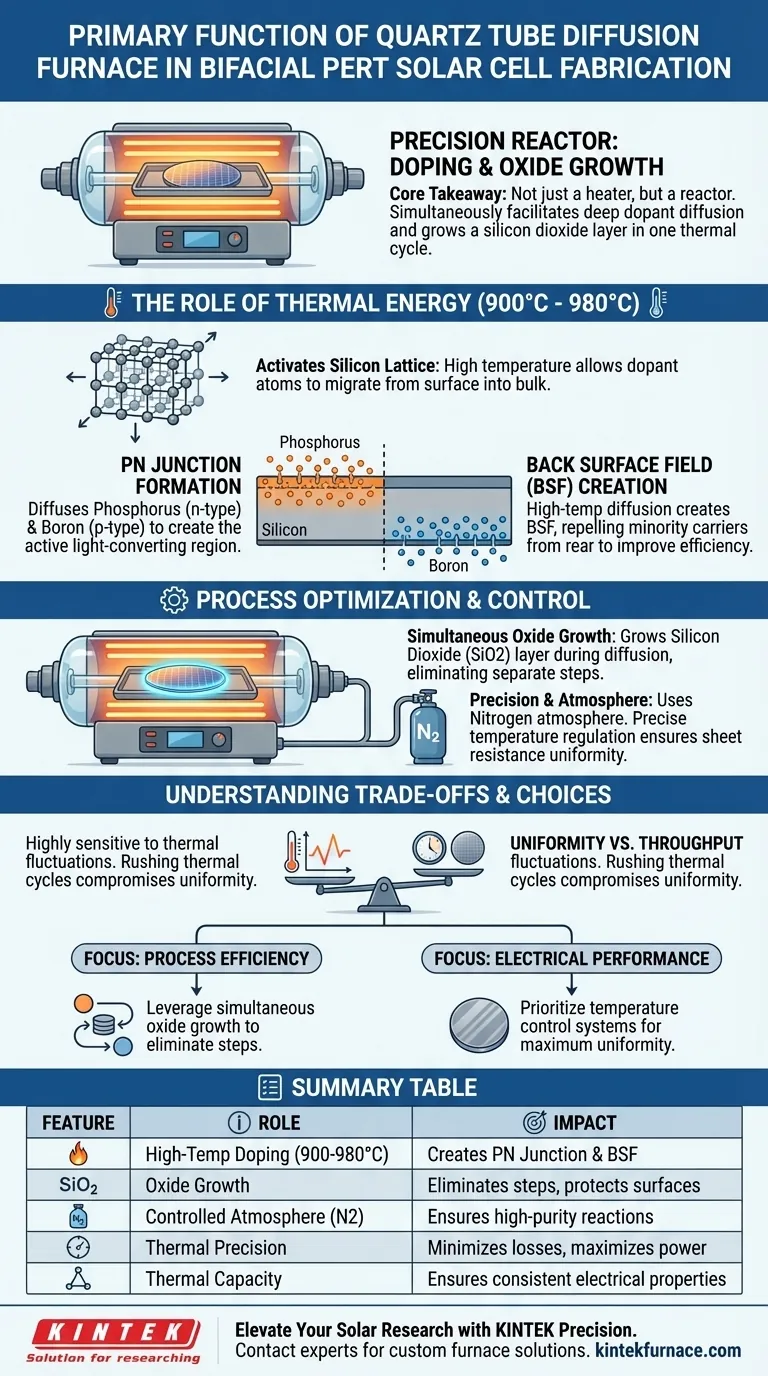
The primary function of a quartz tube diffusion furnace is to provide a strictly controlled high-temperature environment that drives the doping process essential for solar cell operation. Specifically, for bifacial PERT cells, it facilitates the diffusion of boron and phosphorus into the silicon lattice at temperatures between 900°C and 980°C, creating the PN junction and the back surface field.
Core Takeaway The quartz tube furnace is not merely a heater; it is a precision reactor. Its critical value lies in simultaneously facilitating deep dopant diffusion for electrical activation and growing a silicon dioxide layer, thereby combining two essential manufacturing steps into a single thermal cycle.

The Role of Thermal Energy in Doping
Activating the Silicon Lattice
To alter the electrical properties of a silicon wafer, dopant atoms must physically move into the crystal structure.
