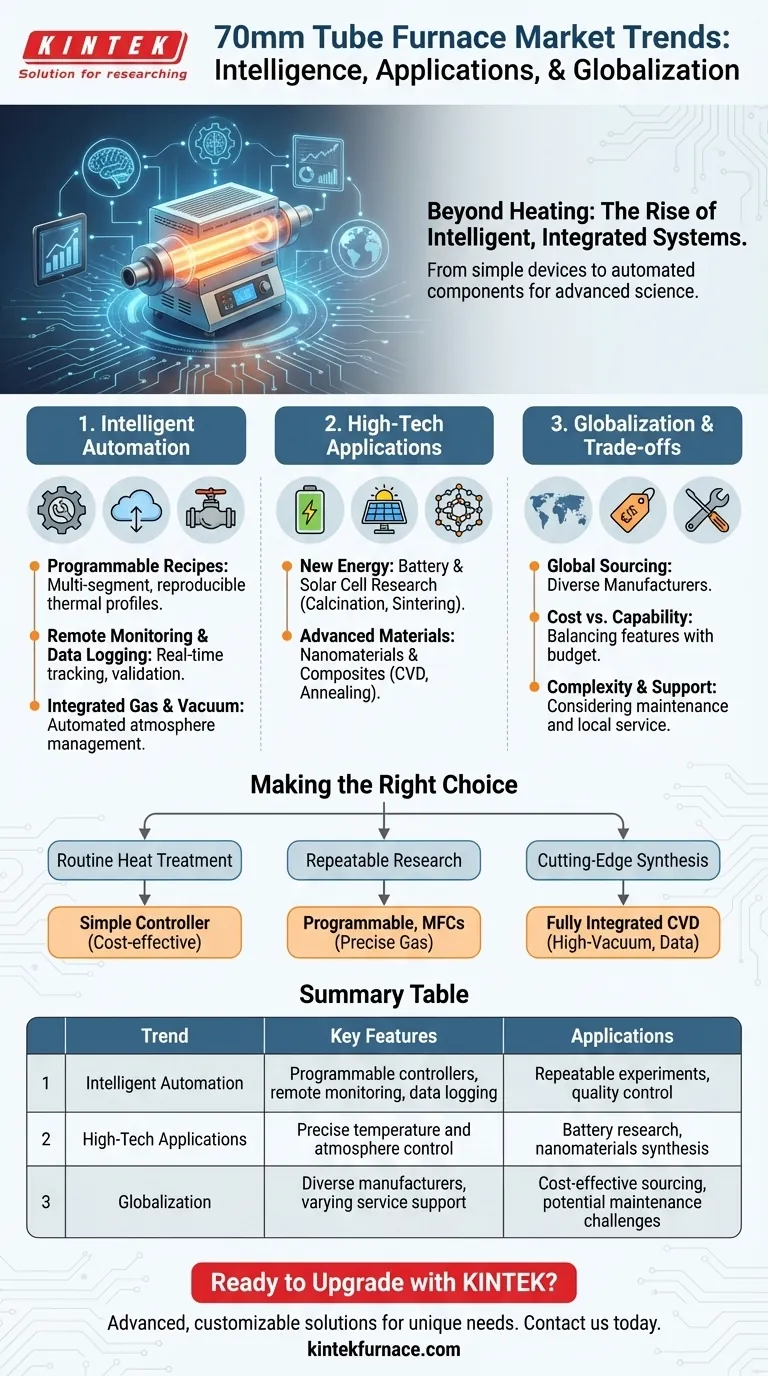
In short, the market for 70mm tube furnaces is driven by three primary trends: a push towards greater intelligence and automation, expansion into new high-tech applications like new energy and materials, and the increasing globalization of manufacturers. These factors are transforming the furnace from a simple heating device into an integrated component of a sophisticated research or production system.
The core takeaway is that selecting a modern 70mm tube furnace is no longer just about temperature and tube size. The decision now hinges on its ability to automate processes, control atmospheres with precision, and integrate into a digital data workflow, reflecting its growing role in advanced materials science and energy research.

