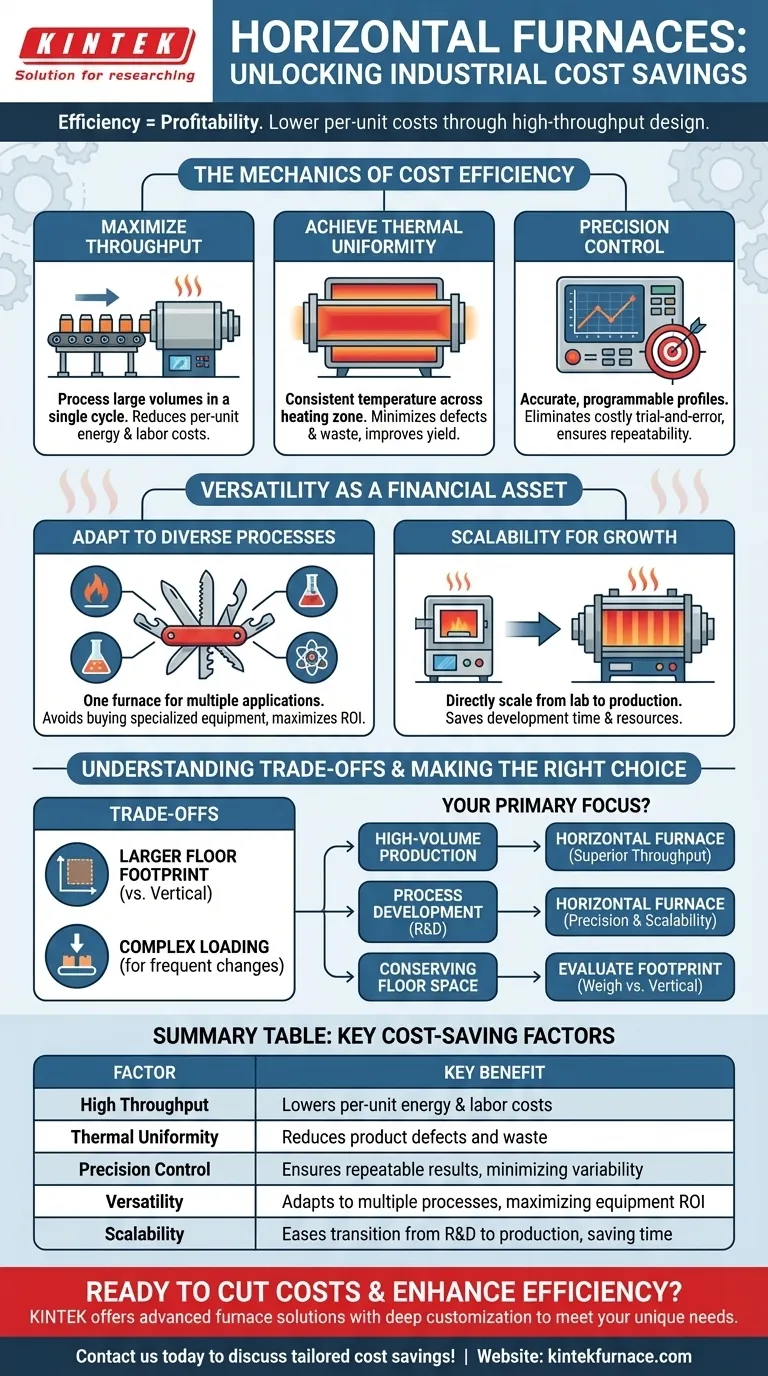
In industrial heating, efficiency is synonymous with profitability. Horizontal furnaces contribute to significant cost savings primarily by processing large volumes of material with exceptional efficiency. Their design is inherently suited for high-throughput production environments, which directly lowers the energy, labor, and operational costs associated with each unit produced.
The true cost savings of a horizontal furnace extend beyond its large capacity. They are a result of a powerful combination: high throughput that lowers per-unit costs, precise thermal uniformity that minimizes product waste, and operational versatility that maximizes the return on your capital investment.
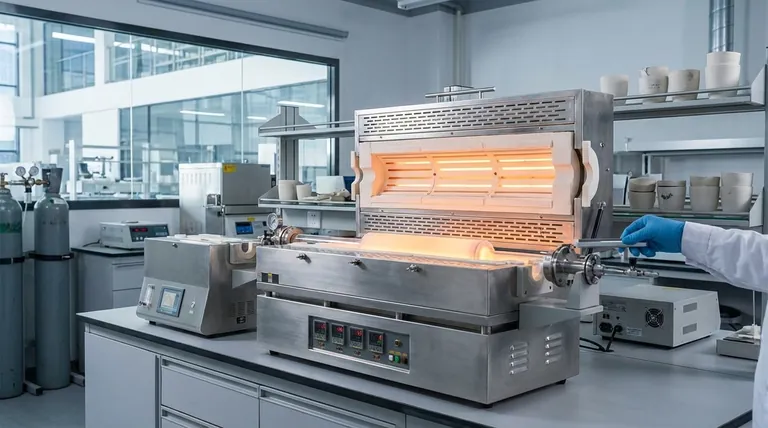

The Mechanics of Cost Efficiency
To understand the financial benefits, we must look at the core operational principles of a horizontal furnace, which is a common type of tube furnace. The design itself drives several key efficiencies.
