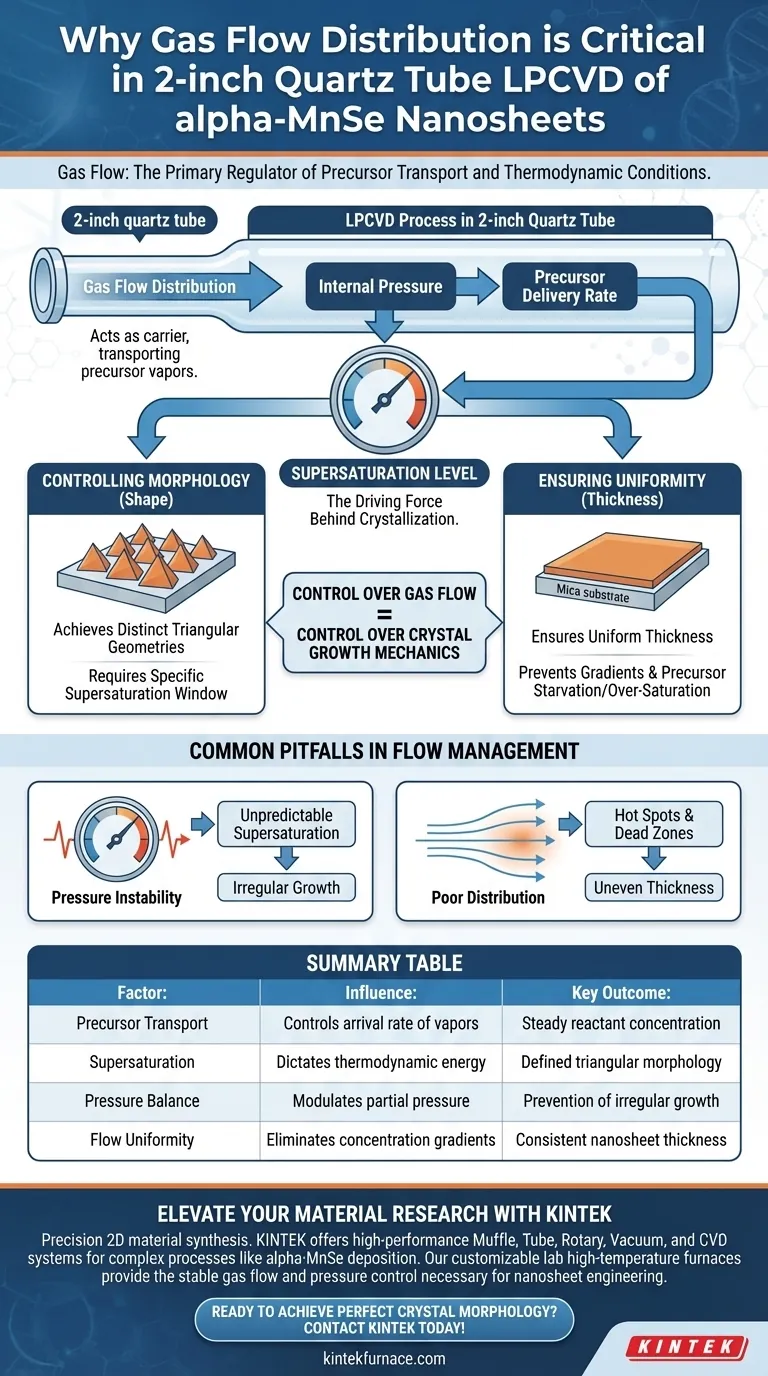
Gas flow distribution serves as the primary regulator of precursor transport and thermodynamic conditions. In a 2-inch quartz tube during Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD), the gas flow acts as the carrier that transports precursor vapors to the downstream substrate. Crucially, the precise control of this flow and the resulting internal pressure dictates the supersaturation level, which is the direct variable responsible for determining the specific shape and thickness of the alpha-MnSe nanosheets.
Control over gas flow is effectively control over crystal growth mechanics. By regulating how precursors reach the mica substrate, you determine the supersaturation state necessary to achieve uniform thickness and distinct triangular morphologies.