The Shift Towards Intelligent and Automated Systems
The most significant trend is the move away from manual operation towards fully automated systems. This enhances repeatability, reduces operator error, and enables more complex thermal processing.
From Manual Control to Programmable Recipes
Older furnaces relied on simple controllers to hold a single temperature. Modern systems feature multi-segment programmable controllers that allow users to define complex thermal profiles with multiple heating, dwelling, and cooling steps.
These "recipes" can be saved and recalled, ensuring that every batch or experiment is run under identical conditions, which is critical for both quality control in production and validity in research.
The Rise of Remote Monitoring and Data Logging
Connectivity is now a key feature. Many furnaces can be connected to a PC or a network, allowing for remote operation and real-time monitoring.
This is coupled with automated data logging, which records the entire temperature profile and system parameters. This digital record is indispensable for process validation, troubleshooting, and meeting quality standards like ISO 9001.
Integration with Gas and Vacuum Systems
A 70mm tube furnace is rarely used in isolation. The trend is toward integrated systems where the furnace controller also manages the process atmosphere.
This includes automated control of gas flow rates via mass flow controllers (MFCs), switching between different gases, and managing vacuum levels. The entire process—from purging with inert gas to heating and cooling under vacuum—can be executed as a single, automated program.
Expanding Applications in Advanced Materials
The capabilities of modern furnaces are being driven by the demanding requirements of new research fields. The 70mm diameter is particularly well-suited for lab-scale and pilot-scale development of these next-generation materials.
New Energy: Battery and Solar Cell Research
Tube furnaces are crucial for developing materials for lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries, and perovskite solar cells.
Processes like the calcination and sintering of cathode and anode powders require extremely precise temperature uniformity and atmospheric control (e.g., argon or nitrogen) to achieve the desired material properties, and 70mm tubes provide a practical volume for this work.
Advanced Materials: Nanomaterials and Composites
The synthesis of materials like graphene, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) often relies on chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or high-temperature annealing.
The precise control over temperature, pressure, and precursor gases offered by modern tube furnaces is essential for controlling the growth and structure of these nanoscale materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While new features are compelling, they introduce new complexities and costs. An objective assessment requires weighing these trade-offs.
Cost vs. Capability
A basic, air-atmosphere tube furnace with a simple controller is a relatively low-cost investment. Each additional feature—programmable control, gas mixing, vacuum capability, advanced data logging—adds significant cost.
It is critical to align the investment with the actual application's needs to avoid overspending on features that will not be used.
Complexity and Maintenance
A fully automated system with integrated vacuum and gas handling is far more complex than a standalone furnace. This increases the learning curve for operators and introduces more potential points of failure.
Maintenance becomes more involved, requiring knowledge of vacuum pumps, seals, and electronic controllers. The reliability of these integrated components is a key factor in the total cost of ownership.
Service and Support
The trend of internationalization means you can source a furnace from anywhere in the world. However, this introduces a critical risk: service and support.
Purchasing a furnace from a manufacturer without strong, local technical support can lead to significant downtime and frustration when service, spare parts, or operational advice is needed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is routine heat treatment in air: A reliable furnace from a reputable brand with a simple, single-setpoint controller is sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is repeatable research with controlled atmospheres: Prioritize a system with a multi-segment programmable controller and integrated mass flow controllers for precise gas management.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge materials synthesis (e.g., CVD): Look for a fully integrated system with high-vacuum capability, extensive data logging, and software that allows for complete process automation.
Ultimately, the goal is to select a tool that not only meets your immediate needs but also empowers your future work.
Summary Table:
| Trend | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Automation | Programmable controllers, remote monitoring, data logging | Repeatable experiments, quality control |
| High-Tech Applications | Precise temperature and atmosphere control | Battery research, nanomaterials synthesis |
| Globalization | Diverse manufacturers, varying service support | Cost-effective sourcing, potential maintenance challenges |
Ready to upgrade your lab with a high-performance 70mm tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and precision. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can empower your research and production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















