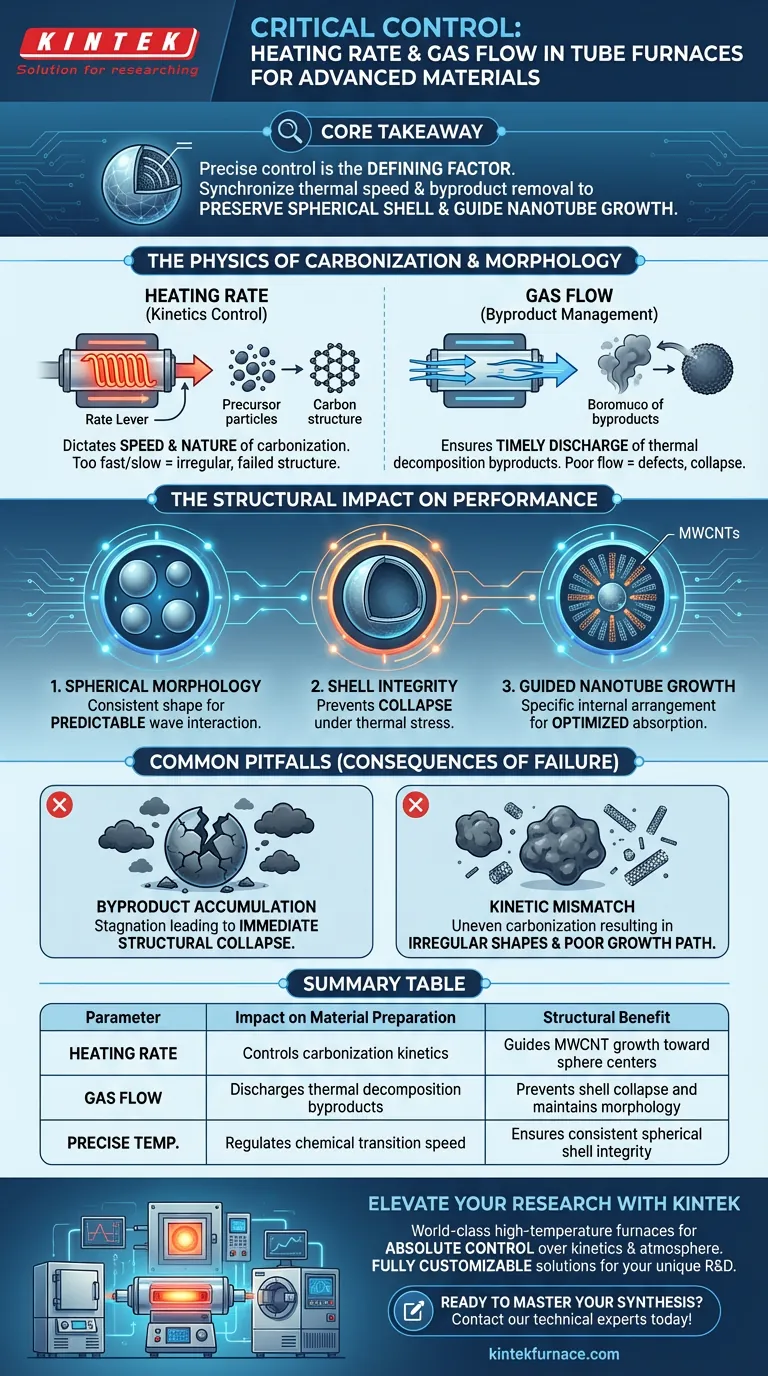
Precise control of heating rate and gas flow is the defining factor in engineering the microstructure of electromagnetic wave absorption materials. The heating rate dictates the kinetics of carbonization, while the gas flow ensures the immediate removal of thermal decomposition byproducts. Together, these parameters prevent structural collapse and enable the precise morphological features required for high performance.
Core Takeaway The electromagnetic performance of your material is directly tied to its physical geometry. By synchronizing the thermal reaction speed with efficient byproduct removal, you preserve the critical spherical shell structure and guide carbon nanotubes to grow inward, maximizing absorption capabilities.
The Physics of Carbonization and Morphology
To understand why these furnace parameters matter, you must look beyond the temperature setting and focus on the dynamic environment inside the tube.
