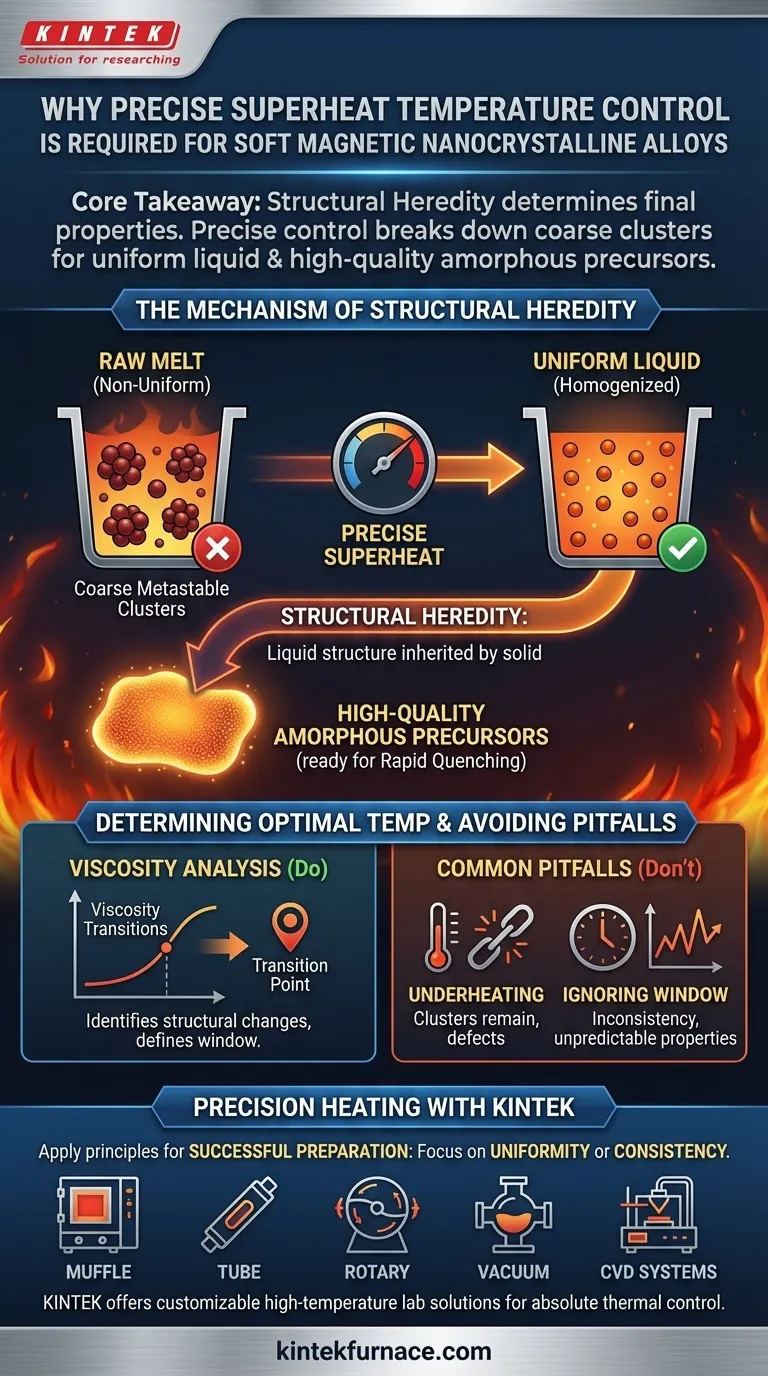
Precise superheat temperature control is the determining factor in the structural quality of soft magnetic nanocrystalline alloys. It is required to manipulate the short-range ordered structure within the molten metal, specifically to break down coarse metastable clusters and ensure a uniform liquid phase prior to rapid quenching.
Core Takeaway The properties of the final solid alloy are dictated by the "structural heredity" of the liquid melt. Precise temperature control allows you to break down coarse clusters into a uniform liquid, which is the prerequisite for forming high-quality amorphous precursors.

The Mechanism of Structural Heredity
Controlling the Melt Structure
The liquid state of these alloys is not merely a chaotic soup; it contains specific short-range ordered structures and cluster distributions.
