In short, modern tube furnaces achieve high energy efficiency through a combination of superior insulation, intelligent control systems, and process-specific designs that minimize heat loss and optimize energy consumption. These features work together to reduce operational costs and environmental impact while delivering precise, repeatable thermal processing.
The core challenge in any high-temperature process is containing and directing energy precisely where it's needed. Modern tube furnaces excel not by using a single trick, but by integrating a suite of technologies—from advanced materials to smart software—that systematically eliminate waste at every stage of the heating cycle.
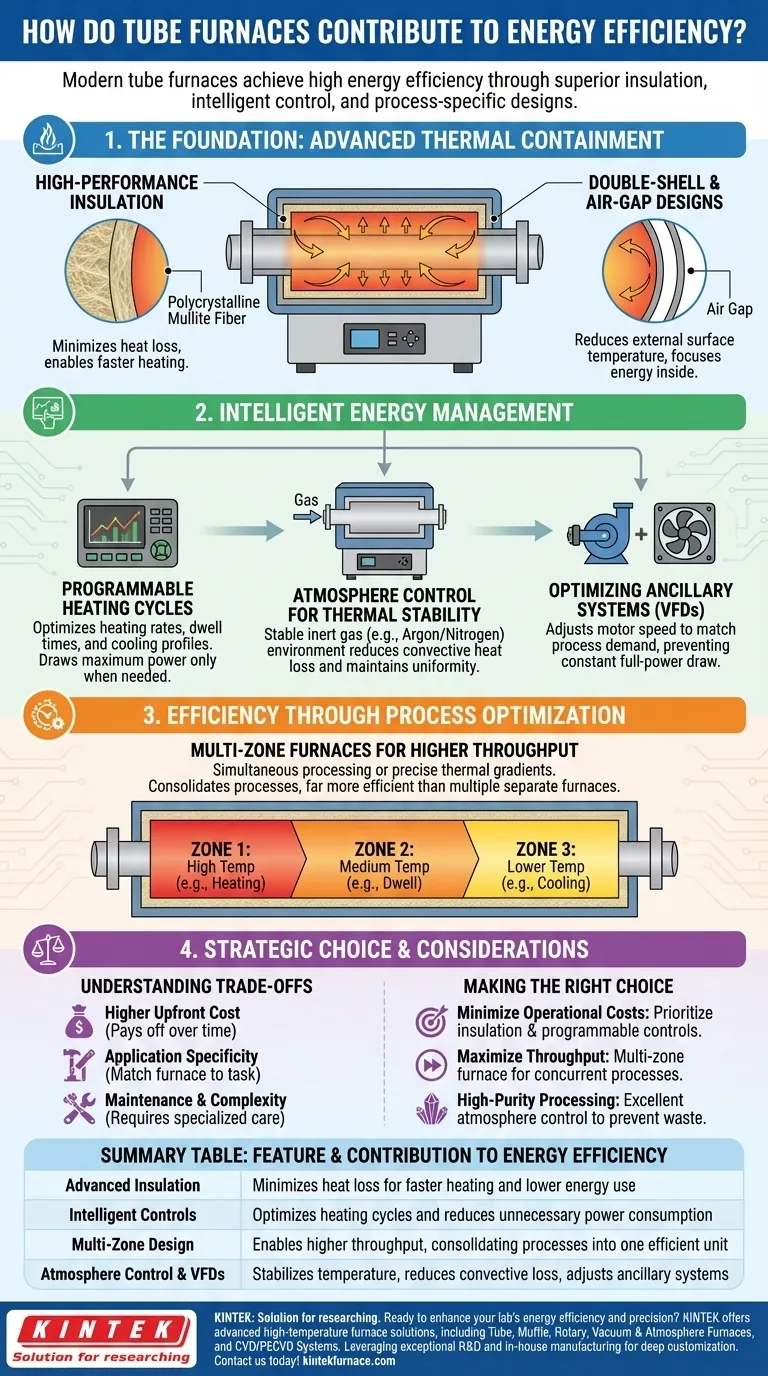
The Foundation: Advanced Thermal Containment
A furnace's primary efficiency metric is its ability to keep heat inside. Modern tube furnaces employ several mechanisms to achieve exceptional thermal containment.
