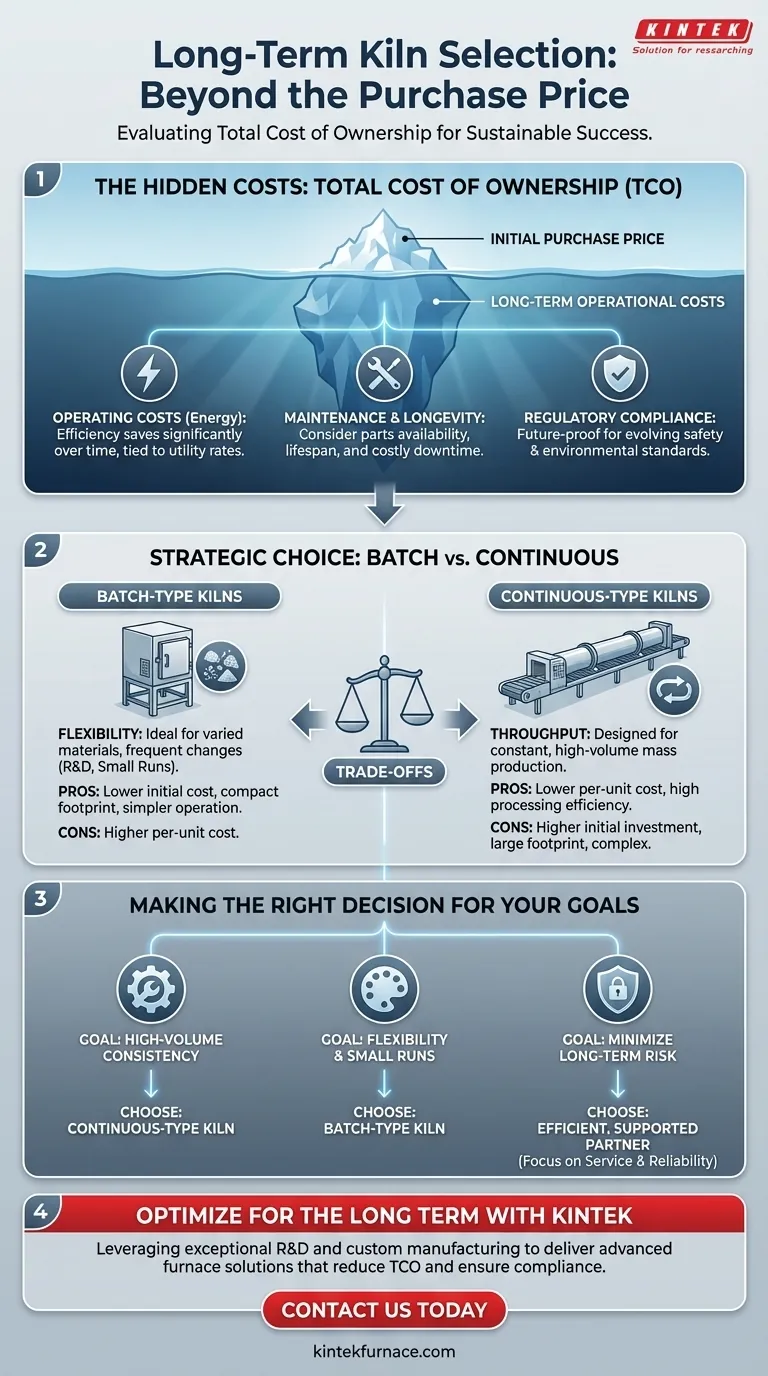
Choosing the right kiln is a decision that extends far beyond its initial purchase price. For a successful long-term investment, you must evaluate ongoing operating costs driven by utility prices, the scope and frequency of maintenance, and the kiln's ability to comply with safety and environmental regulations that may change over time.
The most critical long-term consideration is not the kiln's initial cost, but its total cost of ownership. This requires a deep analysis of how its operational model—batch or continuous—and its maintenance needs align with your specific production volume and future business goals.

Beyond the Purchase Price: Analyzing Total Cost of Ownership
A kiln is a significant capital asset. Thinking about its cost only at the time of purchase is a common but costly mistake. A true assessment requires looking at the entire financial picture over the kiln's operational lifespan.
