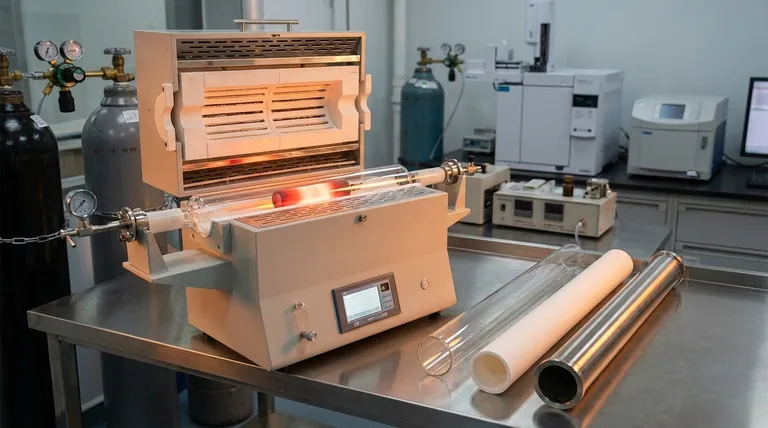
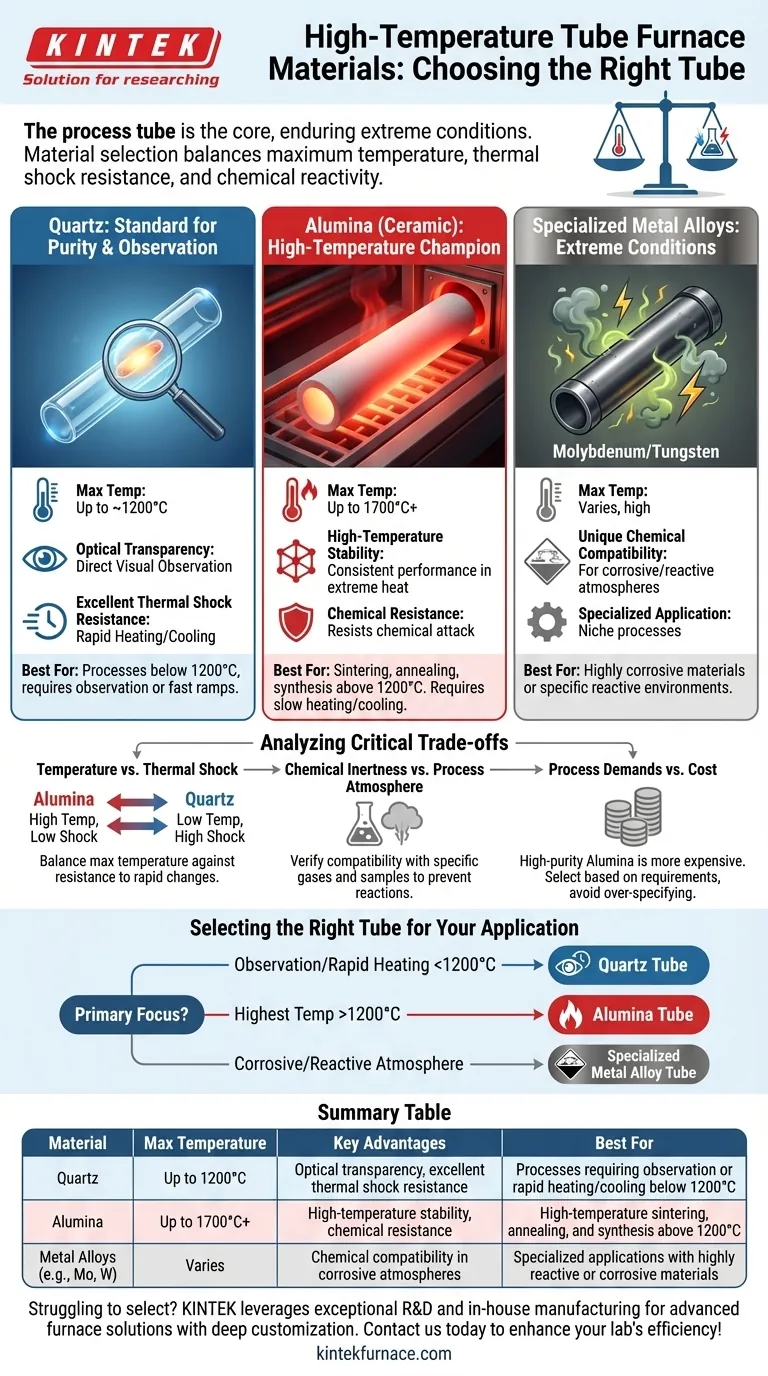
The core of any high-temperature tube furnace is the process tube, which must contain the sample and atmosphere while enduring extreme conditions. The most common materials used for these tubes are quartz, high-purity alumina (a ceramic), and in specialized cases, metal alloys like molybdenum or tungsten. The choice depends entirely on the specific temperature, atmosphere, and heating or cooling rates required for your process.
