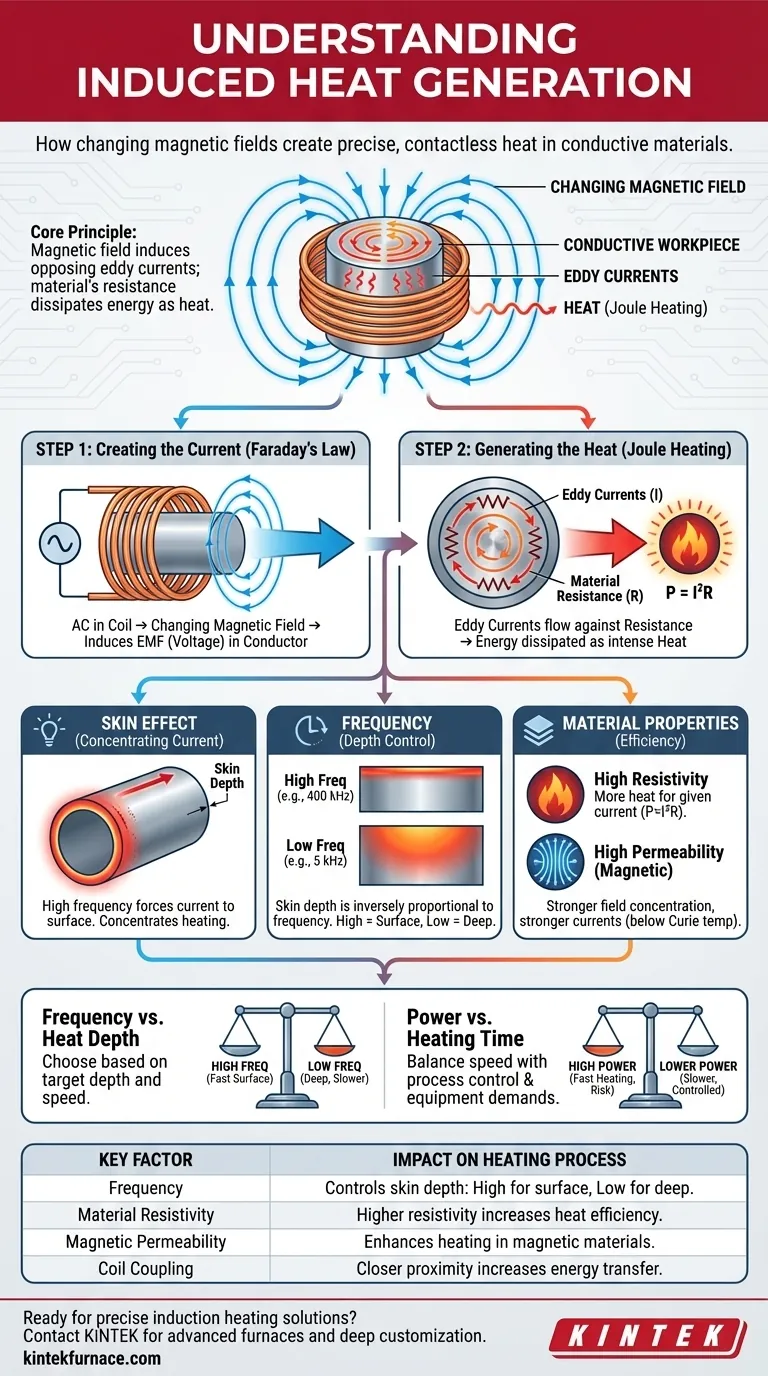
At its core, induced heat is the result of a changing magnetic field creating electrical currents within a conductive material. The material’s own electrical resistance opposes these currents, causing friction at an atomic level that manifests as heat. This process, known as Joule heating, allows for rapid, contactless heating concentrated exactly where it is needed.
A rapidly changing magnetic field induces localized, swirling electrical currents—known as eddy currents—near the material's surface. The material's inherent resistance to the flow of these currents is what generates the intense heat.

The Two-Step Physical Process
To understand induction heating, we must look at two distinct but connected physical principles: electromagnetic induction and resistive heating.
