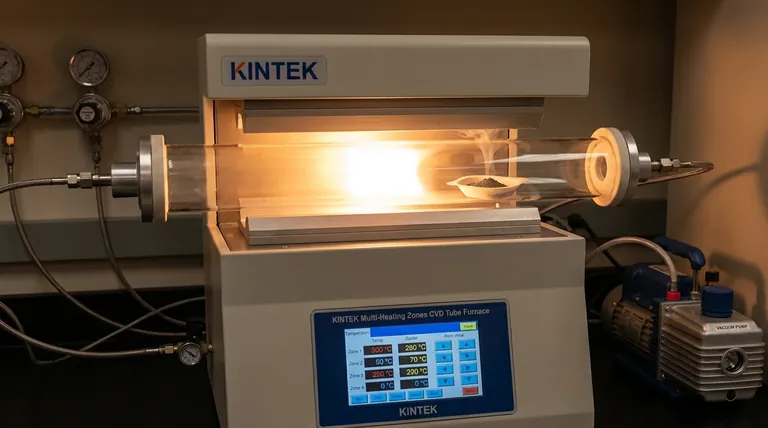
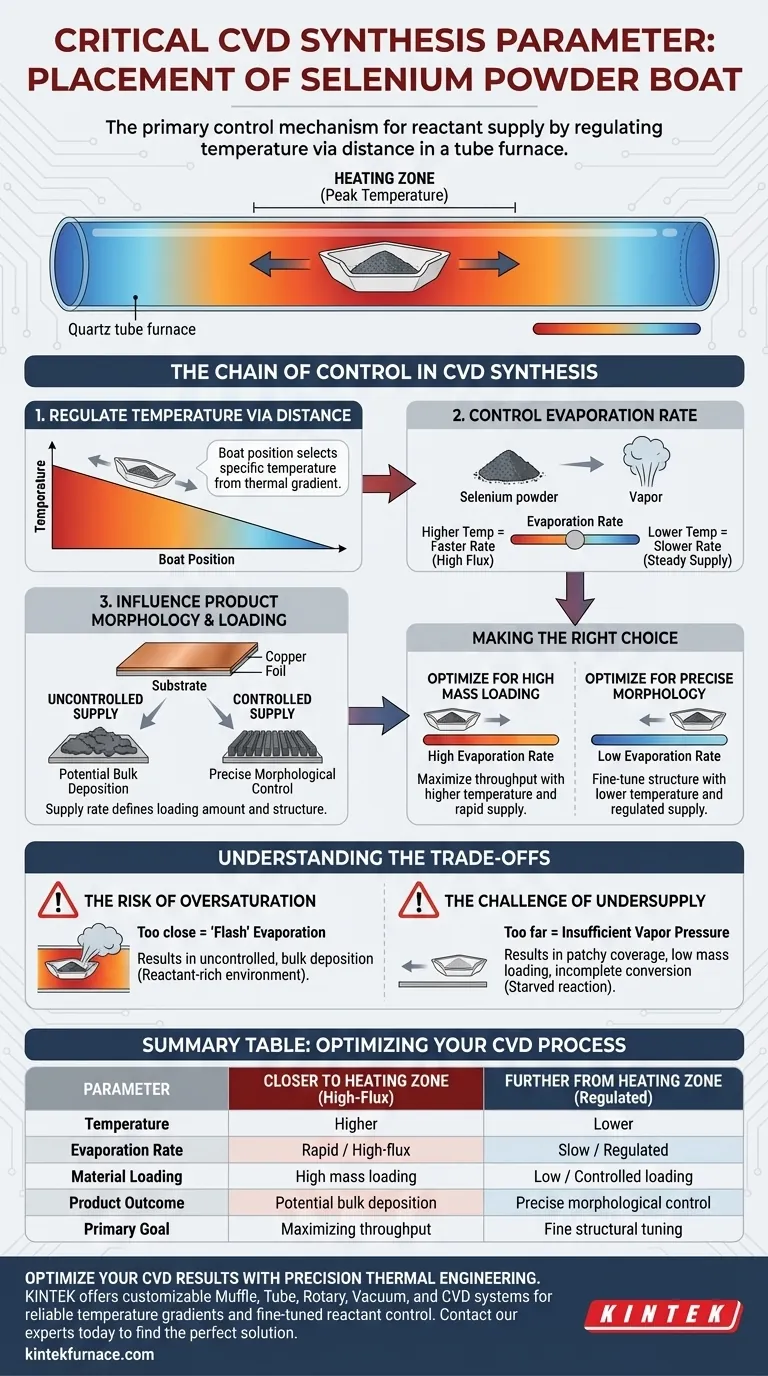
The physical placement of the ceramic boat is the primary control mechanism for reactant supply. By adjusting the boat's distance relative to the central heating zone, you directly determine the specific temperature the selenium powder experiences. This temperature governs the rate of evaporation, allowing you to throttle the supply of selenium vapor introduced into the reaction chamber.