The quartz tube furnace generates the necessary thermal energy, typically maintaining a range of 900°C to 980°C.
At these temperatures, the silicon lattice expands sufficiently to allow foreign atoms to migrate from the surface into the bulk of the material.
Formation of the PN Junction
In bifacial PERT (Passivated Emitter and Rear Totally Diffused) cells, specific regions require different electrical characteristics.
The furnace is used to diffuse phosphorus (typically for the n-type region) and boron (for the p-type region).
This diffusion creates the PN junction, which is the active region where light is converted into electricity.
Creating the Back Surface Field
Beyond the primary junction, the furnace plays a critical role in treating the rear of the cell.
High-temperature diffusion is used to create the Back Surface Field (BSF).
The BSF is crucial for bifacial cells as it repels minority carriers from the rear surface, significantly reducing recombination losses and improving efficiency.
Process Optimization and Control
Simultaneous Oxide Growth
A distinct advantage of the quartz tube diffusion process is its ability to multitask.
During the thermal diffusion step, the environment supports the growth of a silicon dioxide (SiO2) layer.
This eliminates the need for a separate oxidation step, optimizing the overall manufacturing workflow and reducing cycle time.
Precision and Atmosphere
The furnace often operates with a nitrogen atmosphere to manage the chemical environment during boron migration.
Precise regulation of the temperature profile is the deciding factor for quality.
The furnace's ability to hold a steady temperature determines the sheet resistance uniformity across the wafer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Sensitivity of Doping Depth
While the furnace enables deep diffusion, the depth is highly sensitive to thermal fluctuations.
If the temperature deviates even slightly from the target (e.g., 970°C), the doping depth of the emitter will change.
Inconsistent doping depth leads to mismatched electrical properties, reducing the final efficiency of the solar module.
Uniformity vs. Throughput
Achieving perfect sheet resistance uniformity requires rigorous temperature stabilization.
This creates a trade-off between processing speed and quality control.
Rushing the thermal ramp-up or cool-down phases to increase throughput can compromise the uniformity of the diffusion layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The configuration of your diffusion process depends heavily on your specific manufacturing priorities.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Leverage the furnace's ability to grow the silicon dioxide layer simultaneously with doping to eliminate redundant oxidation steps.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Performance: Prioritize the furnace's temperature control systems to ensure maximum uniformity in sheet resistance and doping depth.
Success in PERT cell fabrication relies less on the peak temperature reached, and more on the stability and precision of the thermal environment provided by the furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in PERT Solar Cell Fabrication | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Doping | Facilitates Boron & Phosphorus migration (900°C–980°C) | Creates active PN junction & Back Surface Field |
| Oxide Growth | Simultaneously grows Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) layer | Eliminates separate steps & protects surfaces |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Uses Nitrogen environment for boron migration | Ensures high-purity chemical reactions |
| Thermal Precision | Regulates sheet resistance uniformity | Minimizes recombination losses & maximizes power |
| Thermal Capacity | Manages doping depth sensitivity | Ensures consistent electrical properties across wafers |
Elevate Your Solar Research with KINTEK Precision
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of PERT solar cell fabrication. Whether you need precise thermal profiles for sheet resistance uniformity or customizable systems for unique doping requirements, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the stability your process demands.
Maximize your manufacturing efficiency today. Contact our experts for a custom furnace solution and experience the KINTEK advantage in thermal engineering.
Visual Guide
References
- Thais Crestani, João Victor Zanatta Britto. Optimization of the Boron Back Surface Field Produced with Reduced Thermal Steps in Bifacial PERT Solar Cell. DOI: 10.3390/en18092347
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for NiWO4 calcination? Achieving High-Performance Cathode Materials
- What are the current market trends for 70mm tube furnaces? Discover Key Drivers in Automation and High-Tech Applications
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature vacuum tube furnace for Gr-NDs? Mastering Carbon Phase Transitions
- How do tube furnaces contribute to energy efficiency? Boost Your Lab's Performance with Advanced Thermal Solutions
- What safety precautions should be taken when using a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Essential Tips for Safe Operation
- Why is a high-temperature tubular furnace required for the activation process of walnut shell activated carbon at 700°C?
- What are the technical requirements for a Tube Furnace in nitrogen-doping? Essential Specs for Metal Oxide Processing
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the sintering process of modified graphite felt? Precision Control



