To achieve high-quality magnetic properties, you must manipulate this internal liquid structure.
The superheat temperature directly influences how these atomic clusters are arranged and distributed within the melt.
Eliminating Coarse Metastable Clusters
In their raw state, these melts often contain "coarse metastable clusters"—essentially, large, non-uniform groupings of atoms.
If these clusters are not broken down, they persist into the cooling phase.
Precise heating to an optimal superheat temperature provides the energy required to dissolve these coarse clusters.
Achieving a Uniform Liquid Phase
Once the coarse clusters are broken down, the melt transitions into a more uniform liquid phase structure.
This uniformity is critical because of a principle known as structural heredity.
The structure of the liquid melt is "inherited" by the solid during solidification; a uniform liquid leads to a uniform solid.
The Link to Amorphous Precursors
The ultimate goal of this preparation is to create high-quality amorphous precursors.
These precursors are formed during the subsequent rapid quenching process.
Only a melt that has been homogenized through precise superheat control can consistently produce precursors with the necessary structural integrity.
Determining the Optimal Temperature
The Role of Viscosity Analysis
You cannot select a superheat temperature at random.
The optimal temperature is typically determined through viscosity analysis.
Changes in viscosity indicate transitions in the melt's internal structure, signaling exactly when the coarse clusters have been sufficiently broken down.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of "Good Enough" Heating
It is a mistake to view the melting process simply as a phase change from solid to liquid.
Reaching the melting point is not enough; you must reach the specific superheat target.
f you fail to reach this precise temperature, the original coarse clusters remain intact, compromising the final alloy's microstructure.
Ignoring the Process Window
Just as underheating is detrimental, deviating from the optimal window identified by viscosity analysis leads to inconsistency.
The relationship between temperature and cluster distribution is sensitive.
Lacking precision here breaks the chain of structural heredity, leading to unpredictable magnetic properties in the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful preparation of soft magnetic nanocrystalline alloys, apply these principles:
- If your primary focus is Alloy Uniformity: Prioritize reaching the exact superheat temperature identified to break down metastable clusters, ensuring the liquid phase is homogeneous.
- If your primary focus is Process Consistency: Implement strict viscosity analysis to define and monitor the optimal temperature window for every batch.
By mastering the superheat temperature, you essentially program the quality of the final material while it is still in the liquid state.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Influence on Melt Structure | Impact on Final Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal Superheat | Breaks down coarse metastable clusters | Uniform amorphous precursors with superior magnetic properties |
| Underheating | Persistent large atomic groupings | Structural defects and inconsistent magnetic performance |
| Structural Heredity | Liquid phase uniformity is preserved | Solid state inherits the homogeneous liquid structure |
| Viscosity Analysis | Identifies structural transition points | Defines the precise temperature window for process stability |
Precision Heating for Advanced Material Science
Unlock the full potential of your magnetic alloy production with KINTEK. As experts in high-temperature lab solutions, we understand that achieving the perfect 'structural heredity' requires more than just heat—it requires absolute control.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of nanocrystalline alloy preparation. Our equipment ensures the thermal precision necessary for critical viscosity transitions and melt homogenization.
Ready to elevate your material quality? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yuri N. Starodubtsev, Nadezhda P. Tsepeleva. Melting, Solidification, and Viscosity Properties of Multicomponent Fe-Cu-Nb-Mo-Si-B Alloys with Low Aluminum Addition. DOI: 10.3390/ma17020474
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature laboratory furnace contribute to the formation of high-quality CsV3Sb5 single crystals?
- What additional techniques are used in activated sintering? Boost Efficiency with Advanced Chemical Methods
- What technical requirements are placed on heating equipment for fast pyrolysis? Master High-Yield Bio-Oil Production
- What is quenching, and why is it important? Achieve Superior Material Hardness and Strength
- What role does a laboratory precision ventilated oven play in the post-processing of dispersed carbon nanotubes?
- How does a single-roller melt-spinning system facilitate Fe-based amorphous alloys? Achieve Precision Rapid Quenching
- What is the chemical vapor transport technique? A Guide to High-Purity Crystal Growth
- What is the role of a high-energy ball mill in NiWO4/GO preparation? Master High-Performance Composite Synthesis



















