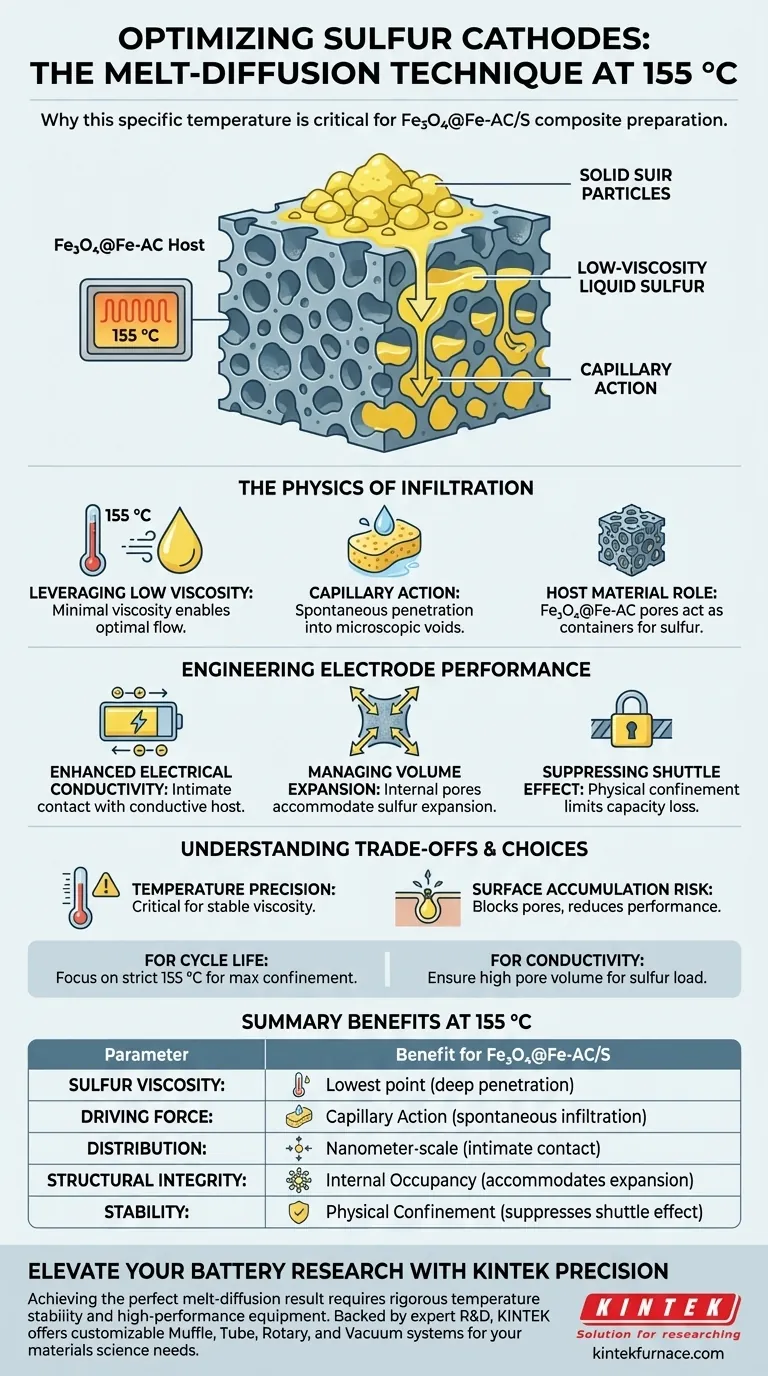
The melt-diffusion technique targets 155 °C specifically to minimize the viscosity of elemental sulfur, enabling optimal flow. At this precise temperature, solid sulfur converts into a low-viscosity liquid that can be driven effectively by capillary forces. This allows the sulfur to spontaneously penetrate the complex porous structure of the Fe3O4@Fe-AC host material, rather than simply coating the surface.
The core objective of heating to 155 °C is to leverage the capillary action of liquified sulfur to achieve physical confinement. This process forces sulfur into the host’s internal pores, creating a uniform, nanometer-scale distribution that is critical for electrical conductivity and battery cycle stability.