Calculating Ongoing Operating Costs
The single largest ongoing expense for most kilns is energy consumption. Whether it runs on electricity or gas, the cost is directly tied to local utility rates, which can fluctuate significantly.
A kiln that is highly efficient may have a higher upfront cost but can save you substantial amounts of money over a decade of operation. Always request energy consumption data and calculate projected annual costs based on your local rates.
Factoring in Maintenance and Longevity
Every kiln requires maintenance, but the cost and complexity can vary dramatically. Consider the availability and price of replacement parts like heating elements, thermocouples, and refractory materials.
A cheaper kiln may use proprietary parts that are difficult to source or require more frequent replacement. Inquire about the expected lifespan of key components and the simplicity of routine maintenance tasks. The cost of downtime during repairs is a major long-term financial factor.
Navigating Safety and Environmental Regulations
Regulations governing emissions, energy efficiency, and workplace safety are constantly evolving. A kiln that is compliant today may not be in five or ten years.
Investing in a kiln from a reputable manufacturer that designs for future standards is a form of risk mitigation. This ensures your operation remains compliant without needing expensive retrofits or a premature replacement.
Aligning Kiln Type with Production Strategy
The fundamental choice between a batch and a continuous kiln will define your operational workflow. This decision must be based on your production volume, material variety, and physical space constraints.
The Case for Batch-Type Kilns
Batch-type kilns are defined by their operational cycle: load, fire, cool, and unload. This makes them exceptionally versatile.
They are the ideal choice for operations that handle small amounts of many different materials, such as in research and development, custom fabrication, or artisanal production where product lines change frequently.
The Case for Continuous-Type Kilns
Continuous-type kilns, often rotary kilns, are designed for a constant, uninterrupted flow of material. Material is fed into one end and processed product is discharged from the other.
These are built for high-volume production of a few specific materials. They offer superior processing capacity and efficiency at scale, making them the standard for industrial mass production.
Considering Physical Footprint and Installation
The physical space required is a critical, practical constraint. Batch kilns are typically more compact and offer more flexibility in placement.
Continuous kilns are often large, complex systems that require significant floor space and a more permanent, disruptive installation process. This long-term commitment to a specific layout must be part of your strategic plan.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
There is no universally "best" kiln; there is only the best kiln for a specific application. Understanding the trade-offs between different models is key to making an informed decision.
Flexibility vs. Throughput
This is the primary trade-off. Batch kilns offer maximum flexibility to change products and firing schedules. Continuous kilns offer maximum throughput for a stable product line. You must choose which of these is more valuable to your business model.
Upfront Investment vs. Per-Unit Cost
Generally, batch kilns have a lower initial purchase and installation cost. However, for large-scale production, the higher efficiency of a continuous kiln results in a significantly lower processing cost per unit of material.
Simplicity vs. Complexity
Batch systems are mechanically and operationally simpler. This often translates to easier maintenance and less required operator training. Continuous systems are more complex, requiring sophisticated control systems and potentially specialized maintenance teams to manage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
To select the best kiln for the long term, anchor your decision in your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent production: A continuous-type kiln will deliver the highest throughput and lowest per-unit operating cost over its lifetime.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for varied materials or smaller runs: A batch-type kiln provides the necessary operational agility and a lower barrier to entry with its smaller initial investment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term risk: Prioritize a kiln that balances energy efficiency with robust construction and is supported by a manufacturer with a strong track record for parts availability and service.
A kiln is a long-term partner in your production process; choose the one that aligns with your operational goals for the decades to come.
Summary Table:
| Consideration | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Total Cost of Ownership | Includes initial cost, energy consumption, maintenance, and downtime expenses over the kiln's lifespan. |
| Operating Costs | Driven by utility rates; high-efficiency kilns reduce long-term energy expenses. |
| Maintenance | Assess part availability, replacement frequency, and ease of routine tasks to minimize costs. |
| Regulations | Ensure compliance with evolving safety and environmental standards to avoid retrofits. |
| Kiln Type | Batch kilns offer flexibility for varied materials; continuous kilns provide high throughput for mass production. |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing with a kiln tailored for long-term success? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you reduce total cost of ownership, enhance efficiency, and stay compliant. Don't let kiln selection hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















