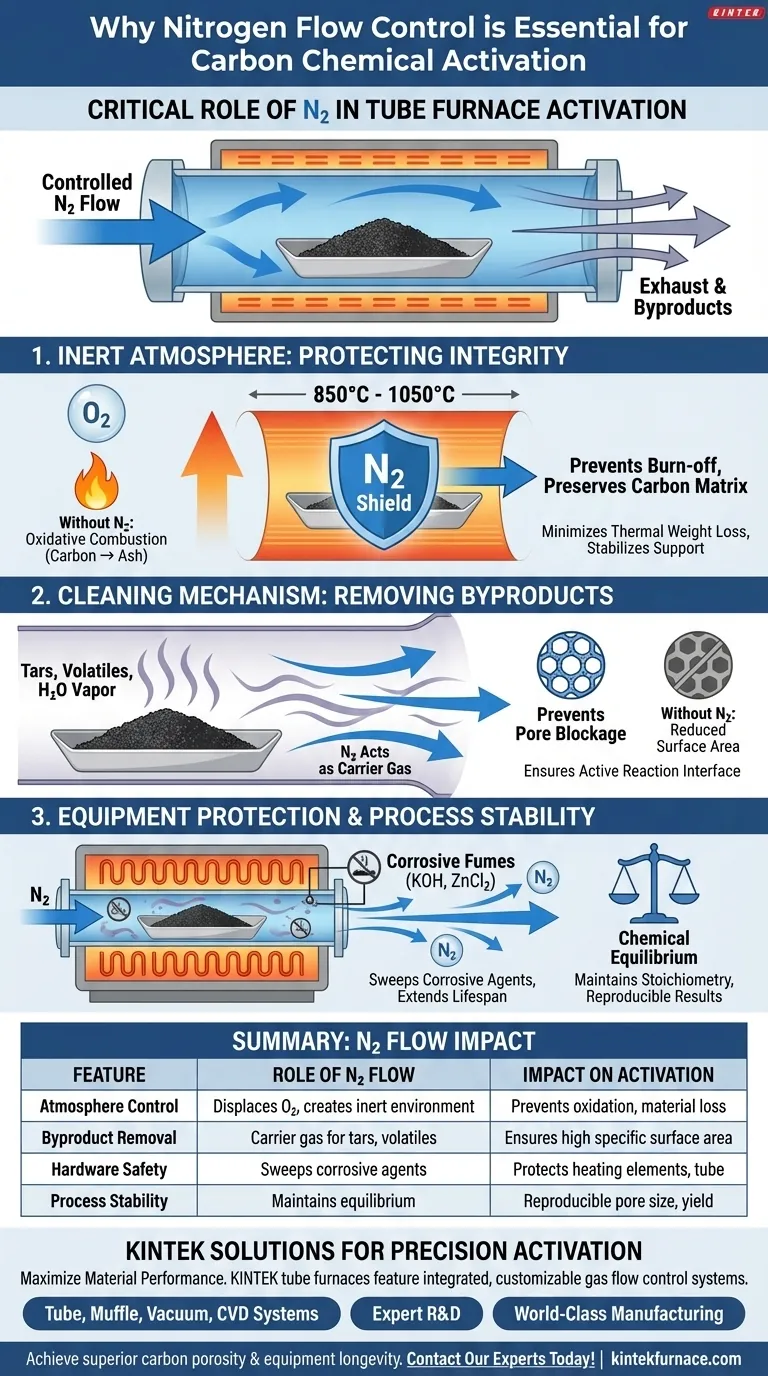
A nitrogen flow control system is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of carbon materials and protecting furnace hardware. During chemical activation with agents like Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) or Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2), this system ensures a strictly inert atmosphere. This prevents the carbon from burning to ash due to oxidation and actively removes hazardous byproducts that could damage the equipment or ruin the sample’s porosity.
Core Takeaway Nitrogen flow acts as both a protective shield and a cleaning mechanism during high-temperature activation. It displaces oxygen to prevent the material from undergoing oxidative combustion while simultaneously acting as a carrier gas to sweep away corrosive volatiles and tars, ensuring the development of high-quality micropores.

The Critical Role of Inert Atmosphere
Prevention of Oxidative Combustion
Chemical activation typically occurs at high temperatures, often ranging from 850 °C to 1050 °C. At these temperatures, carbon is highly reactive with oxygen.
