Stepped temperature control is critical for decoupling the physical removal of solvents from the chemical stabilization of the film. By creating a multi-stage thermal profile, you prevent the destructive effects of rapid boiling while ensuring the final sensor layer is dense, thoroughly dried, and structurally sound.
The core advantage of a stepped approach is that it prioritizes structural integrity first and chemical purity second. It prevents the formation of microscopic defects like pinholes and cracks that occur when solvents are forced out of a film too aggressively.
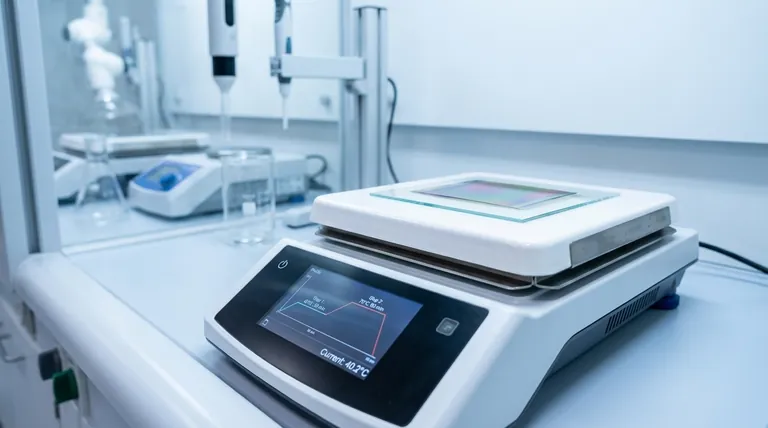

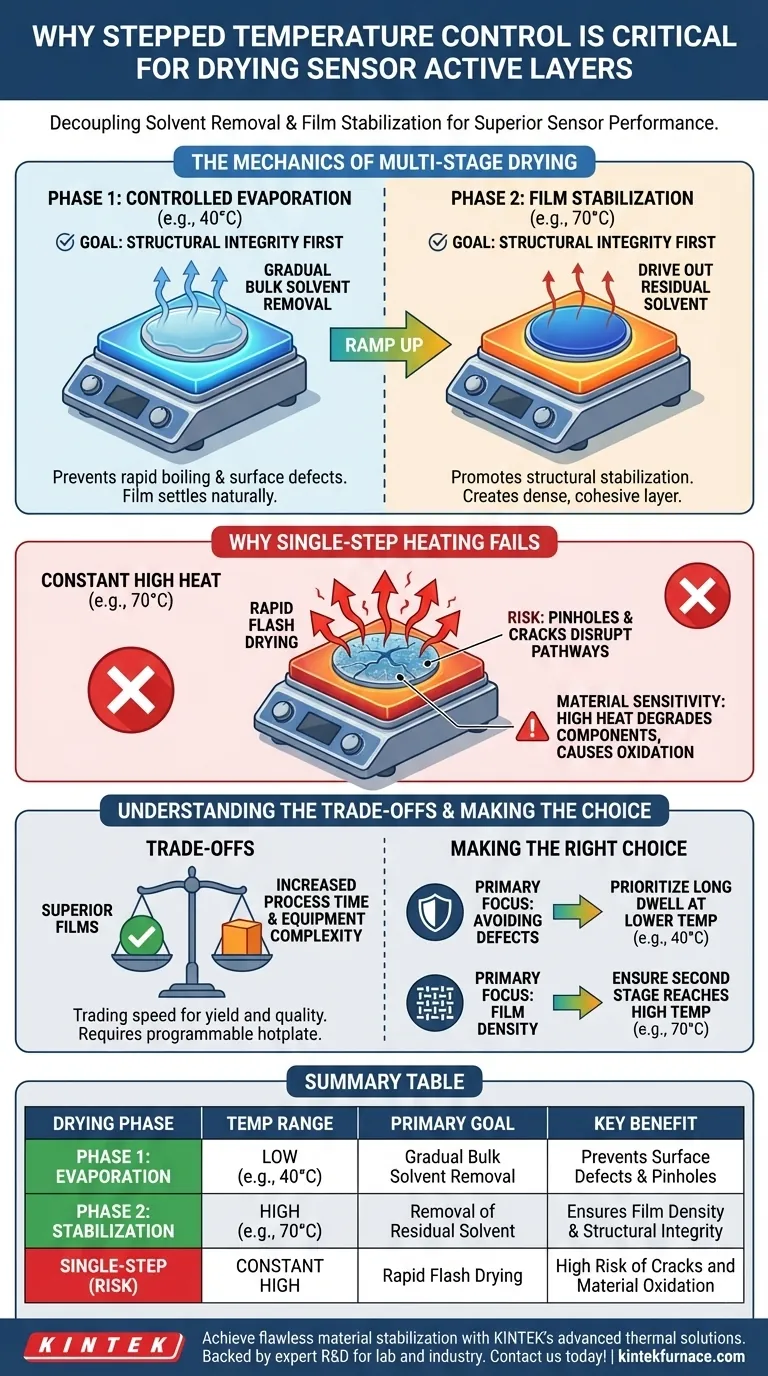
The Mechanics of Multi-Stage Drying
To create a high-performance sensor, the active layer must be uniform and free of defects. Stepped temperature control achieves this by breaking the drying process into two distinct phases.
