calibration of the gas flow rate, as this governs how much material is delivered to the substrate over time.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is not just a heater, but a precise instrument for manipulating the thermodynamics of phase change to build materials atom by atom.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in WSe2 Preparation | Impact on Thin Film Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Sublimation Temp | Reaches up to 1190°C | Converts solid powder to high-purity vapor |
| Carrier Gas (Ar) | Controlled vapor transport | Ensures uniform film thickness and prevents oxidation |
| Thermal Gradient | Creates hot/cool zones | Dictates the crystallization and deposition rate |
| Chamber Integrity | Atmospheric isolation | Ensures atomic-level purity and prevents contaminants |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of high-quality WSe2 thin film growth. At KINTEK, we understand that atomic-level accuracy requires superior thermal control. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements.
Whether you are focusing on film purity or thickness control, our high-temperature solutions provide the stability and precision your research demands. Contact us today to optimize your deposition process.
Visual Guide
References
- Chuanwen Chen, Ping Chen. X-Ray Irradiation Improved WSe2 Optical–Electrical Synapse for Handwritten Digit Recognition. DOI: 10.3390/nano15181408
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the controlled atmosphere capabilities of a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Gas Control for Your Lab
- Why is high-precision temperature control in a tube furnace critical for rhenium catalysts? Ensure Optimal Alumina Calcination
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for PCN exfoliation? Unlock Superior 2D Nanosheet Catalysis
- How does a tube furnace convert energy to achieve heating? Master Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What are the primary applications of lab tubular furnaces in material science and engineering? Precision Heat for Advanced Materials
- What auxiliary functions does a tube preheating furnace perform in flash sintering? Master Environmental Control
- Why is a tube furnace equipped with an ammonia flow control system necessary for GaN nanopowder synthesis?
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in NC framework preparation? Master Precision Carbonization



















