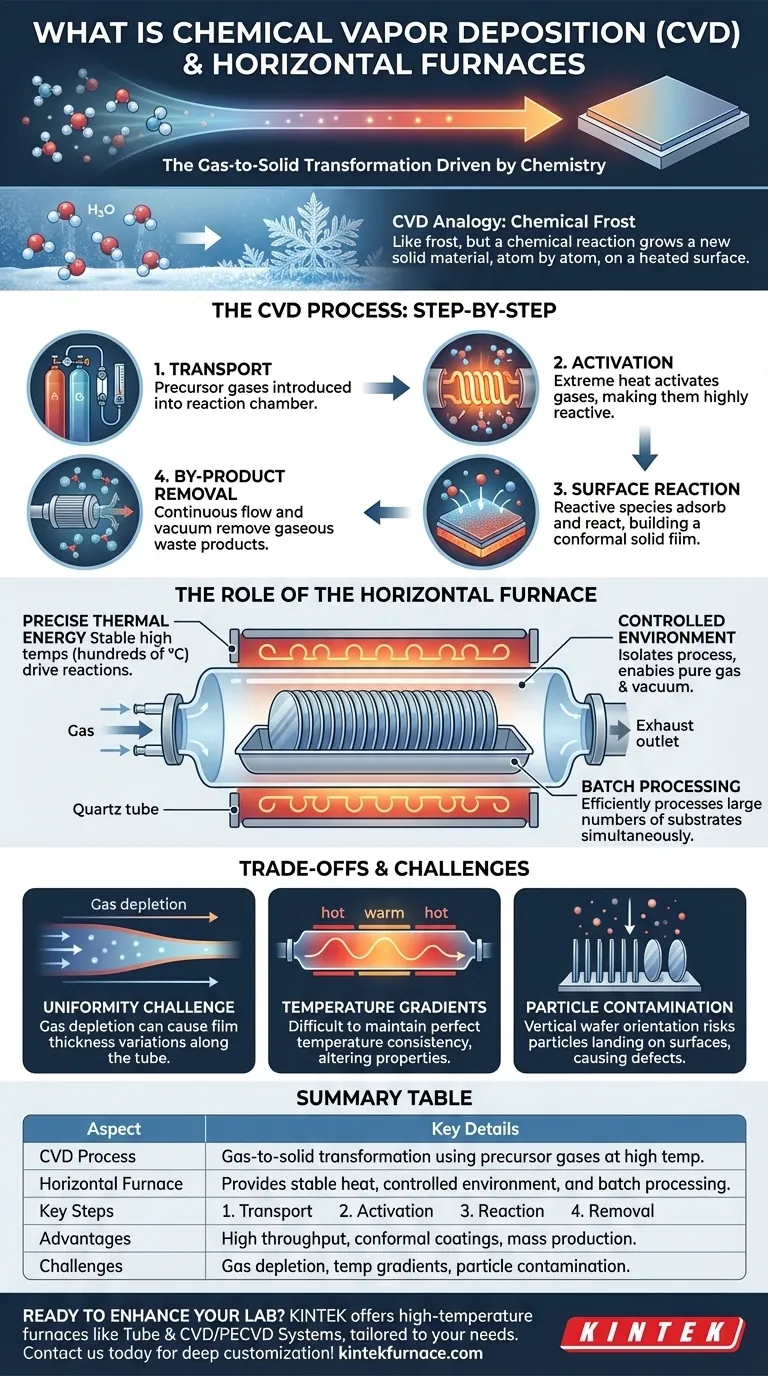
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated manufacturing process that builds a high-purity, solid thin film onto a surface from a gaseous state. It achieves this by introducing specific precursor gases into a high-temperature chamber where they chemically react and deposit onto a substrate, atom by atom. A horizontal furnace is a critical piece of equipment that provides the stable, high-temperature, and controlled environment required for these chemical reactions to occur successfully.
The central concept to grasp is that CVD is fundamentally a gas-to-solid transformation driven by chemistry. The furnace is not just a heater; it is the reaction chamber that enables this precise transformation by providing the necessary thermal energy and environmental control.
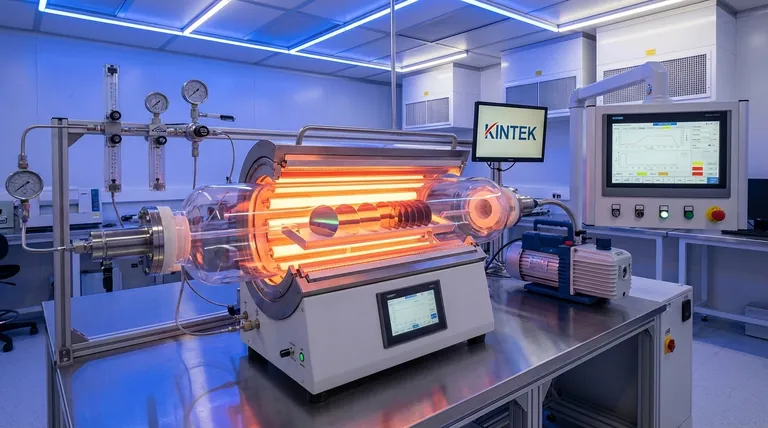

The Fundamental Principle: Building from Gas
The Core Concept
Chemical Vapor Deposition is best understood as a method of "growing" a material. Instead of melting or sputtering a solid source, CVD starts with carefully selected gases, known as precursors.
