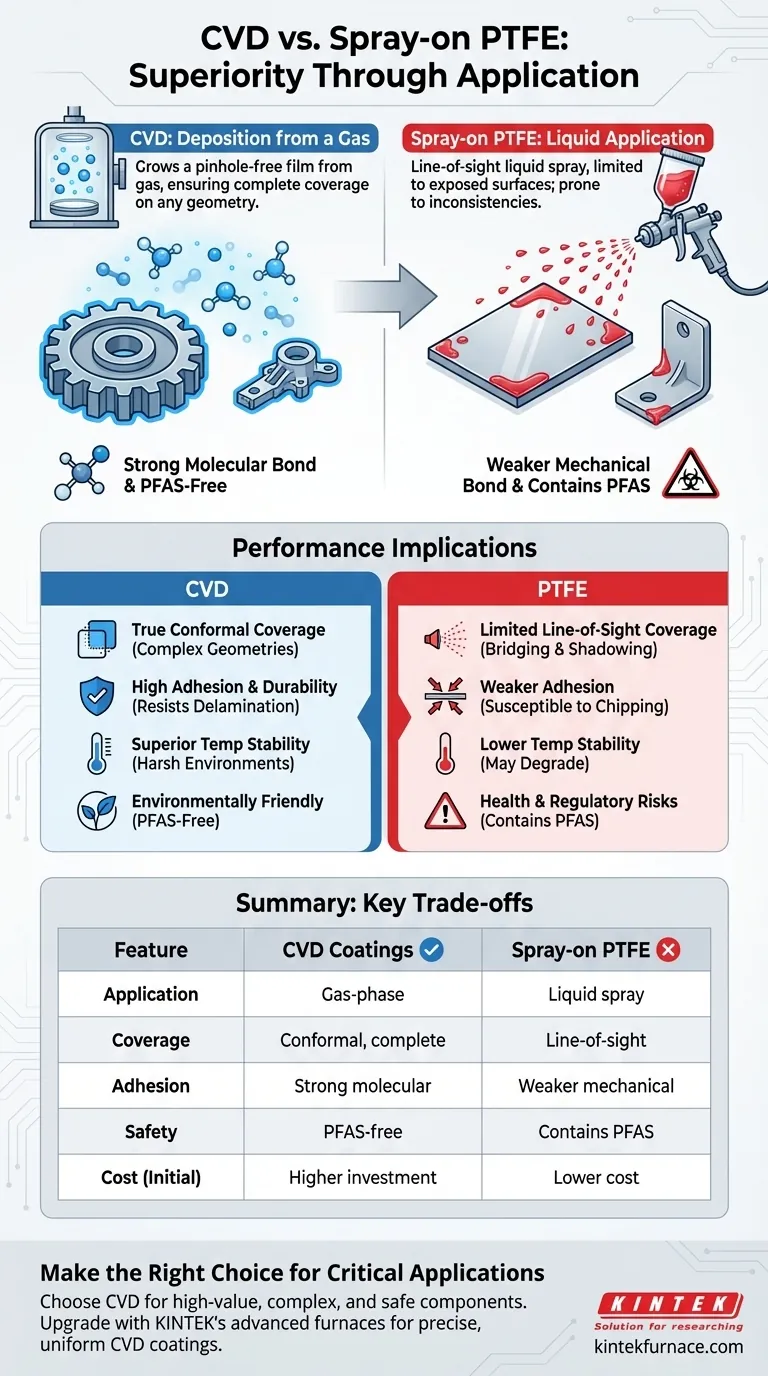
At a fundamental level, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) coatings are superior to spray-on Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coatings in nearly every performance category. CVD provides a perfectly uniform, pinhole-free layer that covers every surface of a component, regardless of complexity, while spray-on PTFE is a line-of-sight application that cannot protect intricate geometries. Furthermore, CVD polymer coatings offer higher temperature stability and are free from the toxic PFAS chemicals inherent to PTFE.
The core difference is not simply the material, but the application method. CVD "grows" a coating from a gas, ensuring complete and uniform coverage, whereas spray-on PTFE is a liquid paint application, which is inherently limited and less consistent.
The Fundamental Difference: Application Method
To understand the vast difference in performance, you must first understand how each coating is applied. The method dictates the outcome.
