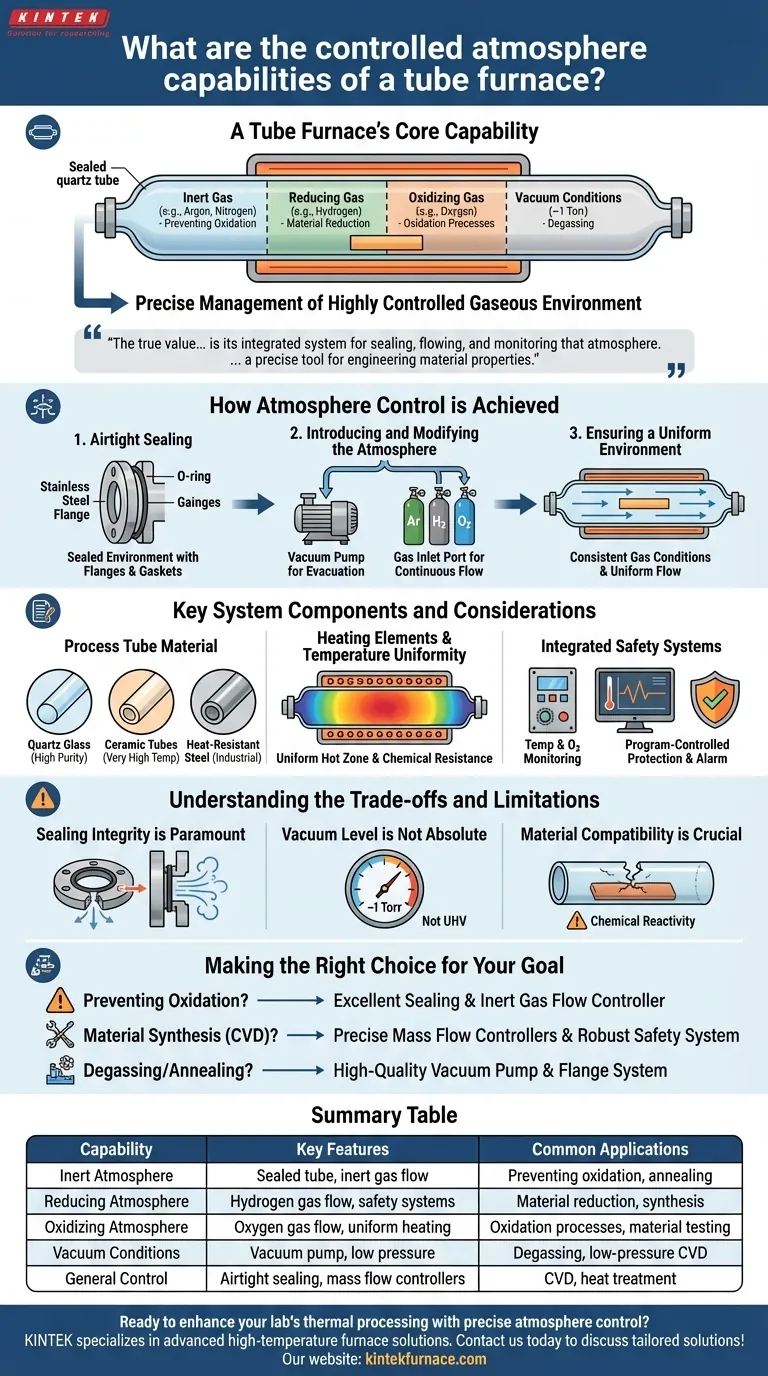
A tube furnace's core capability is its ability to create and maintain a highly controlled gaseous environment during thermal processing. Unlike open-air muffle furnaces, it uses a sealed tube to precisely manage the atmosphere, allowing for operations under inert, reducing, or oxidizing gases, as well as under vacuum conditions.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to introduce a gas, but its integrated system for sealing, flowing, and monitoring that atmosphere. This system transforms it from a simple heater into a precise tool for engineering material properties.
