At its core, a tubular furnace is used for high-precision thermal processing where temperature uniformity and atmospheric control are non-negotiable. Its unique, cylindrical chamber is not an arbitrary design choice but the key to its function, making it indispensable for applications like purifying materials, annealing metals, and developing advanced coatings.
The fundamental reason for using a tubular furnace is its geometry. The tube shape is the most effective design for guaranteeing uniform 360-degree heating while creating a perfectly sealed, controlled atmosphere to protect or process sensitive materials.
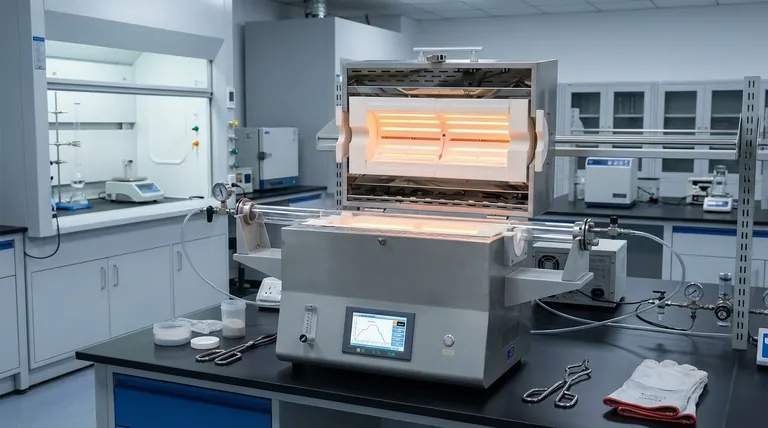

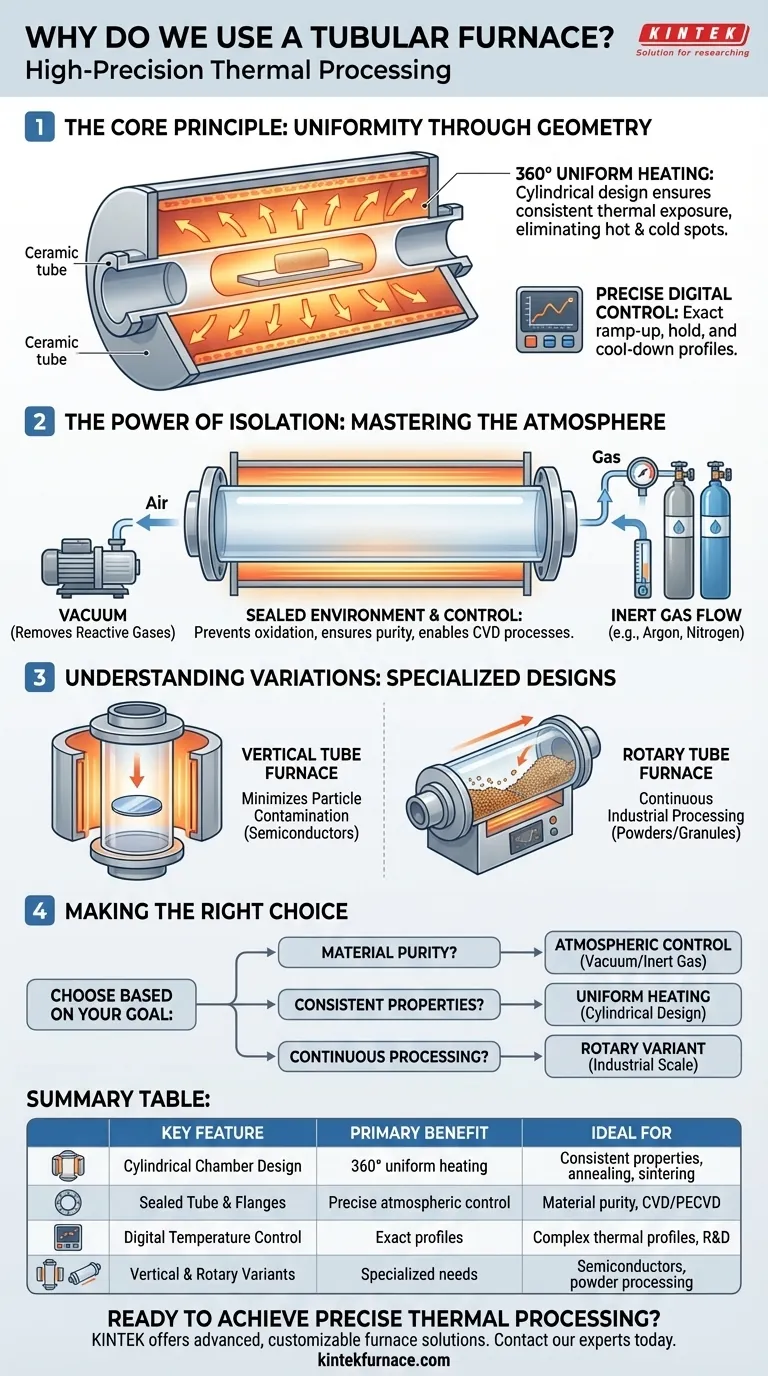
The Core Principle: Uniformity Through Geometry
The primary advantage of a tubular furnace comes directly from its physical form. This design is engineered to solve the common problem of inconsistent heating found in other furnace types.
