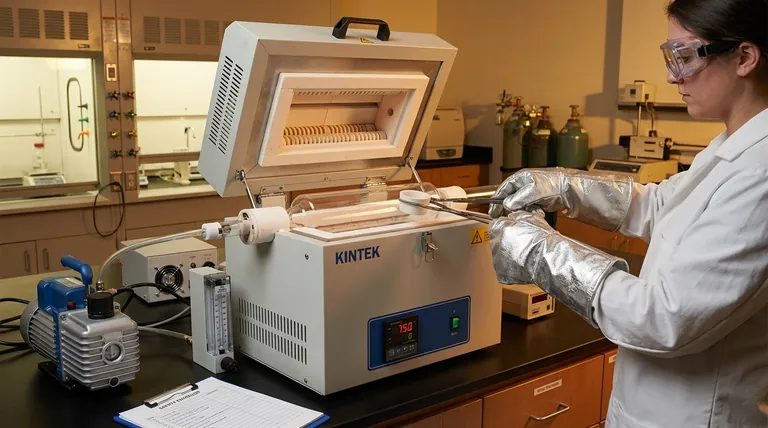
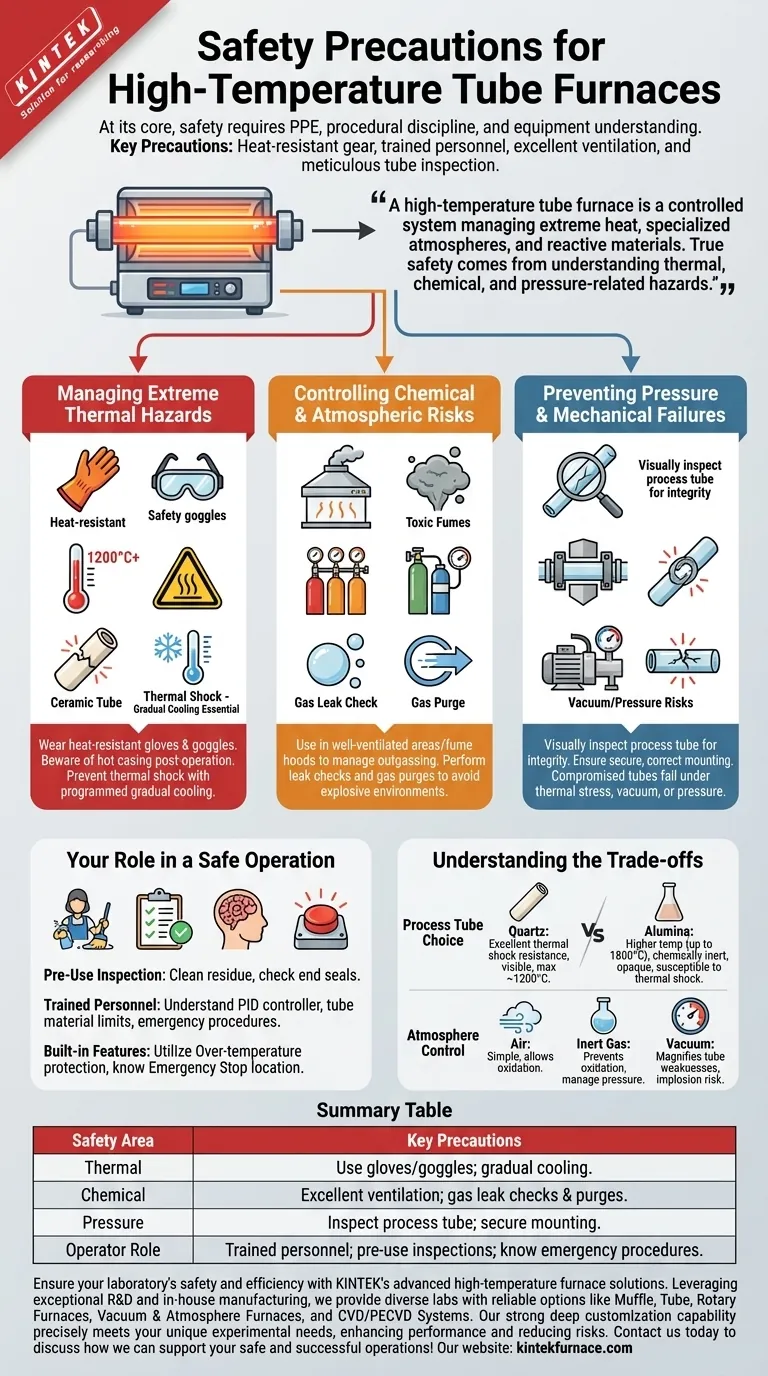
At its core, ensuring safety with a high-temperature tube furnace requires a combination of personal protective equipment, procedural discipline, and a thorough understanding of the equipment. Key precautions include using heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles, restricting operation to trained personnel only, ensuring excellent ventilation, and meticulously inspecting the furnace and process tube for integrity before every use.