The Physics of Infiltration
Leveraging Low Viscosity
The primary reason for selecting 155 °C is the physical state of sulfur at this thermal point. While sulfur melts at a slightly lower temperature, 155 °C provides a low-viscosity window where the liquid flows almost like water.
Capillary Action as the Driving Force
Because the sulfur is so fluid at this temperature, it does not require high external pressure to move. Instead, it relies on capillary action. The liquid sulfur is naturally drawn into the microscopic voids of the material, similar to how a sponge soaks up water.
The Role of the Host Material
The Fe3O4@Fe-AC host is engineered with abundant, highly developed pores. These pores act as the "container" for the sulfur. The melt-diffusion process ensures the sulfur occupies these internal spaces rather than aggregating on the exterior.
Engineering Electrode Performance
Enhancing Electrical Conductivity
Elemental sulfur is naturally insulating, which is a major hurdle for battery performance. By diffusing sulfur into the Fe3O4@Fe-AC host, the sulfur comes into intimate contact with the conductive carbon/iron framework, significantly improving electron transport.
Managing Volume Expansion
Sulfur expands significantly when the battery charges and discharges. By infiltrating the pores at 155 °C, the technique leaves room within the internal structure to accommodate this volume change, preventing the electrode from cracking or degrading.
Suppressing the Shuttle Effect
The process achieves physical confinement of the sulfur. By locking the sulfur deep within the carbon skeleton, the technique limits the "shuttle effect"—a phenomenon where sulfur compounds dissolve and migrate, causing capacity loss.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Precision is Critical
This technique relies heavily on maintaining a stable temperature field. If the temperature deviates significantly, the viscosity of sulfur can change, preventing deep infiltration or causing uneven distribution.
The Risk of Surface Accumulation
If the melt-diffusion is incomplete or the temperature is not maintained, sulfur may solidify on the surface of the host. This blocks pores and leads to poor conductivity and rapid degradation of the battery during cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the melt-diffusion technique, consider the following based on your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Cycle Life: Ensure the heating equipment maintains a strict 155 °C environment to maximize capillary infiltration and suppress the shuttle effect through physical confinement.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity: Verify that the host material (Fe3O4@Fe-AC) has a sufficiently high pore volume to accommodate the sulfur load without leaving residue on the surface.
Success in this process relies not just on melting the sulfur, but on achieving the precise viscosity required for deep, uniform pore saturation.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Influence at 155 °C | Benefit for Fe3O4@Fe-AC/S |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfur Viscosity | Lowest point (liquid state) | Enables deep penetration into microscopic pores |
| Driving Force | Capillary Action | Spontaneous infiltration without high external pressure |
| Distribution | Nanometer-scale | Ensures intimate contact with conductive host |
| Structural Integrity | Internal Pore Occupancy | Accommodates volume expansion during cycling |
| Stability | Physical Confinement | Suppresses the shuttle effect and capacity loss |
Elevate Your Battery Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect melt-diffusion result requires rigorous temperature stability and high-performance equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique materials science needs.
Whether you are developing advanced sulfur cathodes or next-generation composites, our precision heating solutions ensure you maintain the exact 155 °C environment necessary for optimal sulfur infiltration. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Ka Chun Li, Xijun Hu. Fe<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>@Fe Core–Shell Okara-Derived Activated Carbon for Superior Polysulfide Control in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5c02606
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using solution impregnation for PtS/Ti3C2Tx? Superior In-Situ Growth vs. Mixing
- What methods are used to analyze and characterize graphene samples? Unlock Key Techniques for Accurate Material Analysis
- What experimental conditions does a high-temperature continuous flow fixed-bed reactor provide for Zn-Cr catalysts?
- Why is the precision of a temperature control system critical in copper brazing? Ensure Perfect Joints Every Time
- What role do low-temperature carbonization furnaces play in carbon fiber manufacture? Build a Strong Structural Foundation
- Why is thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) necessary for modified hard carbon? Optimize Stability & Composition
- What is the objective of GC-MS analysis on bio-oil? Unlock Chemical Value and Industrial Utility
- How is induced heat generated in a conductive material exposed to a magnetic field? Master Rapid, Contactless Heating



