How the Cylindrical Design Ensures Even Heating
A tubular furnace works by arranging heating elements around a central, tube-shaped chamber.
This geometry ensures that heat radiates inward evenly from all directions, blanketing the sample. This eliminates the hot and cold spots that can occur in simple box furnaces.
As a result, any material placed inside the tube receives a highly uniform thermal exposure along its entire length, leading to consistent and predictable results.
The Importance of Precise Temperature Control
Modern tubular furnaces are paired with sophisticated digital controllers.
These systems allow operators to program and maintain exact temperatures, often reaching several thousand degrees Celsius. They also manage precise ramp-up and cool-down rates.
This level of control is critical for complex thermal processes like sintering or annealing, where the final material properties are determined by a specific and exacting heat treatment profile.
The Power of Isolation: Mastering the Atmosphere
Beyond uniform heat, the second defining feature of a tubular furnace is its ability to create a completely controlled internal environment.
Creating a Sealed Environment
The enclosed tube can be easily sealed at both ends with specialized flanges.
This simple but powerful feature allows you to completely isolate the atmosphere inside the furnace from the air outside.
From here, you can pull a vacuum to remove reactive gases like oxygen or introduce a flow of specific inert gases, such as argon or nitrogen, to create a protective environment.
Why Atmospheric Control Is Critical
For many advanced materials, exposure to oxygen at high temperatures can cause unwanted oxidation, ruining the sample.
A controlled atmosphere prevents these detrimental reactions, ensuring the final material's purity and integrity.
Furthermore, it enables specialized chemical processes, like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), that can only occur in specific gaseous environments or a vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While incredibly versatile, the standard tubular furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations and specialized variants is key to proper application.
Common Applications and Versatility
The combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control makes these furnaces essential in both research laboratories and industrial production.
Key uses include the heat treatment of metal alloys, sintering of ceramic powders, purification of organic and inorganic compounds, and accelerated aging tests.
Specialized Designs: Vertical vs. Rotary
For specific needs, the basic design is adapted. Vertical tube furnaces are often used in semiconductor manufacturing, as their orientation minimizes particle contamination on wafers.
Rotary tube furnaces are designed for continuous industrial processing, tumbling loose materials like powders or granules through the heat zone for efficient, large-scale production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines whether a tubular furnace is the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing contamination: The ability to create a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere is the key advantage.
- If your primary focus is consistent material properties: The exceptional temperature uniformity ensures every part of your sample is treated identically.
- If your primary focus is continuous processing of loose materials: A specialized rotary tube furnace is the optimal choice for industrial scale.
Ultimately, a tubular furnace is chosen whenever the quality, consistency, and purity of the final product are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Chamber Design | 360° uniform heating, eliminates hot/cold spots | Consistent material properties, annealing, sintering |
| Sealed Tube with End Flanges | Precise atmospheric control (vacuum, inert gas) | Material purity, oxidation prevention, CVD/PECVD processes |
| Digital Temperature Control | Exact ramp-up, hold, and cool-down profiles | Complex thermal profiles, R&D, quality testing |
| Vertical & Rotary Variants | Minimized contamination or continuous processing | Semiconductor manufacturing, powder/granule processing |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing with a tubular furnace tailored to your unique needs?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether your application requires the uniform heating of a standard tube furnace, the contamination-free environment of a vertical model, or the continuous throughput of a rotary design, we offer deep customization to meet your exact experimental or production requirements.
Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, and specialized Vacuum, Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK tubular furnace can enhance your process quality and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