High-Performance Insulation
The first line of defense against heat loss is insulation. Many high-performance furnaces use materials like high-quality polycrystalline mullite fiber.
This advanced insulation enables very fast heating rates because less energy is wasted seeping into the furnace body, allowing more of it to heat the chamber directly.
Double-Shell and Air-Gap Designs
To further enhance this effect, many furnaces feature a double-layer shell. This design creates an air gap between the inner and outer furnace walls.
This gap acts as an additional layer of insulation, significantly reducing the external surface temperature and keeping thermal energy focused within the processing tube.
Intelligent Energy Management
Containing heat is only half the battle; using it wisely is just as critical. Intelligent controls ensure no energy is wasted during the process.
Programmable Heating Cycles
Programmable controllers are the brains of an efficient furnace. They allow users to define precise heating rates, dwell times, and cooling profiles.
This optimization ensures the furnace only draws maximum power when necessary and can ramp down to conserve energy, eliminating the waste associated with simple on/off systems.
Atmosphere Control for Thermal Stability
In atmosphere furnaces, a controlled environment using inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) does more than just prevent oxidation.
This stable gas atmosphere also helps to reduce convective heat loss from the sample, ensuring uniform temperature and minimizing the energy required to maintain it. The control system automatically adjusts parameters to maintain these optimal conditions, using energy only as needed.
Optimizing Ancillary Systems
Efficiency extends beyond the heating elements. Advanced systems may incorporate variable frequency drives (VFDs) for pumps and fans.
VFDs adjust the motor speed of these components to match the exact demand of the process, preventing the constant energy draw of running them at full power unnecessarily.
Efficiency Through Process Optimization
Tube furnaces also deliver efficiency by improving the workflow itself, allowing you to achieve more with less energy and time.
Multi-Zone Furnaces for Higher Throughput
A three-zone tube furnace can maintain different temperature profiles across its length.
This allows for simultaneous processing of multiple samples under varied conditions or for creating a precise thermal gradient for specialized applications like chemical vapor deposition. This consolidation into one machine is far more efficient than running multiple separate furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, these advanced features come with considerations that every user must weigh.
Higher Upfront Cost
Features like multi-zone controls, advanced insulation, and VFDs increase the initial purchase price of the furnace. This investment is typically recouped over time through lower operational costs.
Application Specificity
The most efficient furnace is one that is correctly matched to its task. A complex, multi-zone atmosphere furnace is an inefficient choice for a simple air-based annealing process that a more basic model could handle.
Maintenance and Complexity
More sophisticated systems, especially those with advanced controllers and gas-handling equipment, may require more specialized maintenance and operator training compared to simpler, less efficient models.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace requires aligning its features with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: Prioritize models with the highest quality insulation and a precision programmable controller.
- If your primary focus is maximizing experimental throughput: A multi-zone furnace is the most energy-efficient choice for running multiple processes concurrently.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing: Invest in a furnace with excellent atmosphere control to prevent product loss and reduce heat waste.
Ultimately, choosing an energy-efficient tube furnace is a strategic decision that pays dividends in cost, performance, and sustainability.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Contribution to Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Advanced Insulation | Minimizes heat loss for faster heating and lower energy use |
| Intelligent Controls | Optimizes heating cycles and reduces unnecessary power consumption |
| Multi-Zone Design | Enables higher throughput, consolidating processes into one efficient unit |
| Atmosphere Control | Stabilizes temperature and reduces convective heat loss |
| Variable Frequency Drives | Adjusts ancillary systems to match process demands, cutting energy waste |
Ready to enhance your lab's energy efficiency and precision? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can reduce your operational costs and boost performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