Step 1: Creating the Current (Faraday's Law)
The process begins with an inductor, typically a copper coil, through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed.
This AC generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space around the coil. When a conductive material (the workpiece) is placed within this field, the magic happens.
According to Faraday's Law of Induction, a changing magnetic field passing through a conductor will induce a voltage, or electromotive force (EMF), within that conductor.
Step 2: Generating the Heat (Joule Heating)
This induced voltage forces electrons within the material to move, creating closed loops of electrical current. These are called eddy currents because they resemble swirling eddies in a fluid.
No material is a perfect conductor; all possess some electrical resistance. As the eddy currents flow through this resistance, energy is dissipated in the form of heat.
This phenomenon is described by the Joule heating principle (P = I²R), where the power converted to heat (P) is proportional to the square of the current (I) multiplied by the resistance (R).
Key Factors Controlling Induced Heat
The efficiency and characteristics of induction heating are not accidental. They are controlled by several interconnected factors.
The Skin Effect: Concentrating the Current
At the high frequencies used in induction heating, the eddy currents do not flow uniformly through the material. They are forced to flow in a thin layer near the surface.
This phenomenon is known as the skin effect. It concentrates the current, and therefore the heating, in a well-defined surface region.
The Role of Frequency
The depth of this heated layer, known as the skin depth, is inversely proportional to the frequency of the alternating magnetic field.
A high frequency results in a very thin skin depth, concentrating immense power on the surface for applications like case hardening. A low frequency allows the heat to penetrate deeper into the part, suitable for melting or through-heating.
The Impact of Material Properties
A material's resistivity directly influences how much heat is generated. Higher resistivity leads to more heat for a given amount of eddy current, making heating more efficient.
For magnetic materials like iron and steel, high magnetic permeability dramatically strengthens the magnetic field concentration below the Curie temperature, leading to much stronger eddy currents and far more efficient heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right parameters for induction heating involves balancing competing factors to achieve the desired outcome.
Frequency vs. Heat Depth
The most critical trade-off is frequency. High frequencies provide extremely fast surface heating but cannot effectively heat the core of a large part. Low frequencies penetrate deeper but heat the entire volume more slowly.
Power vs. Heating Time
Applying more power will increase the magnitude of the eddy currents, heating the part much faster according to the I² relationship. However, this requires a more robust power supply and can risk overheating or damaging the surface if not controlled carefully.
Coil Coupling and Geometry
The efficiency of energy transfer depends entirely on the coupling, or proximity of the induction coil to the workpiece. A closer coil transfers energy more efficiently but increases the risk of arcing. The coil's shape must also be designed to conform to the part to ensure the magnetic field is delivered where needed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles allows you to control the application of thermal energy with remarkable precision.
- If your primary focus is rapid surface hardening: Use very high frequencies (100 kHz to 400 kHz+) to concentrate intense heat in a shallow surface layer.
- If your primary focus is deep, bulk heating or melting: Use lower frequencies (1 kHz to 50 kHz) to achieve a greater skin depth and heat the part more uniformly.
- If your primary focus is heating a complex shape: Design a custom induction coil that conforms to the geometry of the workpiece to ensure an even and efficient transfer of energy.
By mastering the interplay between frequency, power, and material properties, you can transform induction from a physical phenomenon into a precise and powerful engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Heating Process |
|---|---|
| Frequency | Controls skin depth: high frequency for surface heating, low frequency for deep penetration. |
| Material Resistivity | Higher resistivity increases heat generation efficiency. |
| Magnetic Permeability | Enhances heating in magnetic materials below the Curie temperature. |
| Coil Coupling | Closer proximity increases energy transfer efficiency and heating rate. |
Ready to apply precise, localized induction heating to your thermal processing challenges? At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you require rapid surface hardening with high-frequency induction or deep, uniform heating for melting applications, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Let our experts help you optimize frequency, power, and coil design for maximum efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our induction heating solutions can enhance your lab's performance and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What are some specific applications of vacuum hot press furnaces? Unlock Advanced Material Fabrication
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability



