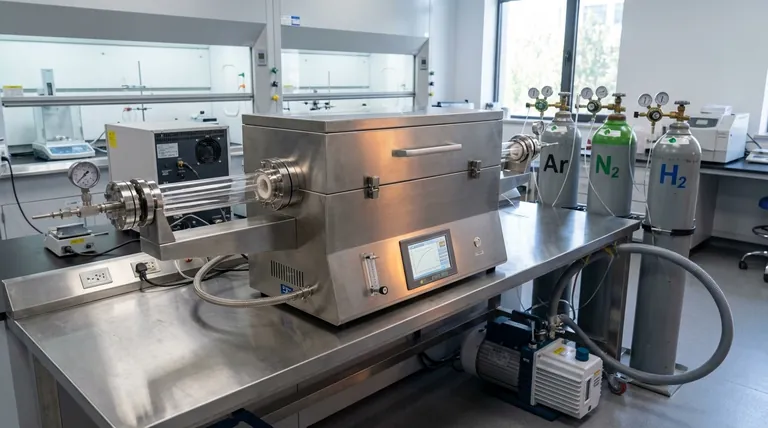

How Atmosphere Control is Achieved
A controlled atmosphere doesn't happen by chance. It is the result of a coordinated system where each component plays a critical role in isolating the sample from unwanted environmental factors.
The Foundation: Airtight Sealing
The entire system relies on creating a sealed environment. This is typically achieved with stainless steel sealing flanges that are clamped onto both ends of the furnace tube.
These flanges contain O-rings or other gaskets to form an airtight seal, preventing external air from leaking in and contaminating the internal atmosphere.
Introducing and Modifying the Atmosphere
Once sealed, the atmosphere can be modified in two primary ways.
First, a vacuum pump can be connected to a port on the flange to evacuate the existing air. This is essential for processes requiring low-pressure environments and for purging the tube before introducing a different gas.
Second, a specific gas or gas mixture is introduced through a dedicated inlet port. This allows for a continuous flow of an inert gas like argon, a reducing gas like hydrogen, or an oxidizing gas like oxygen.
Ensuring a Uniform Environment
Effective control requires more than just introducing a gas. The system is designed to ensure uniform atmosphere flow throughout the length of the tube.
This consistency ensures that the entire sample is exposed to the same gas conditions, which is crucial for achieving repeatable and predictable results in processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Key System Components and Considerations
The capabilities of a tube furnace are defined by the quality and compatibility of its core components.
The Process Tube Material
The tube itself is the heart of the furnace. The material choice is dictated by the maximum temperature and the chemical reactivity of your process.
Common materials include quartz glass for its high purity and visibility, ceramic tubes (like alumina) for very high temperatures, and heat-resistant steel for certain industrial applications.
Heating Elements and Temperature Uniformity
The heating elements are designed to not only reach high temperatures but also to withstand the specific chemical atmosphere inside the tube without degrading.
The furnace's design ensures a uniform hot zone, providing stable and consistent temperature distribution across the sample.
Integrated Safety Systems
Handling reactive or flammable gases like hydrogen requires robust safety features.
Modern furnaces include a program-controlled protection system that monitors critical parameters like furnace temperature and internal oxygen content. If an abnormality is detected, the system can trigger an alarm or initiate an automatic shutdown to protect the operator, the sample, and the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a tube furnace's effectiveness depends on understanding its operational boundaries.
Sealing Integrity is Paramount
The single most common point of failure is an imperfect seal. A small leak in a flange gasket can introduce oxygen and nitrogen, completely compromising a process that requires an inert or vacuum environment.
Vacuum Level is Not Absolute
A standard tube furnace can typically achieve a low vacuum, often around 1 Torr. This is suitable for many degassing and low-pressure processes but is not an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) system.
Material Compatibility is Crucial
You must ensure that your sample, the process gas, and the furnace tube material are all chemically compatible at your target temperature. Certain reactive gases can etch a quartz tube or react with a ceramic one, leading to equipment failure and sample contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your furnace configuration based on the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation: You need a system with excellent sealing integrity and a reliable inert gas (Argon or Nitrogen) flow controller.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis (like CVD): You need precise mass flow controllers for precursor gases and a robust safety system for handling potentially hazardous materials.
- If your primary focus is degassing or annealing under vacuum: You need a high-quality vacuum pump and flange system capable of reaching and holding your target pressure.
By understanding these components, you can configure a tube furnace to create the precise, repeatable atmosphere your process demands.
Summary Table:
| Capability | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Sealed tube, inert gas flow (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) | Preventing oxidation, annealing |
| Reducing Atmosphere | Hydrogen gas flow, safety systems | Material reduction, synthesis |
| Oxidizing Atmosphere | Oxygen gas flow, uniform heating | Oxidation processes, material testing |
| Vacuum Conditions | Vacuum pump, low pressure (~1 Torr) | Degassing, low-pressure CVD |
| General Control | Airtight sealing, mass flow controllers, temperature uniformity | Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), heat treatment |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with precise atmosphere control? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can improve your material synthesis, oxidation prevention, and more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