Ideally, the furnace position acts as a precise thermal dial. By exploiting the natural temperature gradient of the tube furnace, you can control the selenium evaporation rate—and consequently the final material structure—without altering the main furnace settings.

The Chain of Control in CVD Synthesis
Regulating Temperature via Distance
In a standard tube furnace, the temperature is not uniform throughout the length of the tube. The center represents the peak temperature (the heating zone), while the areas toward the ends are significantly cooler.
By moving the ceramic boat along this axis, you are effectively selecting a specific temperature point on this thermal gradient. This allows you to expose the selenium powder to a precise heat level that is distinct from the substrate's reaction temperature.
Controlling the Evaporation Rate
The temperature of the selenium powder dictates its vapor pressure and, consequently, how fast it sublimates or evaporates.
If the boat is placed closer to the heating zone, the higher temperature drives a rapid phase change, creating a high-flux environment. Conversely, placing it further away reduces the temperature, resulting in a slow, steady release of selenium vapor.
Impact on Product Morphology
The rate of selenium supply is the critical variable that defines the outcome on the substrate. The primary reference indicates that this supply rate directly controls the loading (amount of material deposited) and the morphology (shape and structure) of the copper selenide formed on the copper foil.
A controlled supply is necessary to achieve specific structural characteristics, whereas an unregulated supply can lead to unintended growth patterns.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Oversaturation
Placing the boat too deeply into the heating zone can cause "flash" evaporation. This releases the selenium too quickly, creating a reactant-rich environment that may lead to uncontrolled, bulk deposition rather than precise growth.
The Challenge of Undersupply
Positioning the boat too far from the heat source may result in insufficient vapor pressure. This "starves" the reaction, potentially leading to patchy coverage, low mass loading, or incomplete conversion of the copper foil into copper selenide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
To optimize your Chemical Vapor Deposition process, you must calibrate the boat's position based on your specific target properties.
- If your primary focus is high mass loading: Position the boat closer to the heating zone to maximize temperature and increase the selenium evaporation rate.
- If your primary focus is precise morphological control: Shift the boat further from the heating zone to lower the evaporation rate, ensuring a slower, more regulated supply of reactants.
Mastering this spatial parameter gives you fine-tuned command over the reaction kinetics without altering the global reactor conditions.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Closer to Heating Zone | Further from Heating Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher | Lower |
| Evaporation Rate | Rapid / High-flux | Slow / Regulated |
| Material Loading | High mass loading | Low / Controlled loading |
| Product Outcome | Potential bulk deposition | Precise morphological control |
| Primary Goal | Maximizing throughput | Fine structural tuning |
Optimize Your CVD Results with Precision Thermal Engineering
Achieving the perfect material morphology requires more than just high temperatures—it requires the precise spatial control and thermal stability found in KINTEK lab equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Whether you are synthesizing copper selenide or advanced 2D materials, our high-temp furnaces provide the reliable temperature gradients necessary for fine-tuned reactant control.
Ready to elevate your synthesis precision? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Rajesh Rajasekharan, Manikoth M. Shaijumon. Bifunctional Current Collectors for Lean‐Lithium Metal Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202502473
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is Ar/H2 Flow Control Critical for V2O5 Nanosheet CVD? Master Redox Potential and Morphology
- Why is gas flow distribution critical in LPCVD alpha-MnSe synthesis? Master Precise Nanosheet Morphology
- How does CVD compare to PVD in deposition rates? PVD is faster, but CVD offers versatility.
- What are the steps involved in the CVD process? Master Atomic-Level Thin Film Deposition
- What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), and how do horizontal furnaces facilitate it? Unlock High-Purity Thin Films
- What role does a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system play in 2D material synthesis? Master Scalable Material Growth
- What are some applications of CVD furnaces in the semiconductor industry? Essential for Thin Film Deposition in Chip Making
- What are the advantages of chemical vapour deposition? Achieve Superior, Uniform Coatings on Complex 3D Surfaces



