The selection of a furnace tube is a critical decision based on a trade-off. You must balance the maximum required temperature against the material's resistance to thermal shock and chemical reactivity to ensure the integrity of your experiment and the longevity of the furnace.

Understanding the Core Tube Materials
The material of the process tube is not an afterthought; it is a fundamental component that dictates the operational limits of your furnace. Each material offers a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses.
Quartz: The Standard for Purity and Observation
Quartz tubes are a versatile and common choice, especially for processes up to approximately 1200°C. Their primary advantage is optical transparency, allowing for direct visual observation of the sample during heating.
They also exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning they can withstand relatively rapid changes in temperature without cracking. This makes them suitable for processes that require faster heating or cooling ramps.
Alumina (High-Purity Ceramic): The High-Temperature Champion
When your process demands temperatures exceeding 1200°C, alumina is the standard. These opaque, ceramic tubes can operate consistently at temperatures up to 1700°C or even higher, depending on their purity.
Alumina offers exceptional high-temperature stability and is highly resistant to chemical attack. It is the go-to material for high-temperature sintering, annealing, and synthesis applications.
Specialized Metal Alloys: For Extreme Conditions
For certain niche applications involving highly corrosive materials or specific reactive atmospheres, neither quartz nor alumina may be suitable. In these cases, tubes made from molybdenum or tungsten can be used.
These metal tubes are chosen for their unique chemical compatibility under conditions that would degrade or destroy ceramic alternatives. Their use is highly specialized and tailored to very specific process requirements.
Analyzing the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing the right tube material involves navigating a series of critical trade-offs. Misunderstanding these can lead to failed experiments, sample contamination, or damaged equipment.
Temperature vs. Thermal Shock Resistance
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Alumina can reach the highest temperatures but is more susceptible to cracking from thermal shock. It must be heated and cooled slowly and controllably.
Conversely, quartz has a lower maximum operating temperature but can handle much faster temperature changes. Pushing a quartz tube beyond its thermal limit will cause it to soften and deform.
Chemical Inertness vs. Process Atmosphere
While both quartz and alumina are considered highly inert, they are not immune to all chemicals. For example, alumina can be attacked by certain alkaline environments at high temperatures.
It is crucial to verify the compatibility of your chosen tube material with the specific gases and sample materials you will be using to prevent unwanted reactions and ensure process purity.
Process Demands vs. Cost
High-purity alumina tubes are generally more expensive than quartz tubes. The cost increases with the tube's diameter, length, and purity level. Therefore, it is most practical to select the material that meets your requirements without over-specifying for conditions you will never need.
Selecting the Right Tube for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated by the specific goals of your work. Use these guidelines to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is process observation or rapid heating cycles below 1200°C: A quartz tube is the ideal choice for its optical clarity and excellent thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (above 1200°C): An alumina tube is necessary for its superior stability and performance in extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is working with highly corrosive agents or unique reactive atmospheres: You must investigate a specialized metal alloy tube designed for your specific chemical environment.
By matching the tube material to your operational parameters, you ensure the safety of your equipment, the integrity of your process, and the reliability of your results.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1200°C | Optical transparency, excellent thermal shock resistance | Processes requiring observation or rapid heating/cooling below 1200°C |
| Alumina | Up to 1700°C+ | High-temperature stability, chemical resistance | High-temperature sintering, annealing, and synthesis above 1200°C |
| Metal Alloys (e.g., Molybdenum, Tungsten) | Varies | Chemical compatibility in corrosive atmospheres | Specialized applications with highly reactive or corrosive materials |
Struggling to select the right tube material for your high-temperature furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we tailor our products to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs



