Phase 1: Controlled Evaporation
The initial stage typically involves a lower temperature setting, such as 40°C. This moderate heat allows for the gradual removal of bulk solvents.
By keeping the temperature low, you prevent the solvent from boiling or evaporating rapidly. This ensures the film settles naturally without undergoing violent phase changes that disrupt the material's surface.
Phase 2: Film Stabilization
Once the bulk solvent is removed, the temperature is ramped up to a higher setpoint, such as 70°C. This stage is necessary to drive out any stubborn, residual solvent molecules trapped deep within the layer.
This higher temperature promotes the stabilization of the thin film structure. It creates a denser, more cohesive layer that is essential for accurate sensing performance.
Why Single-Step Heating Fails
Attempting to dry a sensor layer in a single, high-heat step often compromises the device's reliability.
The Risk of Rapid Evaporation
If a wet film is immediately exposed to high heat (e.g., jumping straight to 70°C), the solvent evaporates too quickly. As the gas forces its way out of the material, it creates pinholes and cracks.
These physical defects disrupt the electrical pathways in the sensor active layer, leading to inconsistent readings or total device failure.
Material Sensitivity
Beyond physical defects, precise thermal control is required to protect the material itself. Just as laboratory ovens are used to dehydrate carbon nanotube films without oxidizing them or damaging delicate substrates, hotplates must respect the thermal limits of the active layer.
Sudden high heat can degrade sensitive organic components or cause oxidation, altering the chemical properties of the sensor before it is even finished.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While stepped temperature control produces superior films, it introduces specific operational considerations.
Increased Process Time
A multi-stage process is inherently slower than a "flash dry" approach. You are trading speed for yield and quality. The total processing time increases because the film must dwell at the lower temperature before the final cure.
Equipment Complexity
To execute this reliably, you require a hotplate capable of programmable ramping or precise manual adjustment. Standard analog hotplates may struggle to maintain the distinct temperature plateaus (e.g., holding exactly 40°C then ramping to 70°C) required for repeatable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When defining your thermal processing protocol, consider the specific requirements of your sensor material.
- If your primary focus is Avoiding Defects: Prioritize a long dwell time at the lower temperature stage (approx. 40°C) to ensure gentle solvent off-gassing.
- If your primary focus is Film Density: Ensure your second stage reaches the necessary threshold (approx. 70°C) to fully stabilize the structure and remove residual impurities.
By matching the thermal profile to the volatility of your solvent, you transform a chaotic evaporation process into a controlled manufacturing step.
Summary Table:
| Drying Phase | Temperature Range | Primary Goal | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Evaporation | Low (e.g., 40°C) | Gradual bulk solvent removal | Prevents surface defects & pinholes |
| Phase 2: Stabilization | High (e.g., 70°C) | Removal of residual solvent | Ensures film density & structural integrity |
| Single-Step (Risk) | Constant High | Rapid flash drying | High risk of cracks and material oxidation |
Achieve flawless material stabilization with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the precise needs of laboratory researchers and industrial manufacturers. Whether you are drying sensitive sensor layers or processing advanced carbon nanotubes, our equipment ensures the repeatable accuracy your work demands. Contact KINTEK today to optimize your thermal profile!
Visual Guide
References
- Perpetual Eze-Idehen, Krishna Persaud. Design, Fabrication and Validation of Chemical Sensors for Detecting Hydrocarbons to Facilitate Oil Spillage Remediation. DOI: 10.3390/chemosensors13040140
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Why use nitrogen and flow meters in sludge pyrolysis? Ensuring Superior Biochar Quality and Anaerobic Integrity
- What is the graphite furnace technique? A Guide to Ultra-Trace Metal Analysis
- What is the purpose of performing a 1200°C solution treatment for high-entropy alloys? Achieve Total Homogenization
- What is the function of solution and aging heat treatment furnaces? Optimize 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Properties
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Unlock Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What long-term considerations are important when selecting a kiln? Ensure Cost-Effective, Compliant Operations
- Why is a laboratory constant temperature drying oven necessary for biomass adsorbents? Ensure Precision & Integrity
- Why is a vacuum drying oven required for processing MXene solutions and NPC@MoS2 nanostructures? Key Benefits Revealed



