A high-temperature tube furnace is not just a hot box; it is a controlled system managing extreme heat, specialized atmospheres, and potentially reactive materials. True safety comes from understanding and mitigating the three primary risks: thermal, chemical, and pressure-related hazards.

The Three Pillars of Furnace Safety
Safe operation is not a checklist, but a mindset built on understanding the fundamental risks. Every safety procedure is designed to address one or more of these core hazards.
Managing Extreme Thermal Hazards
The most obvious danger is the intense heat, which can exceed 1200°C or higher. This heat poses a burn risk not just during operation, but long after the power is off.
Proper management includes wearing heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles at all times when loading or unloading the furnace. The furnace casing itself becomes extremely hot and should not be touched without protection.
A critical, often overlooked risk is thermal shock. Rapidly cooling a hot ceramic or quartz process tube can cause it to crack or shatter violently. Always follow programmed, gradual cooling cycles to prevent this.
Controlling Chemical and Atmospheric Risks
Tube furnaces are often used to create specific chemical reactions or process materials in a controlled atmosphere. This introduces chemical hazards.
Heating certain materials can cause outgassing, releasing moisture or volatile, potentially toxic, or flammable fumes. This is why operating in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood is non-negotiable.
If using process gases (like argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen), a leak can displace oxygen or create an explosive environment. Always perform a leak check on gas lines before heating and use the gas purge function to ensure the tube is filled with the desired atmosphere.
Preventing Pressure and Mechanical Failures
The process tube is the heart of the furnace and its most fragile component. Its failure is a primary safety incident.
Before every run, visually inspect the process tube for any cracks, chips, or cloudiness. A compromised tube can fail under thermal stress, vacuum (implosion), or slight positive pressure from gas flow (explosion).
Ensure the tube is securely and correctly mounted. An improperly seated tube can shift or crack during heating, compromising the entire process and creating a significant hazard.
Your Role in a Safe Operation
Built-in safety features are essential, but the operator is the most critical safety component. Your knowledge and diligence are what prevent accidents.
The Importance of Pre-Use Inspection
Before powering on the furnace, perform a routine check. This includes cleaning any residue from the process tube and furnace interior, which could cause unwanted reactions when heated.
Confirm that end seals and gaskets are in good condition to prevent leaks when using a vacuum or a controlled gas atmosphere.
Why "Trained Personnel" is a Critical Requirement
Training goes beyond reading the manual. A qualified operator understands the furnace's specific PID controller, knows the thermal limits of different tube materials (e.g., quartz vs. alumina), and is prepared to execute emergency shut-off procedures.
They also understand the specific materials being processed and the potential hazards associated with them at high temperatures.
Leveraging Built-in Safety Features
Modern furnaces include crucial safety interlocks. Over-temperature protection prevents the furnace from exceeding a set maximum temperature, protecting both the heating elements and your sample.
Familiarize yourself with the location and function of the emergency stop button or main power disconnect. In the event of an unexpected reaction or equipment malfunction, this is your first line of defense.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Your choice of components has a direct impact on safety and operational success. Understanding these trade-offs is the mark of an expert user.
The Critical Choice of Process Tube
The material of your process tube is a primary consideration. Quartz tubes offer excellent thermal shock resistance and visibility but typically have a lower maximum operating temperature (around 1200°C).
Alumina tubes can withstand much higher temperatures (up to 1800°C) and are more chemically inert, but they are opaque and more susceptible to cracking from rapid temperature changes. Choosing the wrong tube for your temperature or material can lead to catastrophic failure.
The Impact of Atmosphere Control
Processing in air is the simplest method but allows for oxidation. Using an inert gas like argon prevents oxidation but requires careful management of gas lines and flow rates to avoid over-pressurizing the tube.
Applying a vacuum creates its own risks. Any weakness in the process tube is magnified under vacuum, increasing the chance of an implosion. Always use a vacuum-rated tube and check for damage before every run.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific safety focus will shift depending on the nature of your work.
- If your primary focus is simple air-atmosphere annealing: Your main concern is thermal safety, so prioritize PPE and preventing thermal shock to the tube during cooling.
- If your primary focus is processing with inert or reactive gases: You must prioritize leak-free connections, proper purging procedures, and robust ventilation in addition to thermal safety.
- If your primary focus is working under vacuum: Your most critical step is the meticulous inspection of the process tube for any micro-cracks or defects that could lead to an implosion.
Ultimately, a safe process is a successful process, ensuring the integrity of your results and the well-being of your team.
Summary Table:
| Safety Area | Key Precautions |
|---|---|
| Thermal Hazards | Use heat-resistant gloves and goggles; prevent thermal shock with gradual cooling. |
| Chemical Hazards | Ensure excellent ventilation; perform gas leak checks and purges. |
| Pressure Hazards | Inspect process tube for cracks; secure mounting to avoid failures. |
| Operator Role | Restrict to trained personnel; conduct pre-use inspections; know emergency procedures. |
Ensure your laboratory's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and reducing risks. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your safe and successful operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