CVD: Deposition from a Gas Phase
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process where a part is placed in a vacuum chamber. A solid raw material, known as a dimer, is heated into a gas.
This gas is then pyrolyzed, or cracked with heat, to create reactive monomers. These gaseous monomers enter the deposition chamber at room temperature and polymerize directly onto every exposed surface, "growing" an ultra-thin, perfectly conformal film.
Think of it like frost forming on a windowpane on a cold morning—it covers every single curve and imperfection with absolute uniformity.
Spray-on PTFE: Application of a Liquid
Spray-on PTFE is applied much like standard paint. Liquid PTFE dispersions are atomized and sprayed onto a surface.
This method is entirely line-of-sight, meaning the coating can only adhere to surfaces directly in the path of the spray nozzle. Areas in shadow, inside tight crevices, or under components will receive little to no coating.
The liquid carrier must then be baked off, which can introduce inconsistencies in thickness and density, and may not be suitable for heat-sensitive components.
Performance Implications of Each Method
The differences in application lead to critical distinctions in performance, reliability, and part integrity.
Coverage and Conformality
CVD coatings provide a truly conformal layer. This means the coating thickness is perfectly uniform across flat surfaces, sharp edges, and even deep inside complex internal geometries or crevices. This ensures complete, pinhole-free encapsulation.
Spray-on PTFE, by contrast, suffers from bridging, pooling in corners, and thinning on sharp edges. It cannot penetrate complex geometries, leaving critical areas completely unprotected.
Adhesion and Durability
Because CVD coatings are formed at a molecular level, they create an extremely strong bond with the substrate. The resulting film is flexible, durable, and highly resistant to delamination or cracking.
Spray-on coatings rely on a mechanical bond, which is weaker and more susceptible to chipping, flaking, and peeling, especially under physical stress or thermal cycling.
Material Integrity and Safety
CVD polymer coatings are exceptionally pure and dense, providing a superior barrier against moisture and chemicals. Critically, they are PFAS-free.
PTFE is a member of the PFAS family of "forever chemicals," which are facing increasing regulatory scrutiny and are known to be persistent environmental and health hazards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While CVD offers superior technical performance, the choice depends on the specific requirements of the application.
When Spray-on PTFE Might Suffice
For simple, non-critical applications on flat, easy-to-access surfaces where cost is the primary driver, a spray-on coating may be adequate. If all you need is a basic, low-friction surface on a simple shape and complete protection is not required, its lower application cost can be attractive.
The Investment in CVD
The CVD process is more complex, requiring specialized vacuum deposition equipment. This typically results in a higher cost and longer lead times compared to spraying. However, for high-value, critical components where failure is not an option—such as in medical devices, aerospace, or electronics—this cost is an investment in reliability and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be driven by the performance requirements and long-term reliability needs of your product.
- If your primary focus is protecting complex, high-value components: Choose CVD for its complete, pinhole-free conformal coverage that guarantees total protection.
- If your primary focus is performance in harsh environments: Choose CVD for its superior temperature stability, flexibility, and robust barrier properties.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance and safety: Choose PFAS-free CVD coatings to eliminate the health, environmental, and business risks associated with PTFE.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost coating for a simple, non-critical surface: Spray-on PTFE can be a viable option, provided you fully accept its coverage and durability limitations.
Ultimately, understanding the core process—vapor deposition versus liquid spray—is the key to selecting a coating that ensures long-term performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Coatings | Spray-on PTFE Coatings |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Gas-phase deposition for uniform coverage | Line-of-sight liquid spray |
| Coverage | Conformal, pinhole-free on complex geometries | Limited to exposed surfaces, prone to inconsistencies |
| Adhesion | Strong molecular bond, durable and flexible | Weaker mechanical bond, susceptible to chipping |
| Temperature Stability | High, suitable for harsh environments | Lower, may degrade under high heat |
| Safety | PFAS-free, environmentally friendly | Contains PFAS, potential health and regulatory risks |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, ideal for critical uses | Lower cost, suitable for simple, non-critical applications |
Upgrade your coating solutions with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored CVD systems, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, and more to ensure precise, uniform coatings for your critical components. Our deep customization capability meets your unique experimental needs, enhancing reliability and compliance. Don't compromise on performance—contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-value applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