These precursors contain the atoms needed for the final film. When heated, they decompose or react near a substrate, and the resulting solid material deposits onto it, forming a thin, uniform layer.
An Analogy: Chemical Frost
Imagine how water vapor in the air forms intricate frost patterns on a cold window. The water molecules transition directly from a gas to a solid on the surface.
CVD operates on a similar principle but is more complex. Instead of a simple phase change, it involves a chemical reaction. The precursor gases react to create an entirely new solid material on the hot substrate surface, while unwanted by-products are vented away.
Deconstructing the CVD Process Step-by-Step
The entire process occurs within the furnace and can be broken down into four critical stages that happen in continuous succession.
Step 1: Transport of Precursors
First, the precursor gases are precisely metered and introduced into the reaction chamber (the furnace tube). The gas flows over the substrates, which are typically silicon wafers in semiconductor manufacturing.
Step 2: Gas-Phase Activation
The extreme heat inside the furnace provides the activation energy for the chemical reactions. This causes the precursor gas molecules to become highly reactive, either by breaking down or by reacting with other gases present.
Step 3: Surface Reaction and Film Growth
These reactive chemical species adsorb onto the hot substrate surface. Here, they undergo further reactions that result in the formation of the desired solid film. This deposition occurs across all exposed surfaces, creating a highly conformal coating.
Step 4: Removal of By-products
The chemical reactions produce the solid film but also create gaseous by-products. A continuous gas flow and vacuum system remove these waste products from the chamber, preventing them from contaminating the film.
The Role of the Horizontal Furnace
The horizontal furnace is the workhorse that creates the ideal conditions for CVD. It is not merely an oven but a highly controlled piece of process equipment.
Providing Precise Thermal Energy
The primary function of the furnace is to maintain a stable, uniform, and high temperature—often hundreds of degrees Celsius. This thermal energy is what drives the chemical reactions essential for deposition.
Creating a Controlled Environment
The long quartz tube of a horizontal furnace acts as the reaction chamber. It isolates the process from the outside atmosphere, allowing for a pure gas environment at a specific, controlled pressure (often a vacuum).
Facilitating Batch Processing
A key advantage of the horizontal configuration is its ability to process a large number of substrates at once. Wafers can be loaded onto a "boat" and pushed into the tube, making it highly efficient for mass production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While effective, the horizontal furnace CVD process has inherent challenges that engineers must manage.
The Challenge of Uniformity
As precursor gases flow from the front of the furnace tube to the back, they are consumed. This gas depletion effect can cause the film to be thicker on wafers at the front of the boat and thinner on wafers at the back.
Managing Temperature Gradients
Maintaining a perfectly consistent temperature across the entire length of a long process tube is difficult. Even small temperature variations can significantly alter the deposition rate and film properties from one wafer to another.
Risk of Particle Contamination
Because the wafers are oriented vertically, any particles that form in the gas phase can fall and land on the wafer surfaces below them. This is a major source of defects that can ruin a device.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles allows you to select and optimize the CVD process for a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: Horizontal furnace CVD offers excellent throughput for batch processing, but you must actively compensate for depletion and temperature effects to ensure product consistency.
- If your primary focus is advanced research and development: The versatility of CVD allows for the creation of novel materials, but achieving precise film properties requires rigorous control over gas flows, temperature, and pressure.
- If your primary focus is creating durable protective coatings: CVD is exceptional for producing dense, conformal, and pinhole-free films that protect underlying components from corrosion and wear.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition is a cornerstone technology that enables much of the modern world, from computer chips to advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| CVD Process | Gas-to-solid transformation using precursor gases in a high-temperature chamber for thin film deposition |
| Horizontal Furnace Role | Provides stable high-temperature environment, controlled gas flow, and batch processing for efficient CVD |
| Key Steps | 1. Transport of precursors 2. Gas-phase activation 3. Surface reaction and film growth 4. Removal of by-products |
| Advantages | High throughput, conformal coatings, suitability for mass production |
| Challenges | Gas depletion effects, temperature gradients, particle contamination risks |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced CVD solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Tube and CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization can optimize your thin film processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab



