The Mechanics of Supersaturation
Regulating Precursor Delivery
The gas flow in the quartz tube is not simply a transport mechanism; it defines the chemical environment at the reaction site.
By managing the distribution of gas, you control the rate at which precursor vapors arrive at the downstream substrate. This delivery rate establishes the local concentration of reactants available for deposition.
Defining the Supersaturation Level
The interaction between gas flow distribution and internal pressure determines the supersaturation level of the precursors.
Supersaturation is the driving force behind crystallization. If this level fluctuates due to inconsistent flow, the thermodynamic conditions required for specific crystal growth modes will become unstable.
Controlling Morphology and Uniformity
Achieving Distinct Geometries
The morphology of alpha-MnSe nanosheets is highly sensitive to the deposition environment.
Specifically, the primary reference indicates that precise flow control facilitates the formation of distinct triangular structures. Without stable gas distribution, the system may fail to maintain the specific growth mode required for this geometric perfection.
Ensuring Thickness Uniformity
Beyond shape, the gas flow distribution is responsible for the physical consistency of the material.
A uniform flow ensures that the precursor vapor is evenly distributed across the mica substrate. This prevents gradients in deposition rates, thereby ensuring that the resulting nanosheets maintain a uniform thickness across the sample.
Common Pitfalls in Flow Management
The Impact of Pressure Instability
It is critical to remember that flow cannot be viewed in isolation from internal pressure.
Changes in gas flow distribution directly alter the internal pressure within the restricted volume of the 2-inch tube. If pressure varies, the partial pressure of the precursor changes, leading to unpredictable shifts in supersaturation.
Consequences of Poor Distribution
If the gas flow is not distributed evenly, "hot spots" or "dead zones" of precursor concentration can occur.
This spatial variance leads to samples where one area may exhibit perfect triangular nanosheets, while adjacent areas suffer from irregular growth or uneven thickness due to precursor starvation or over-saturation.
Optimizing Your LPCVD Process
To maximize the quality of alpha-MnSe nanosheets in a 2-inch quartz tube setup, align your flow parameters with your specific structural goals.
- If your primary focus is Geometric Precision (Triangles): Prioritize stable internal pressure and flow rates to maintain the specific supersaturation "window" required for triangular growth modes.
- If your primary focus is Sample Uniformity: Ensure the gas flow distribution is spatially consistent across the tube diameter to prevent thickness gradients on the mica substrate.
Mastering the gas flow is the key to transitioning from random deposition to controlled, high-quality crystal engineering.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Influence on alpha-MnSe Growth | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Transport | Controls arrival rate of vapors at substrate | Steady reactant concentration |
| Supersaturation | Dictates thermodynamic crystallization energy | Defined triangular morphology |
| Pressure Balance | Modulates partial pressure of reactants | Prevention of irregular growth |
| Flow Uniformity | Eliminates concentration gradients | Consistent nanosheet thickness |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the heart of 2D material synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for complex processes like alpha-MnSe deposition. Our customizable lab high-temperature furnaces provide the stable gas flow and pressure control necessary for your most demanding nanosheet engineering projects.
Ready to achieve perfect crystal morphology? Contact our technical team today to find the ideal furnace solution for your unique research needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Ye Zhao, Xiaohong Xu. Magnetic exchange coupling and photodetection multifunction characteristics of an MnSe/LaMnO<sub>3</sub> heterostructure. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra06719c
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vapor phase deposition? Build Ultra-Thin Films for High-Tech Applications
- What is the function of a high vacuum pump in CVD? Ensure High-Purity ITO Thin Film Growth
- What biomedical applications do CVD furnaces have? Enhance Implant Safety and Drug Delivery
- How do CVD coatings compare to spray-on PTFE coatings? Discover Superior Performance and Safety
- What are some common applications of CVD? Discover Versatile Coating Solutions for Your Industry
- What is Hot-filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD)? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films with Precision Control
- Why is a vacuum deposition chamber an essential hardware environment? Unlock High-Performance Thermal Power Coatings
- What future trends are expected in the development of CVD tube furnaces? Discover Smarter, More Versatile Systems



