Maximizing Throughput with Batch Processing
Horizontal furnaces are engineered to handle large quantities of material in a single cycle or in a continuous flow. This is a fundamental advantage for mass production.
By processing more material at once, you significantly reduce the cost per item. This includes lower per-unit energy consumption and reduced labor requirements for loading and unloading cycles.
Achieving Thermal Uniformity
A key feature of modern tube furnaces is their ability to maintain a highly uniform temperature across the entire heating zone. This consistency is critical for financial performance.
When every part of your workload experiences the same temperature, you drastically reduce the rate of defects and rejected products. Less waste translates directly into cost savings by improving the overall yield of your process.
Precision Control for Repeatable Results
These furnaces offer accurate, programmable temperature control. This allows for the development of highly specific and repeatable thermal profiles for processes like gas processing, biomass conversion, or materials testing.
This level of precision minimizes process variability and eliminates costly trial-and-error runs. Once a process is perfected, it can be executed identically time after time, ensuring predictable outcomes and stable operational costs.
Versatility as a Financial Asset
A single piece of equipment that can perform multiple functions is a powerful financial lever. The adaptability of horizontal furnaces is one of their most overlooked cost-saving attributes.
Adapting to Diverse Processes
The versatile configuration of horizontal tube furnaces means they can be adapted for a wide range of applications, from hydrogen pyrolysis to advanced materials synthesis.
This adaptability can prevent the need to purchase multiple, specialized furnaces. A single, well-chosen horizontal furnace can serve various R&D and production needs, maximizing its uptime and overall value.
Scalability for Future Growth
Processes developed on a small, lab-scale horizontal furnace can often be directly scaled up to larger production-sized models.
This "like-for-like" scalability saves immense time and resources in process development. It reduces the risk and cost associated with moving from a laboratory concept to full-scale manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, horizontal furnaces are not the universal solution. Acknowledging their limitations is key to making a sound investment.
Space and Footprint Considerations
By their nature, horizontal furnaces require a larger floor footprint than their vertical counterparts. In facilities where space is at a premium, the cost of this footprint must be factored into the overall financial equation.
Loading and Ergonomics
Loading and unloading a long horizontal tube can sometimes be more complex than simply dropping material into a top-loading vertical furnace. This can be a factor for processes requiring frequent, smaller batch changes.
Natural Convection Dynamics
In processes that rely heavily on natural convection (the natural rise of hot air or gas), a vertical furnace can sometimes offer a more intuitive thermal dynamic. However, most modern horizontal furnaces mitigate this with advanced heating elements and forced gas flow to ensure uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine if a horizontal furnace is the most cost-effective choice for your operation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: The superior throughput of a horizontal furnace makes it the most direct path to lowering your per-unit manufacturing costs.
- If your primary focus is process development and R&D: The precise control and scalability of a horizontal tube furnace make it an ideal platform for validating processes before committing to larger capital expenditures.
- If your primary focus is conserving facility floor space: You must carefully weigh the throughput benefits of a horizontal furnace against its larger physical footprint compared to a vertical alternative.
By evaluating these principles, you can confidently select a furnace configuration that aligns with both your technical requirements and your financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Cost-Saving Factor | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Throughput | Lowers per-unit energy and labor costs |
| Thermal Uniformity | Reduces product defects and waste |
| Precision Control | Ensures repeatable results, minimizing variability |
| Versatility | Adapts to multiple processes, maximizing equipment ROI |
| Scalability | Eases transition from R&D to production, saving time and resources |
Ready to cut costs and enhance efficiency in your lab or production line? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our horizontal furnaces can deliver tailored cost savings for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What technical role does a laboratory tube furnace play in zone refining simulation? Mastering Material Purification
- How does a vacuum tube furnace support the sintering process of np-CuSn films? Achieve High-Purity Intermetallic Joints
- What safety features are commonly found in modern 70mm tube furnaces? Essential Protection for High-Temperature Labs
- What is the typical workflow when using a multi gradient experimental tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- Why is the temperature control accuracy of a high-purity tube furnace critical? Mastering PCNF Carbonization
- How does high-temperature tube furnace programmed control influence porous carbon? Expert Pore Geometry Insights
- Why is quartz tube vacuum sealing technology utilized during the synthesis of [Pd@Bi10][AlCl4]4 cluster compounds?
- What safety features are included in an atmosphere tube furnace? Essential Systems for Secure High-Temp Operations



