Without a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen to displace air within the tube, the carbon material would react with residual oxygen. This results in unintended combustion, turning your valuable precursor material into ash rather than activated carbon.
Minimizing Thermal Weight Loss
A controlled nitrogen environment is necessary to stabilize the carbon support during pyrolysis. By eliminating oxygen and moisture, the system minimizes unnecessary thermal weight loss.
This ensures that the loss of mass is strictly due to the removal of non-carbon elements and the creation of pores, rather than the destruction of the carbon matrix itself.
Managing Volatiles and Reaction Byproducts
Acting as a Carrier Gas
The activation process generates significant byproducts, including water vapor, tars, and volatile decomposition products. The nitrogen flow serves as a carrier gas to physically transport these substances out of the reaction zone.
Preventing Pore Blockage
If these volatiles are not removed efficiently, they can re-deposit onto the carbon surface. This leads to the blockage of newly formed pores and significantly reduces the specific surface area of the final product.
By maintaining a specific flow rate (e.g., 150 cm³/min), nitrogen ensures the reaction interface remains active and open for chemical agents to function.
Operational Risks and Equipment Protection
Protecting Internal Components
Activation agents like KOH and ZnCl2 generate corrosive volatiles when heated. If these fumes are allowed to linger in the furnace, they can degrade the heating elements, the process tube, and other internal components.
A precision flow control system ensures these corrosive gases are diluted and swept out of the hot zone, significantly extending the lifespan of the tube furnace.
Maintaining Chemical Equilibrium
The primary reference highlights that nitrogen flow is critical for maintaining chemical equilibrium in the reaction.
Precise control over the flow rate prevents fluctuations in the atmosphere that could disrupt the activation stoichiometry. This stability is vital for reproducing results and ensuring consistent pore size distribution across different batches.
Optimizing Your Activation Strategy
If your primary focus is Maximizing Yield: Ensure the nitrogen flow is established well before heating begins to completely displace oxygen and prevent material burn-off.
If your primary focus is Surface Area and Pore Quality: Calibrate the flow rate to effectively remove tars and volatiles without disturbing the thermal stability of the activation agent.
If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Maintain a continuous flow during the cooling phase to prevent corrosive condensates from settling on internal furnace components.
Precision in gas flow control is the difference between generating high-performance activated carbon and producing useless ash.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Nitrogen Flow Control | Impact on Carbon Activation |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Displaces oxygen to create a strictly inert environment | Prevents oxidative combustion and material loss to ash |
| Byproduct Removal | Acts as a carrier gas for tars, water vapor, and volatiles | Prevents pore blockage and ensures high specific surface area |
| Hardware Safety | Sweeps corrosive chemical agents (KOH, ZnCl2) out of the zone | Protects heating elements and process tubes from degradation |
| Process Stability | Maintains chemical equilibrium and thermal consistency | Ensures reproducible pore size distribution and material yield |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Don't let oxidation or corrosive byproducts compromise your research. KINTEK provides state-of-the-art Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically engineered for precision chemical activation. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our high-temperature furnaces feature integrated, customizable gas flow control systems tailored to your unique lab requirements.
Ready to achieve superior carbon porosity and equipment longevity? Contact our experts today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Chaiyan Chaiya, Piyaporn Kampeerapappun. Enhancing the Sustainability of Cotton Spinning Mill Waste Through Thermochemical Processes: Converting Waste into Carbon Materials. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05007
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a dual-zone tube furnace facilitate the synthesis of CrSBr single crystals? Master the CVT Process
- What is the purpose of using a tube furnace with flowing argon for 440C tool steel? Ensure Material Integrity.
- How are horizontal furnaces used in thermal analysis? Precision Heating for Accurate Material Testing
- What other types of reactions can tube furnaces be used for? Explore Versatile Thermal Processes for Your Lab
- What role does a high-vacuum tube furnace play in TF-COF carbonization? Transform Materials with Precision Heat
- What is the function of a gradient temperature horizontal furnace? Expert Growth of Fe4GeTe2 Single Crystals
- What role does a tube furnace play in the high-temperature heat treatment of vermiculite? Precision Control Expert
- How is an industrial tube furnace utilized to evaluate the thermal stability of modified diamond powders?



