Controlling Carbonization Kinetics
The heating rate is the primary lever for controlling the speed and nature of the carbonization process.
It determines the kinetic characteristics of how the precursor materials transform into carbon.
If this rate is not carefully regulated, the fundamental chemical transition will occur too rapidly or too slowly to support the desired structure.
Managing Decomposition Byproducts
As the material heats, it releases thermal decomposition byproducts.
The precision of the gas flow is responsible for the timely discharge of these byproducts from the reaction zone.
If these byproducts are not flushed out efficiently, they can interfere with the developing material, leading to defects or structural failure.
The Structural Impact on Performance
The ultimate goal of regulating the furnace environment is to dictate the physical shape of the composite. The source material highlights three specific structural outcomes that depend on these controls.
Maintaining Spherical Morphology
The composite relies on a specific spherical morphology to function effectively.
Accurate control of the furnace parameters ensures that these spheres form correctly during synthesis.
Without this geometric consistency, the material's interaction with electromagnetic waves becomes unpredictable and less efficient.
Preventing Shell Collapse
The material possesses a delicate shell structure that is prone to failure during high-temperature processing.
Proper gas flow and heating rates prevent this shell from collapsing under the stress of decomposition and thermal expansion.
A collapsed shell destroys the material's internal cavity, rendering it far less effective for wave absorption.
Guiding Nanotube Growth
Perhaps the most intricate requirement is the placement of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs).
Correct processing conditions guide the growth of these MWCNTs toward the center of the spheres.
This specific internal arrangement is a decisive factor in optimizing the material's electromagnetic performance.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
When calibration fails, the material fails. Understanding the consequences of poor control is essential.
The Risk of Byproduct Accumulation
If the gas flow is insufficient, decomposition byproducts linger around the sample.
This stagnation disrupts the formation of the shell, often leading to immediate structural collapse.
Kinetic Mismatch
If the heating rate ignores the kinetic requirements of the precursor, the carbonization will be uneven.
This results in irregular shapes rather than perfect spheres, disrupting the internal growth path of the MWCNTs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve high-performance absorption, you must treat the tube furnace as a precision instrument rather than a simple oven.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize the precision of gas flow to ensure the timely discharge of byproducts and prevent the collapse of the shell structure.
- If your primary focus is Internal Architecture: Fine-tune the heating rate to control carbonization kinetics, ensuring MWCNTs grow specifically toward the center of the spheres.
Mastering these variables transforms raw precursors into a highly engineered architecture capable of superior electromagnetic wave absorption.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Impact on Material Preparation | Structural Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | Controls carbonization kinetics | Guides MWCNT growth toward sphere centers |
| Gas Flow | Discharges thermal decomposition byproducts | Prevents shell collapse and maintains morphology |
| Precise Temp. | Regulates chemical transition speed | Ensures consistent spherical shell integrity |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between structural failure and high-performance innovation. KINTEK provides world-class laboratory high-temperature furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—engineered to give you absolute control over heating kinetics and atmosphere management.
Whether you are engineering complex electromagnetic wave absorbers or advanced carbon composites, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique R&D requirements. Backed by expert manufacturing, KINTEK empowers researchers to achieve the exact morphology their breakthrough materials demand.
Ready to master your synthesis process?
Contact our technical experts today to find your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Ze Wu, Lei Liu. MXene Hollow Spheres Supported by a C–Co Exoskeleton Grow MWCNTs for Efficient Microwave Absorption. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-024-01326-3
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do tube resistance furnaces or high-temperature box furnaces ensure material quality during the heat treatment of Fe60 alloys?
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- What advantages does a dual-zone tube furnace offer for carbon spheres? Enhanced Control & Superior Morphology
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why do we use a tubular furnace? For Unmatched Temperature Uniformity and Atmospheric Control
- How do horizontal furnaces contribute to cost savings in industrial processes? Boost Efficiency & Cut Costs
- What is the function of the quartz glass tube within a coaxial DBD plasma reactor? Ensuring Stable Plasma Discharge
- What is the function of a horizontal tube furnace in biomass carbonization? Master Precision Activation & Pore Design



















